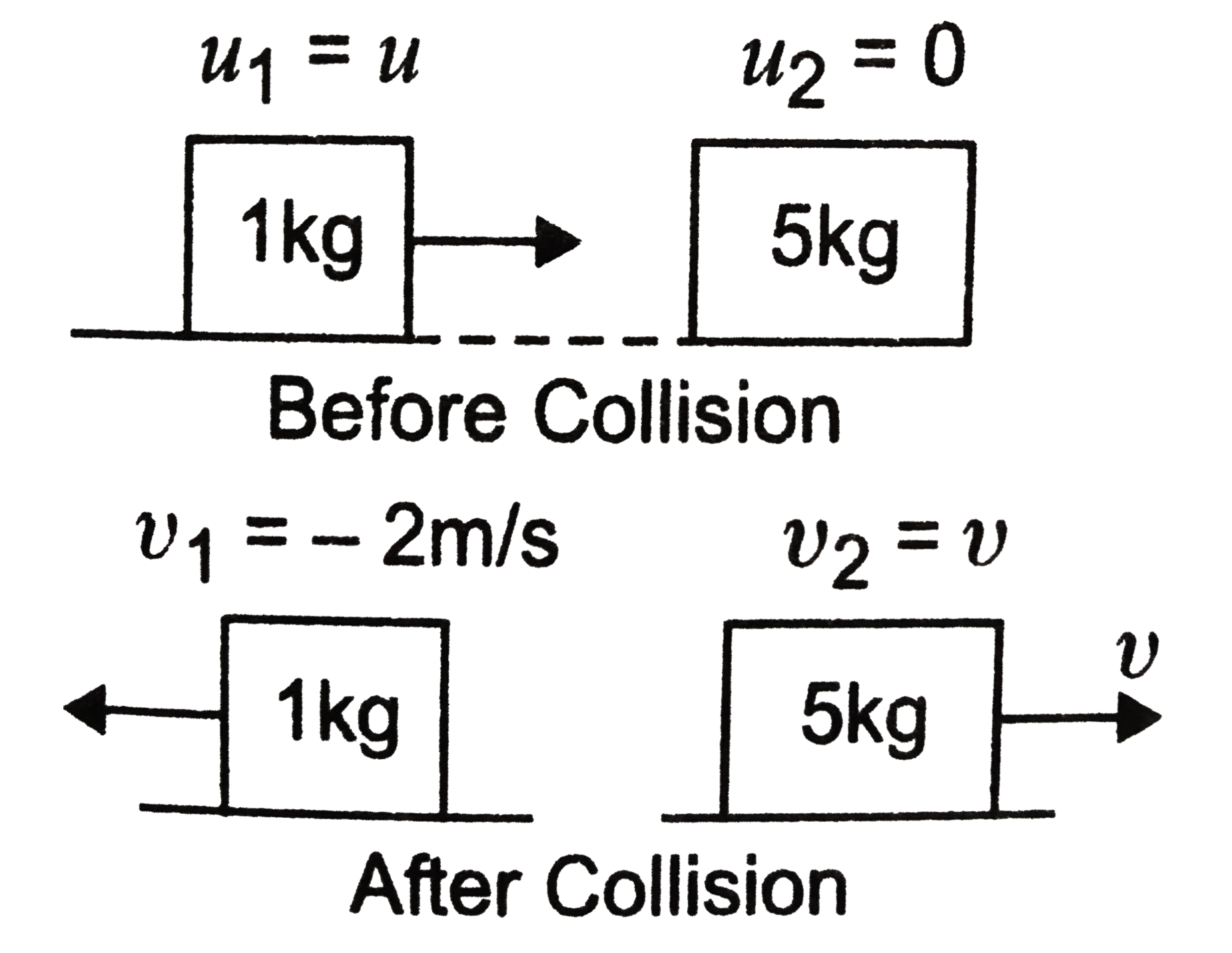
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PRADEEP-WORK, ENERGY AND POWER-Multiple choice question
- For a perfectly elastic collision and a perfectly inelastic collision,...
Text Solution
|
- The balls, having linear momenta vecp1=vecpi and vecp22=-vecpi, underg...
Text Solution
|
- When work done on a particle is positive, then its
Text Solution
|
- A particle is acted upon by a force of constant magnitude which is alw...
Text Solution
|
- You lift a suitcase from the floor and keep it on a table. The work do...
Text Solution
|
- If the force is always perpendicular to motion, then KE remains consta...
Text Solution
|
- A point mass of 1kg collides elastically with a stationary point mass ...
Text Solution
|
- One end of a light spring of spring constant k is fixed to a wall and ...
Text Solution
|
- A 3-kg steel ball strikes a wall with a speed of 10.0ms^(-1) at an ang...
Text Solution
|
- A force F acting on a body depends on its displacement S as FpropS^(-1...
Text Solution
|
- A heavy stone is thrown from a cliff of height h in a given direction....
Text Solution
|
- A ball falls vertically onto a floor with momentum p and then bounces ...
Text Solution
|
- No work is done by a force on an object if
Text Solution
|
- A particle is acted upon by a force of constant magnitude which is alw...
Text Solution
|
- A Force F acting on an object varies with distance x as shown in the h...
Text Solution
|
- The upper half of an inclined plane with inclination phi is perfectly ...
Text Solution
|
- A ball hits a floor and rebounds after an inelastic collision. In this...
Text Solution
|
- A smooth block is released at rest on a 45^@ incline and then slides a...
Text Solution
|
- A body moving towards a finite body at rest collides with it. It is po...
Text Solution
|
- The block of mass M moving on the frictionless horizontal surface col...
Text Solution
|