Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
LAWS OF MOTION
PRADEEP|Exercise Value Based Questions with Answers|5 VideosLAWS OF MOTION
PRADEEP|Exercise Multiple Choice Questions|42 VideosLAWS OF MOTION
PRADEEP|Exercise Short Answer Questions|35 VideosKINEMATICS
PRADEEP|Exercise 1 NCERT Comprehension|4 VideosMATHEMATICAL TOOLS
PRADEEP|Exercise Fill in the blanks|5 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PRADEEP-LAWS OF MOTION-Higher order thinking skills
- A balloon with mass m is descending down with an acceleration a (where...
Text Solution
|
- A batsman deflects a ball by an angle of 45^(@) without changing its i...
Text Solution
|
- A constant force F=20N acts on a block of mass 2 kg which is connected...
Text Solution
|
- Two wooden blocks of masses 1kg and 2kg are separated by a certain di...
Text Solution
|
- A very flexible unifrom chain of mass M and length L is suspended ver...
Text Solution
|
- Assuming the length of a chain to be L and coefficient of static frict...
Text Solution
|
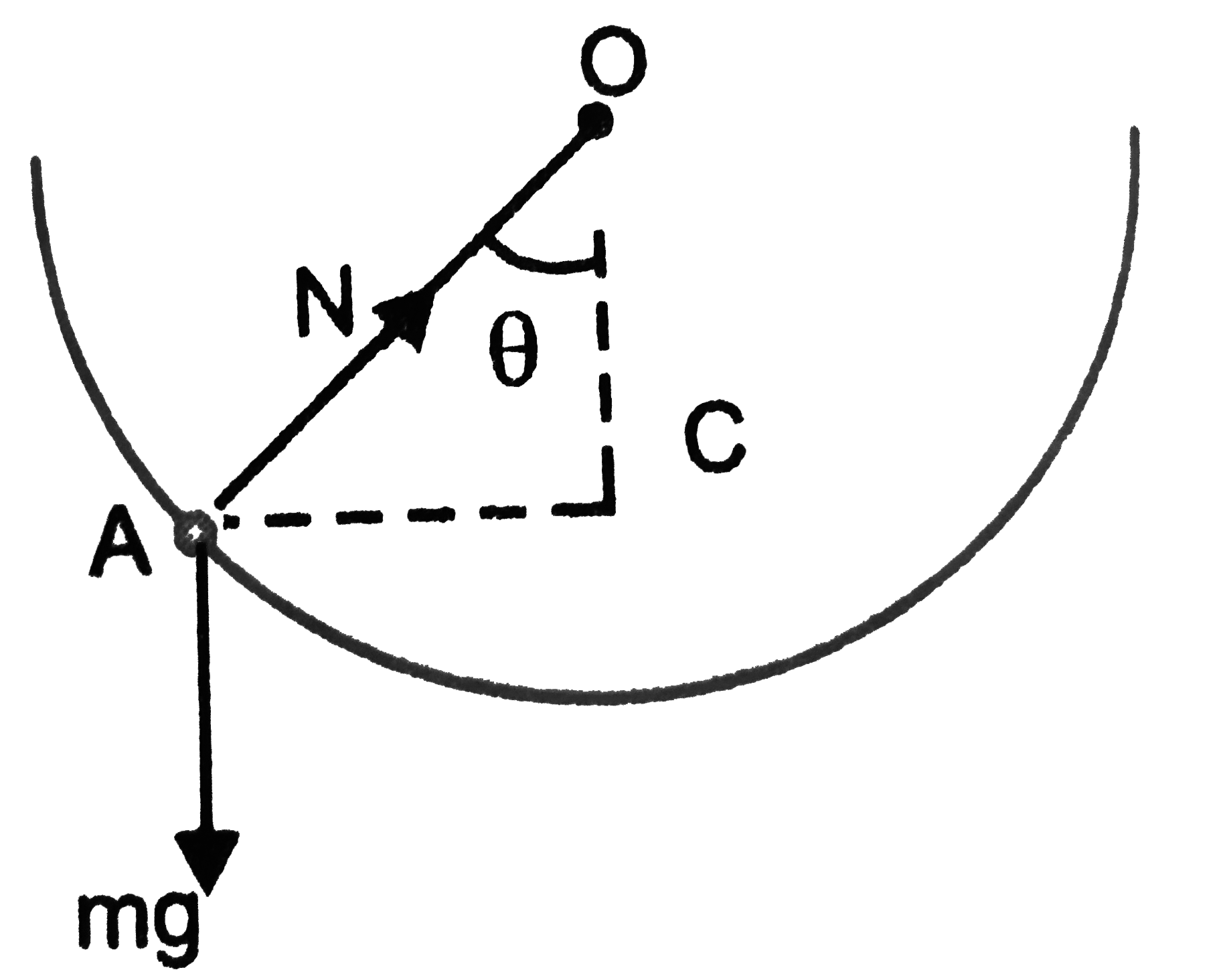
- A hemispherical bowl of radius R is set rotating about its axis of sym...
Text Solution
|
- A railway engine weighing 40 metic ton is travelling along a level tra...
Text Solution
|
- A boy (30 kg) sitting on his horse whips it. the horse speeds up at an...
Text Solution
|
- A block placed on a horizotnal surface is being pushed by a force F ma...
Text Solution
|
 .
.