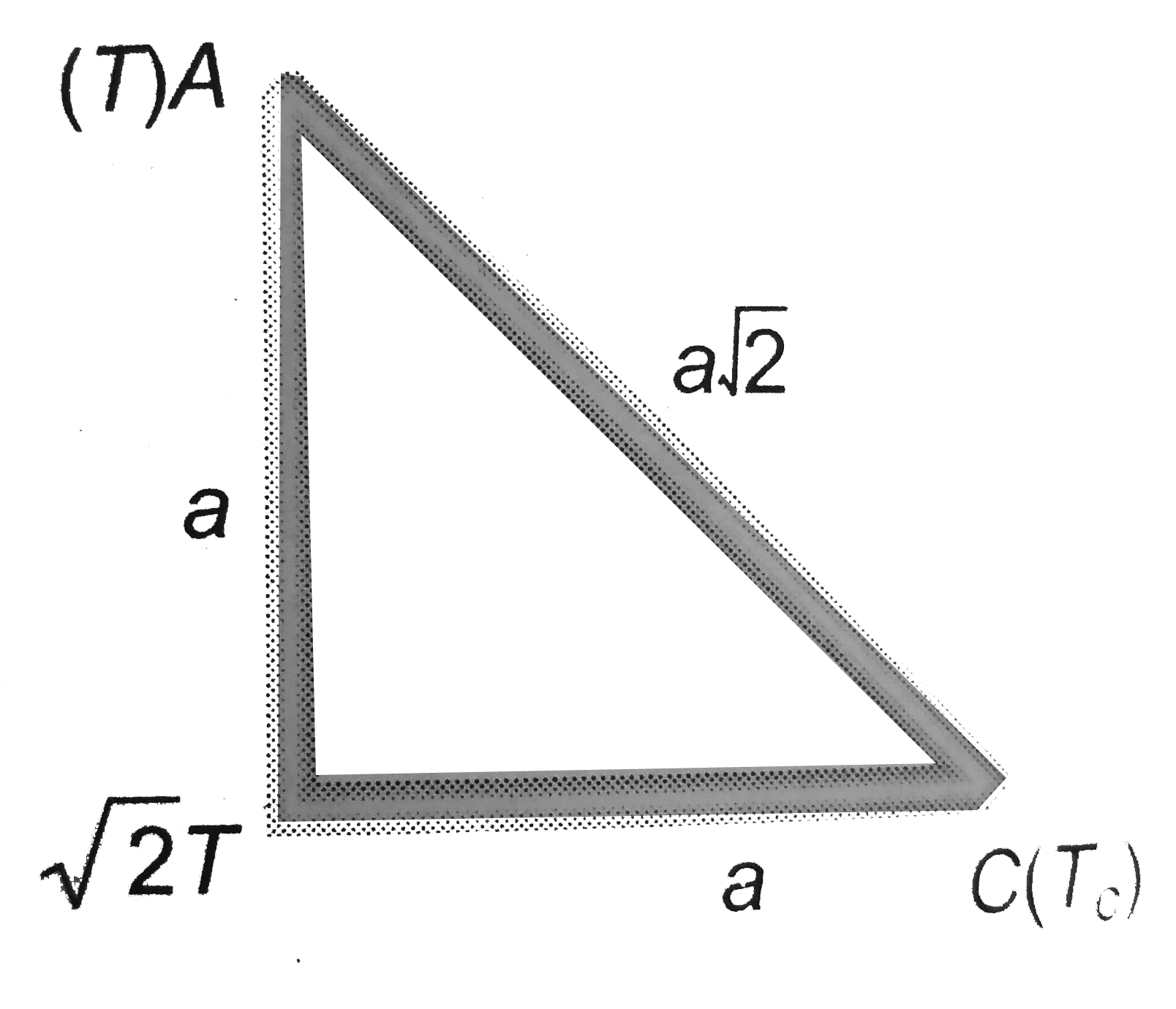
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
A2Z-THERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER-Chapter Test
- According to Newton's law of cooling, the rate of cooling of a body is...
Text Solution
|
- If the temperature of the sun were to increase form T to 2T and its ra...
Text Solution
|
- The temperature of the two outer surfaces of a composite slab consisti...
Text Solution
|
- A sphere a cube and thin circular plate, all made of the same material...
Text Solution
|
- A slab consists of two parallel layers of copper and brass of the time...
Text Solution
|
- A solid copper sphere (density rho and specific heat c) of radius r at...
Text Solution
|
- Two metallic spheres S1 and S2 are made of the same material and have ...
Text Solution
|
- Three rods of identical cross-sectional area and made from the same me...
Text Solution
|
- Two metal cubes A and B of same size are arranged as shown in Figure. ...
Text Solution
|
- The intensity of radiation emitted by the sun has its maximum value at...
Text Solution
|
- A spherical black body with a radius of 12 cm radiates 450 W power at ...
Text Solution
|
- A black body is at a temperature of 5760 K. The energy of radiation em...
Text Solution
|
- The plots of intensity versus wavelength for three black bodies at tem...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal Black-body at room temperature is thrown into a furnace. It i...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows three temperature scales with the freezing and boiling po...
Text Solution
|
- A composite bar of length L = L(1) + L(2) is made up from a rod of mat...
Text Solution
|
- A rail track made of steel having length 10 m is clamped on a railway ...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: According to Newton's law of cooling, the rate of loss of h...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : In change of state from solid to liquid the temperature de...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : A change in the temperature of a body cause change in dime...
Text Solution
|