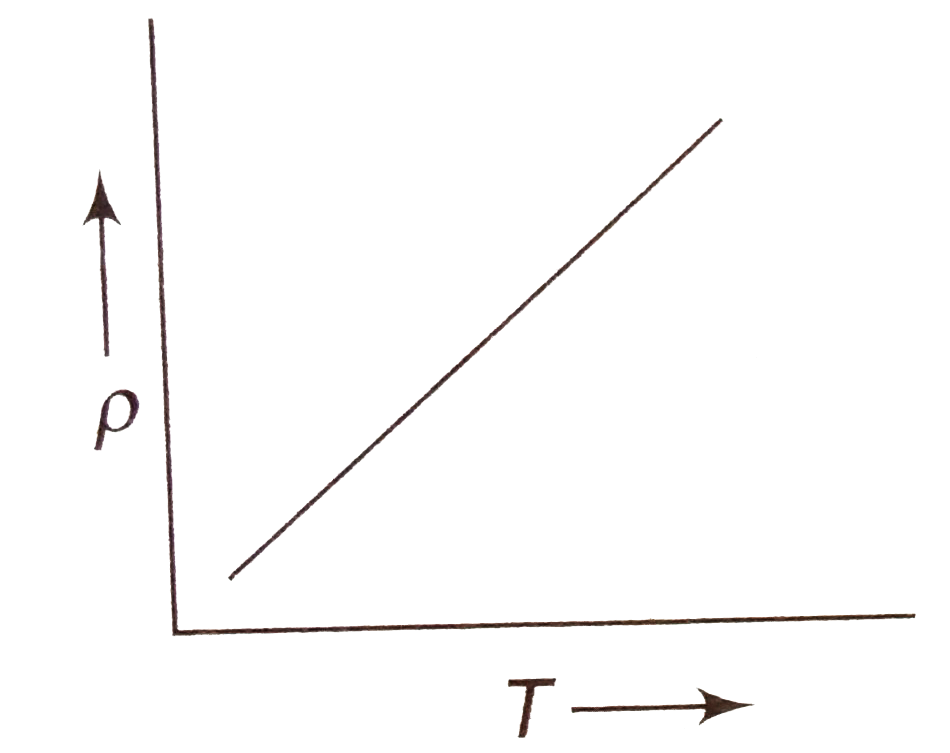
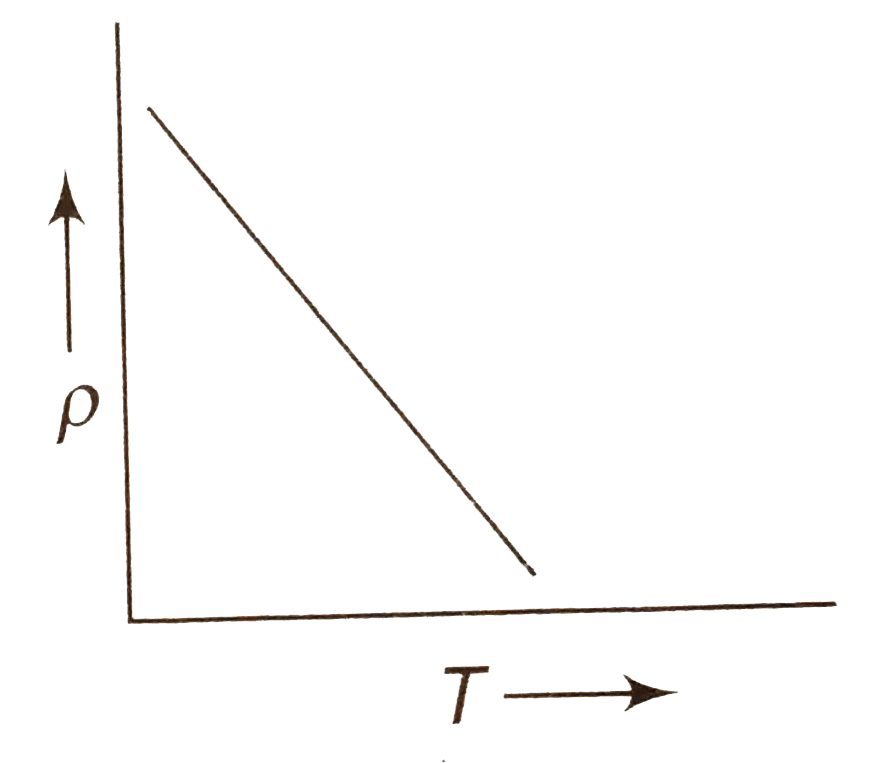
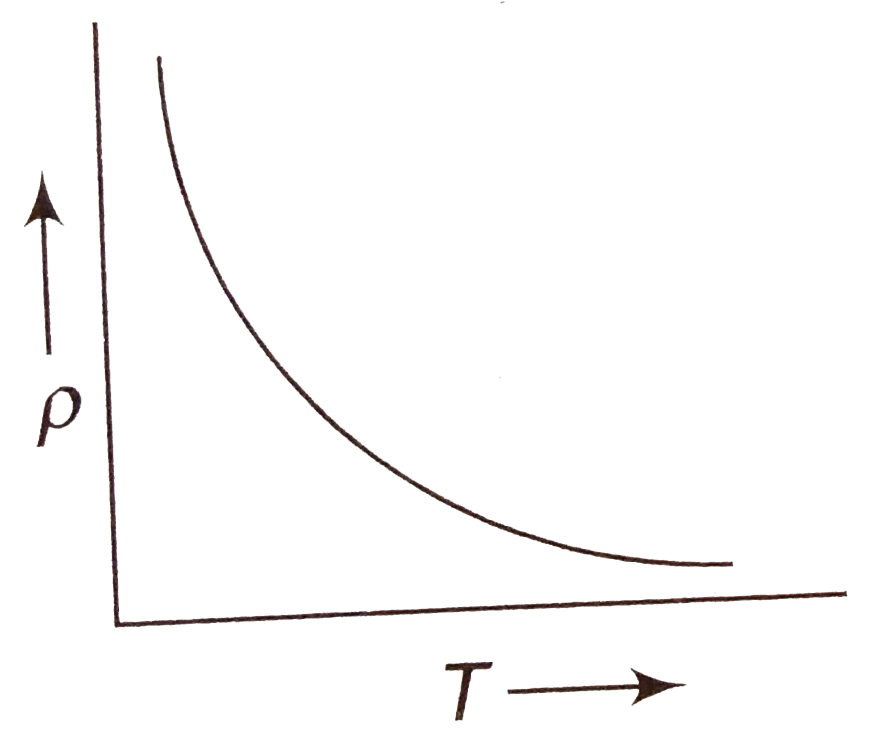
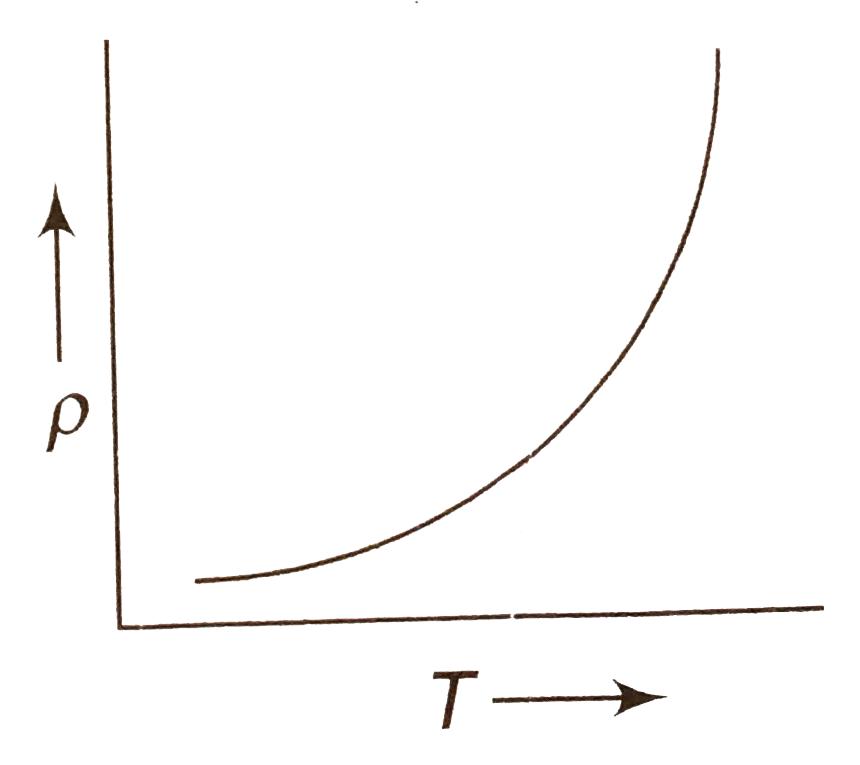
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
A2Z-MOCK TEST-General Kinematics
- A vertical spring with force constant k is fixed on a table. A ball of...
Text Solution
|
- A car travles 6km towards north at an angle of 45^(@) to the east and ...
Text Solution
|
- The speed of light ( c), gravitational constant (G) and plank's consta...
Text Solution
|
- Two bodies of mass m(1) and m(2) are initially at rest placed infinite...
Text Solution
|
- The adjacent graph shows the estension (Deltal) of a wire of length 1m...
Text Solution
|
- What is filled in a cylindrical container to a height of 3 m. The rati...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass (m) is executing oscillations about the origin on t...
Text Solution
|
- A person speaking normally produces a sound intensity of 40 dB at a di...
Text Solution
|
- v(rms), v(av) and v(mp) are root mean square average and most probable...
Text Solution
|
- N moles of a monoatomic gas is carried round the reversible rectangula...
Text Solution
|
- An organ pipe is closed at one end has fundamental frequency of 1500 H...
Text Solution
|
- A bomb of mass 3.0 kg explodes in air into two pieces of masses 2.0 kg...
Text Solution
|
- Suppose the sun expands so that its radius becomes 100 times its prese...
Text Solution
|
- The temperature (T) dependence of resistivity (rho) of a semiconductor...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following velocity-time graphs shows a realistic situatio...
Text Solution
|
- In an orbital motion, the angular momentum vector is :
Text Solution
|
- A sphere of mass M and radius R is falling in a viscous fluid. The ter...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure given below, the position-time graph of a particle of ma...
Text Solution
|
- A bolck of mass 10 kg is moving in x-direction with a constant speed o...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following functionss represents a simple harmonic oscilla...
Text Solution
|