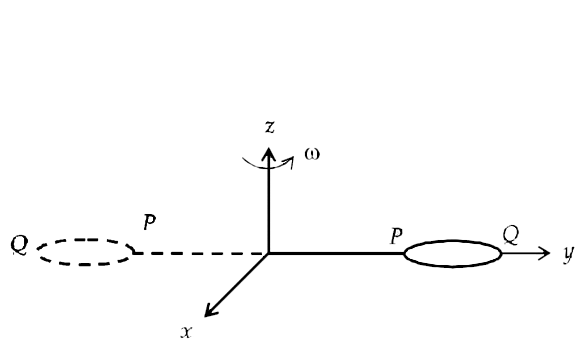
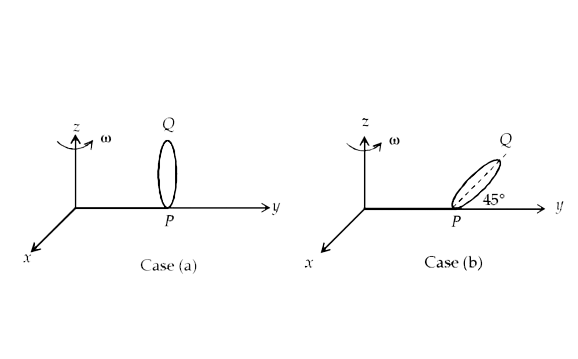
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- The general motion of a rigid body can be considered to be a combinati...
Text Solution
|
- The general motion of a rigid body can be considered to be a combinati...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform disc of mass m and radius R rotates about a fixed vertical a...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform disc of mass m and radius R rotates about a fixed vertical a...
Text Solution
|
- Two thin discs each of mass M and radius r are attached as shown in fi...
Text Solution
|
- The mass of a body cannot be considered to be concentrated at the cent...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform semicircular disc of mass 'm' and radius 'R' is shown in the...
Text Solution
|
- Two thin discs each of mass M and radius r metre are attached to form ...
Text Solution
|
- M.I. of a thin uniform circular disc about one of the diameters is I. ...
Text Solution
|