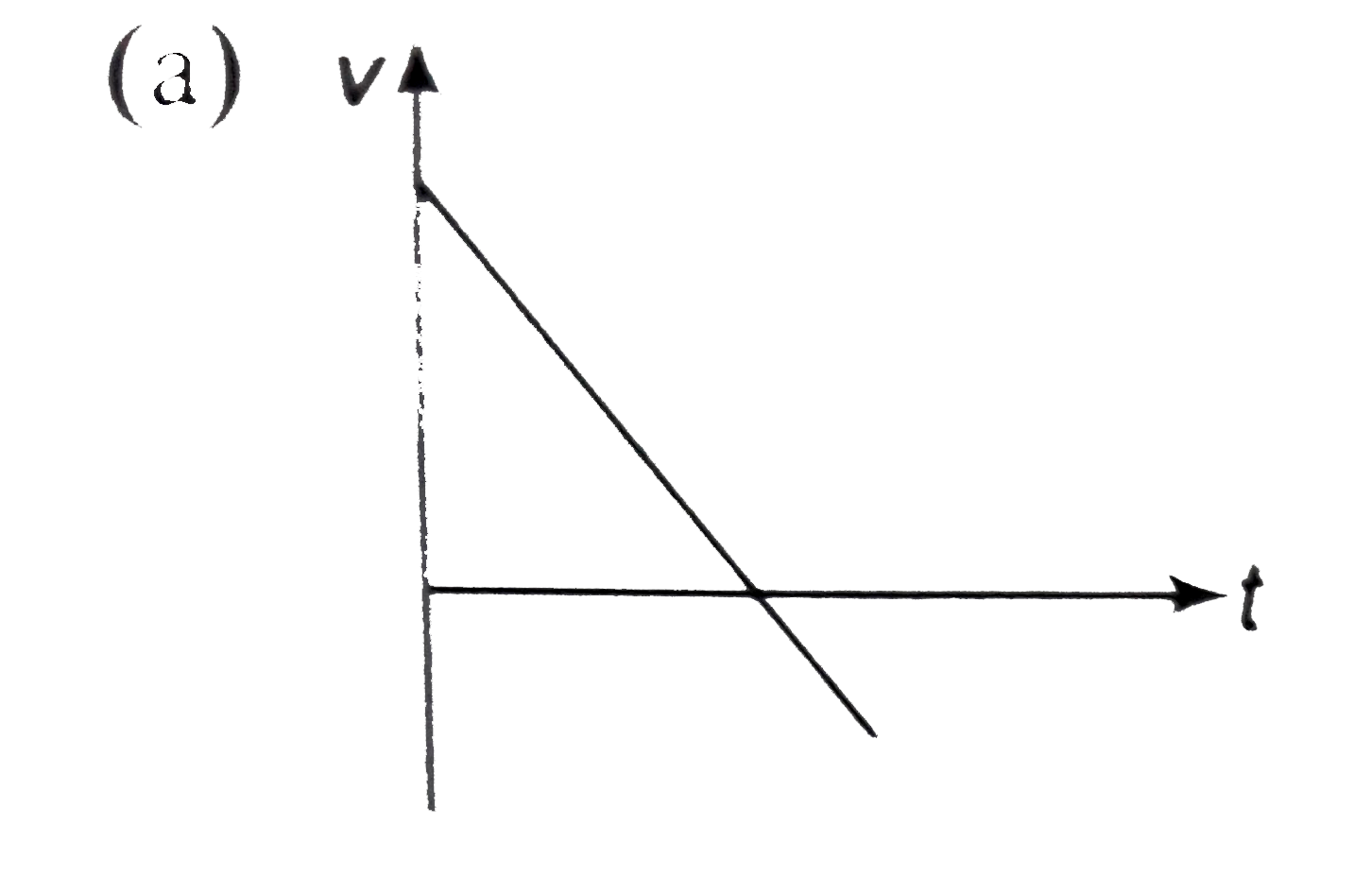
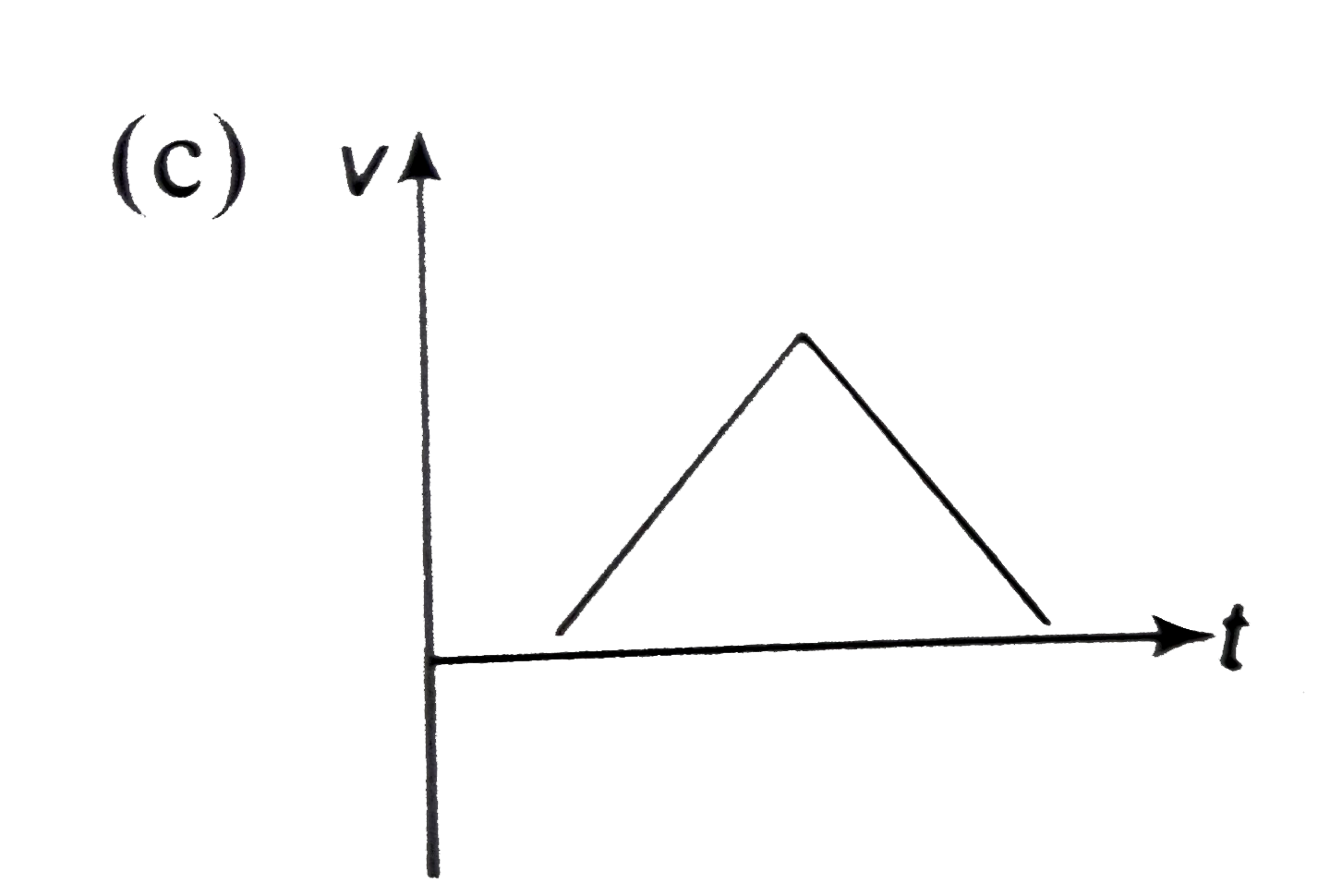
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
A2Z-MOCK TEST-Motion With Constant Acceleration
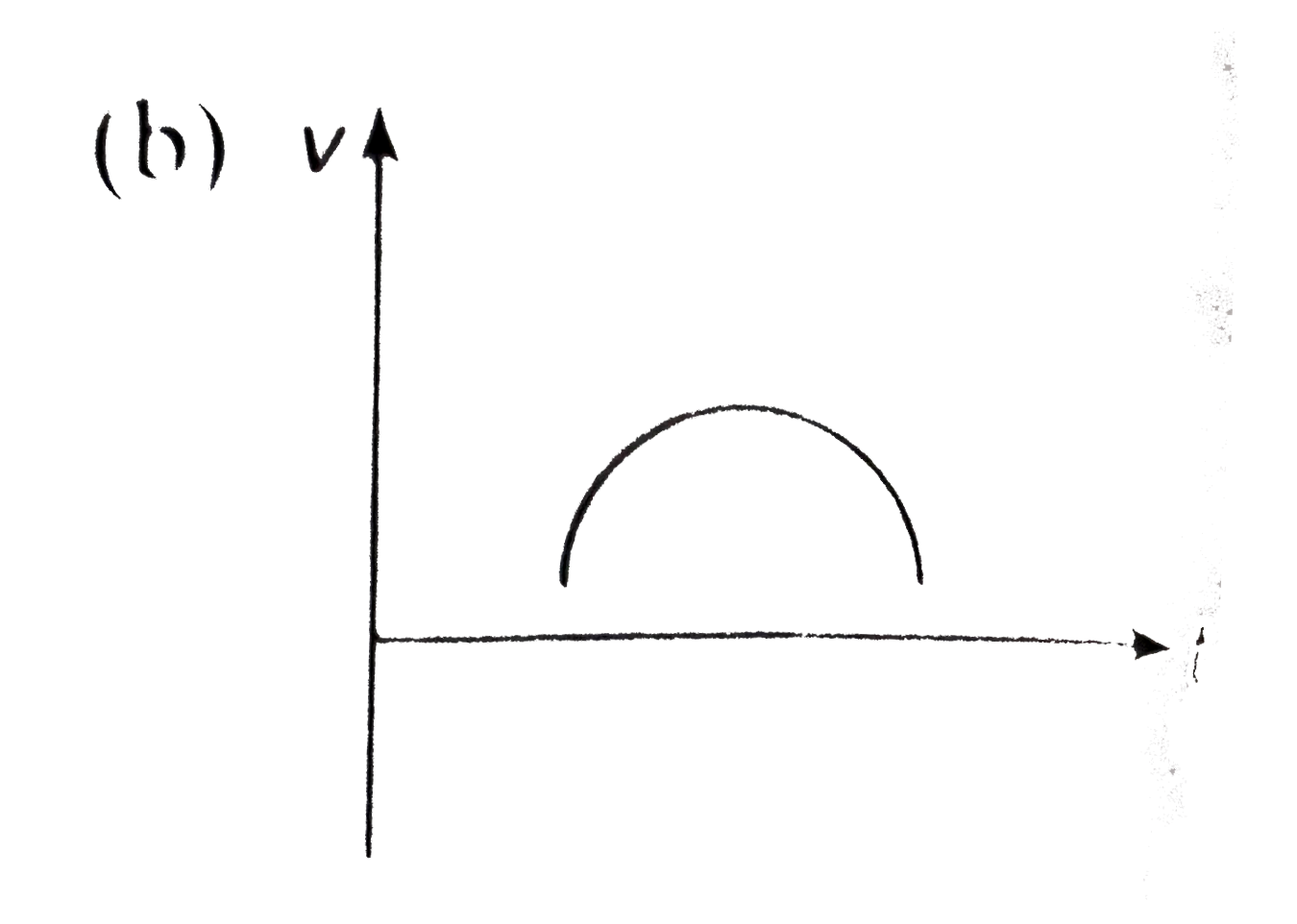
- A particle is thrown above, then correct v-t graph will be
Text Solution
|
- A candle of diameter d is floating on a liquid in a cylindrical contai...
Text Solution
|
- A given shaped glass tube having uniform cross-section is filled with ...
Text Solution
|
- When a ball is thrown up vertically with velocity v0, it reaches a max...
Text Solution
|
- A solid sphere is rolling on a frictionless surface, shown in figure w...
Text Solution
|
- A horizontal platform is rotating with uniform angular velcity around ...
Text Solution
|
- A ladder is leaned against a smooth wall and it is allowed to slip on ...
Text Solution
|
- A person is standing in an elevator. In which situation he finds his w...
Text Solution
|
- A particle having change q and m is projected with velocity vec v = 2 ...
Text Solution
|
- The velocity of a particle moving in the x-y plane is given by (dx)...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is droped from a high rise platform t = 0 starting from rest. A...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: The error in the measurement of radius of sphere is 0.3%. T...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: The isothermal curves intersect each other at a certain poi...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: The velocity of a body at the bottom of an inclind plane of...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: A body of mass 1 kg is making 1 rps in a circle of radius 1...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: The change in air pressure effects the speed of sound. Re...
Text Solution
|