Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PRADEEP-WORK, ENERGY AND POWER-solved examples
- The turbine pits at Niagra Falls are 50m deep. The average horse power...
Text Solution
|
- A railway carriage of mass 9000kg moving with a speed of 36kmh^(-1) co...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is dropped from a heigth H. It rebounds from the ground a numbe...
Text Solution
|
- A plastice ball is dropped from a height of 1m and rebounds several ti...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of 0.1 kg makes an elastic head on collision with a ball of unk...
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass M at rest is struck by a moving body of mass. Prove tha...
Text Solution
|
- In a nuclear reactor, a neutron of high speed (~~10^(7)ms^(-1)) must ...
Text Solution
|
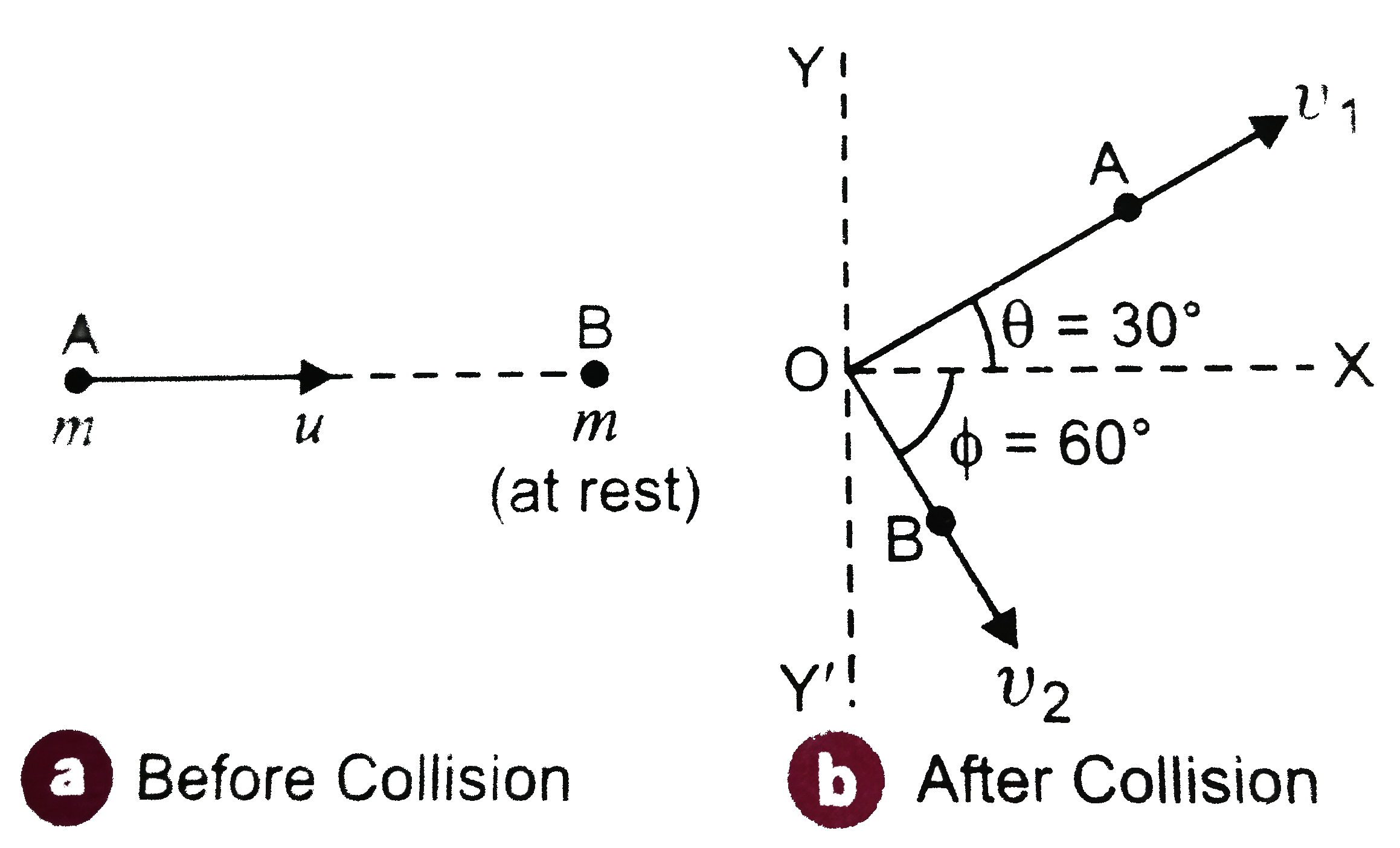
- Consider the collision depicted in Figure, to be between two billiard ...
Text Solution
|
- A and B are two particles having the same mass m. A is moving along X-...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles A and B of masses m and 2m are moving along the X-axis a...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles of masses 0.5 kg and 0.25kg moving with velocity 4.0 m//...
Text Solution
|
- A toy rocket of mass 0.1 kg hass a small fuel of mass 0.02 kg, which i...
Text Solution
|
- A bob of mass m is suspended by a light string of length L. It is impa...
Text Solution
|
- A ball moves along a curved path of radius 5m as shown in figure. It s...
Text Solution
|
- A bullet of mass m hits a target of mass M hanging by a string and get...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform chain of mass m & length L is kept on a smooth horizontal ta...
Text Solution
|
- Aparticle of mass 1 g executes an oscillatory motion on the concave su...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass 0.1kg has an iniital speed of 4ms^(-1) at a point A...
Text Solution
|
- A 100 metric ton engine is moving up a slope of gradient 5^(@) at a s...
Text Solution
|
- A ball moving with a speed of 9m//s strikes an identical ball at rest,...
Text Solution
|