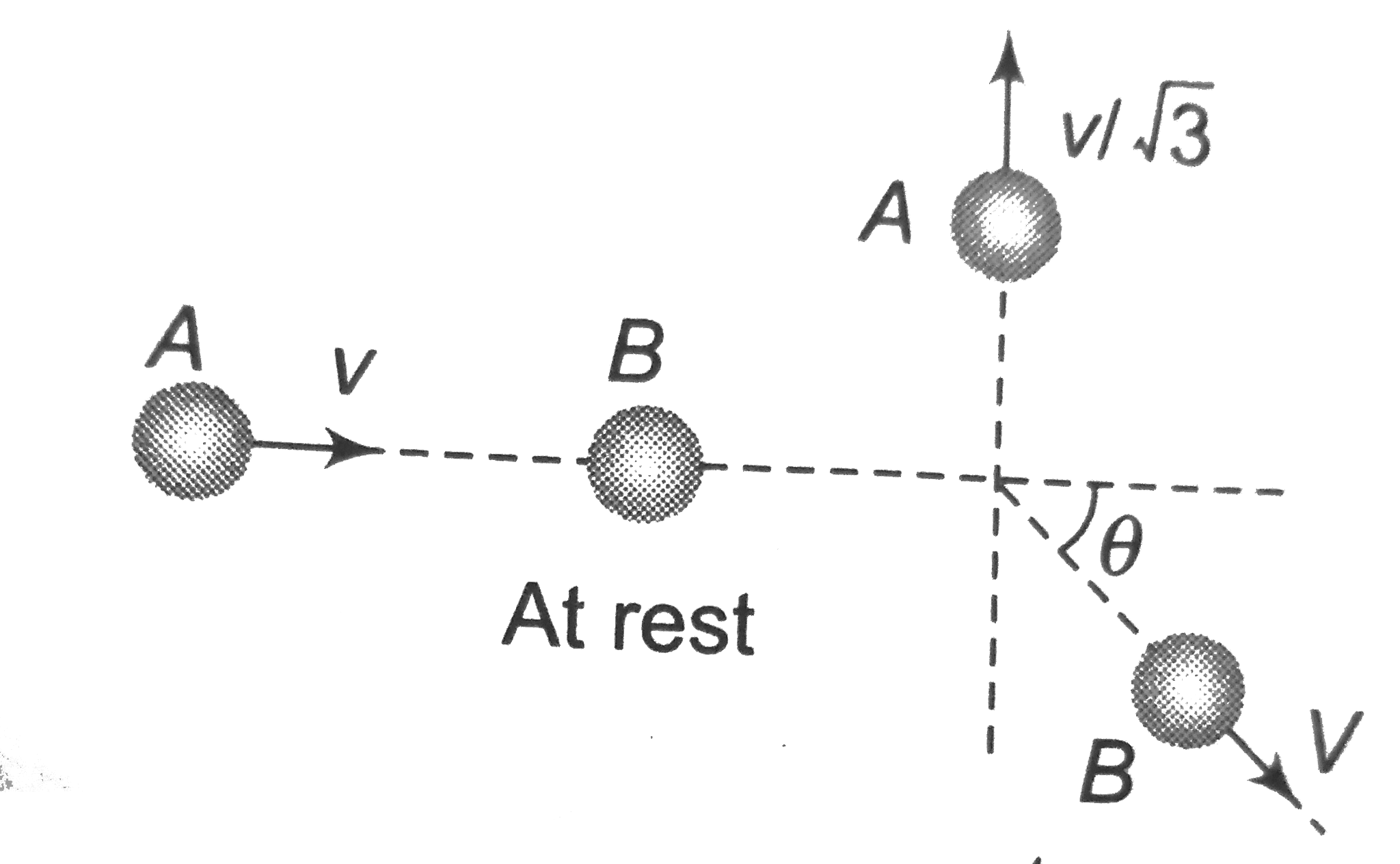
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
WORK, ENERGY, POWER AND COLLISION
A2Z|Exercise Problems Based On Mixed Concepts|32 VideosWORK, ENERGY, POWER AND COLLISION
A2Z|Exercise Assertion Reasoning|17 VideosWORK, ENERGY, POWER AND COLLISION
A2Z|Exercise Circular Motion In Vertical Plane|21 VideosWAVES AND ACOUSTICS
A2Z|Exercise Chapter Test|30 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
A2Z-WORK, ENERGY, POWER AND COLLISION-Collision
- A body is allowed to fall on the ground from a height h(1). If it is r...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is let fall from a height h(0). There are n collisions with the...
Text Solution
|
- A body X with a momentum p collides with another identical stationary ...
Text Solution
|
- A pendulum consists of a wooden bob of mass m and of length L. A bulle...
Text Solution
|
- Two pendulum each of length l are initial situated as shown in figure....
Text Solution
|
- A mass 'm' moves with a velocity 'v' and collides inelastieally with a...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is projected vertically down with an initial velocity from a h...
Text Solution
|
- A partical falls from a height h upon a fixed horizontal plane and re...
Text Solution
|
- The bob A of a simple pendulum is released when the string makes an a...
Text Solution
|
- Two particle moving in the same direction with speeds 4 m//s and 2m//s...
Text Solution
|
- Body A of mass m and B of mass 3m move towards each other with velocit...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass m is moving normally towards a walll of mass M(gt gt m)...
Text Solution
|
- The velocity vector of a sphere after it hits a vertical wall which i...
Text Solution
|
- A partical of mass m(1) collides head on with a stationary partical o...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass 1 kg strikes a heavy platform, elastically, moving upwa...
Text Solution
|
- The sphere A of mass m(1) moves with velocity V on a frictionless hori...
Text Solution
|
- A sphere A of mass m moving with a velocity hits another stationary s...
Text Solution
|
- A ball strickes a horizontal floor at 45^(@). 25% of its kinetic energ...
Text Solution
|
- N identical balls are placed on a smooth horizontal surface. An anothe...
Text Solution
|
- A plank of mass m moving with a velocity v along a frictionless horizo...
Text Solution
|