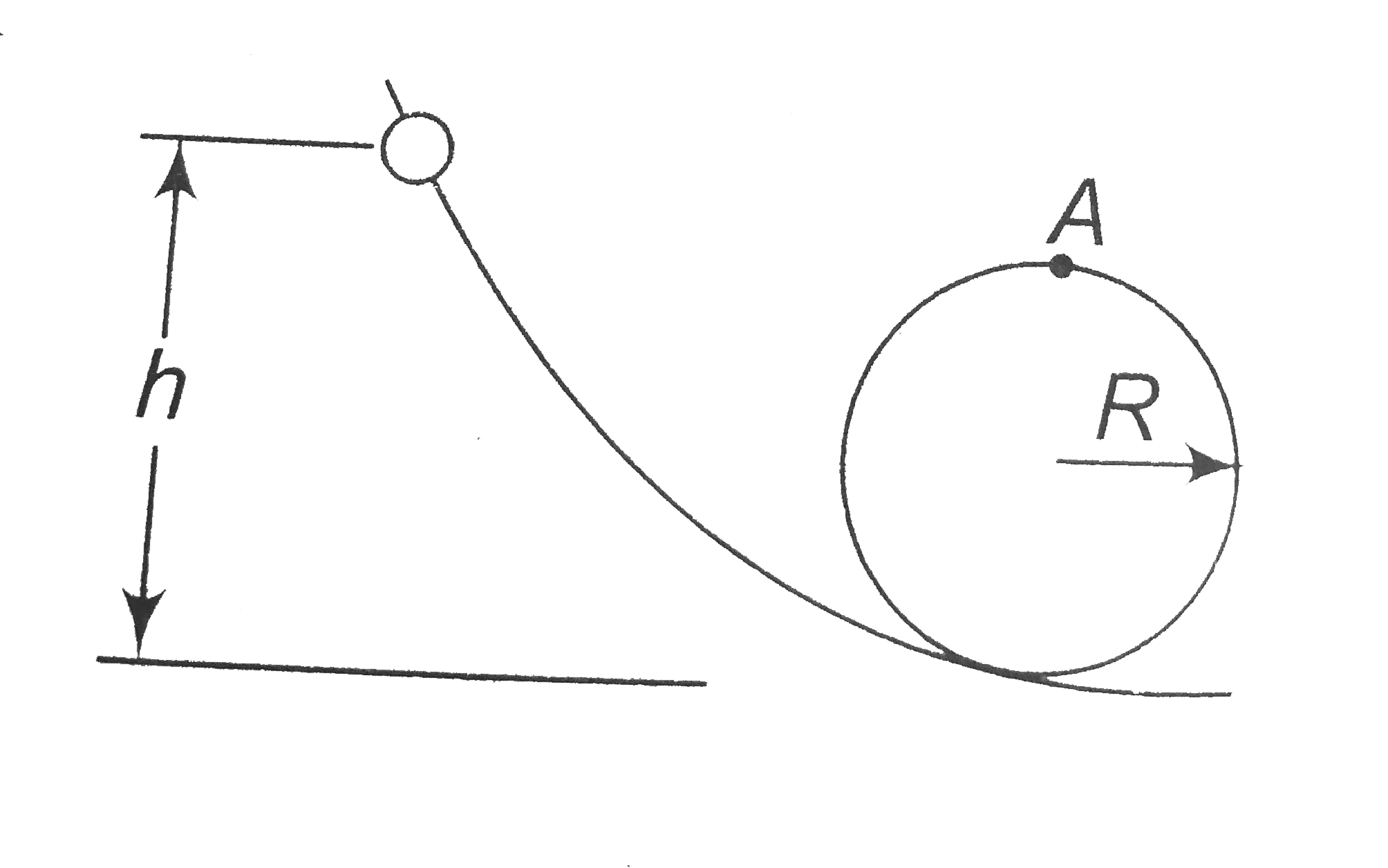
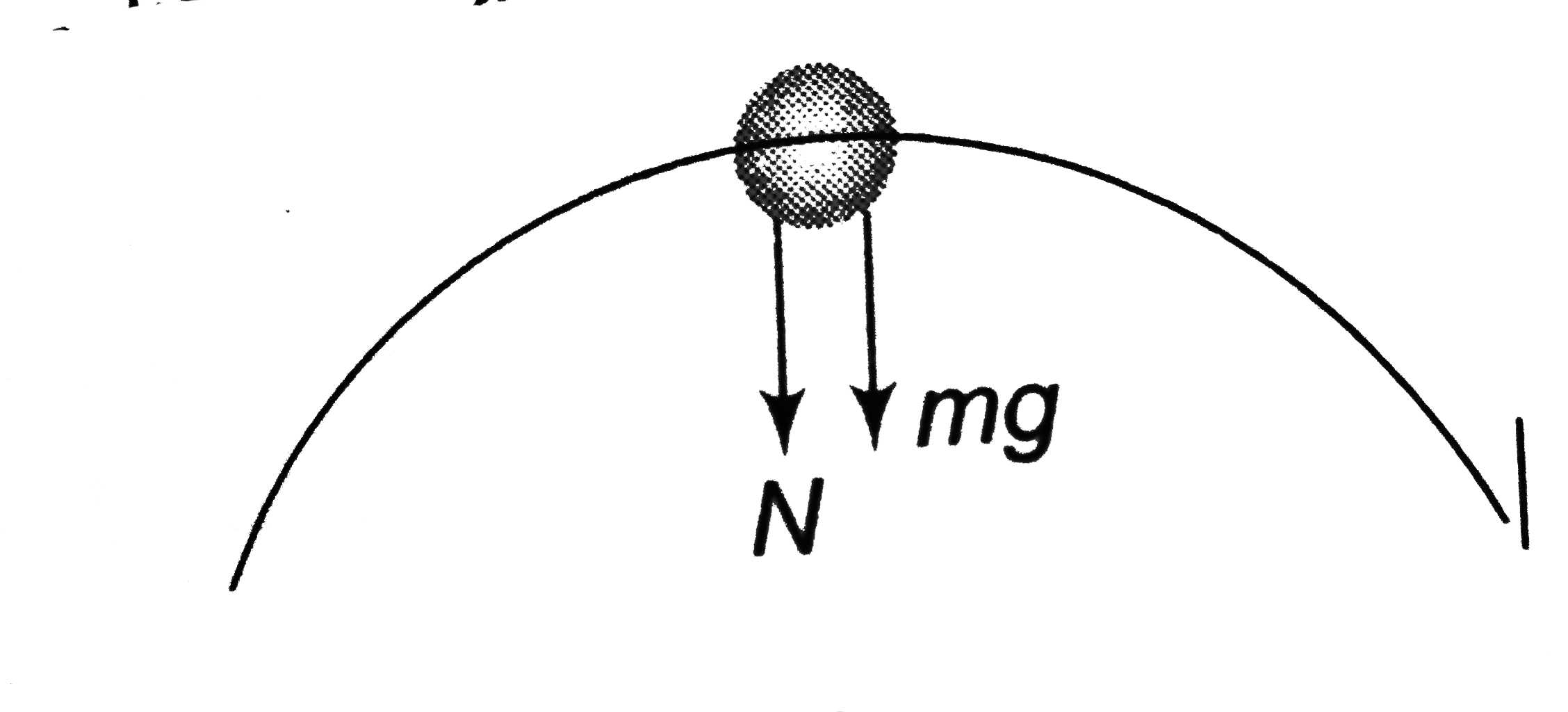
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
A2Z-WORK, ENERGY, POWER AND COLLISION-Circular Motion In Vertical Plane
- A stone is fastened to one end of a string and is whirled in a vertica...
Text Solution
|
- What minimum horizontal speed should be given to the bob of a simple p...
Text Solution
|
- A stone of mass 1 kg tied to a light inextensible string of lenth L=(...
Text Solution
|
- A weightless rod of length 2l carries two equal masses 'm', one tied a...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is rotated in a vertical circle by connecting it to a strin...
Text Solution
|
- A partical originally at rest at the highest point of a smooth vertica...
Text Solution
|
- A small block slides with velocity 0.5sqrt(gr) on the horizontal frict...
Text Solution
|
- A practical moves from rest at A on the surface of a smooth circular c...
Text Solution
|
- In the given system, when the ball of mass m is released, it will swin...
Text Solution
|
- A pendulum bob has a speed 3m/s while passing through its lowest posit...
Text Solution
|
- A heavy particle hanging from a fixed point by a light inextensible st...
Text Solution
|
- The kinetic energy of partical moving along a circule of radius R depe...
Text Solution
|
- With what minimum speed v must a small ball should be pushed inside a ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m is released from a height H on a smooth curved su...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m oscillates along the horizontal diameter AB insi...
Text Solution
|
- A head slide without friction around a loop the (figure). The bead sli...
Text Solution
|
- A light , right rod is 40.0 cm long.Its top end is pivoted on a fricti...
Text Solution
|
- A pendulum comprising a light string of length L and small sphere, swi...
Text Solution
|
- A ball whirls around in a vertical circle at the end of a string . The...
Text Solution
|
- A partical is moving in the vertical plane . It is attached at one end...
Text Solution
|