Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
SYSTEMS OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION
PRADEEP|Exercise CONCEPTUAL PROBLEMS II.|2 VideosSYSTEMS OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION
PRADEEP|Exercise VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS I.|2 VideosSYSTEMS OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION
PRADEEP|Exercise CONCEPTUAL PROBLEMS I.|2 VideosRAY OPTICS
PRADEEP|Exercise Problem For Practice(a)|25 VideosTHERMODYNAMICS
PRADEEP|Exercise Assertion- Reason Type Questions|19 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PRADEEP-SYSTEMS OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION-CONCEPTUAL PROBLEMS
- If a body is rotating, is it necessarily being acted upon by an extern...
Text Solution
|
- Why is the handle of a screw made wide ?
Text Solution
|
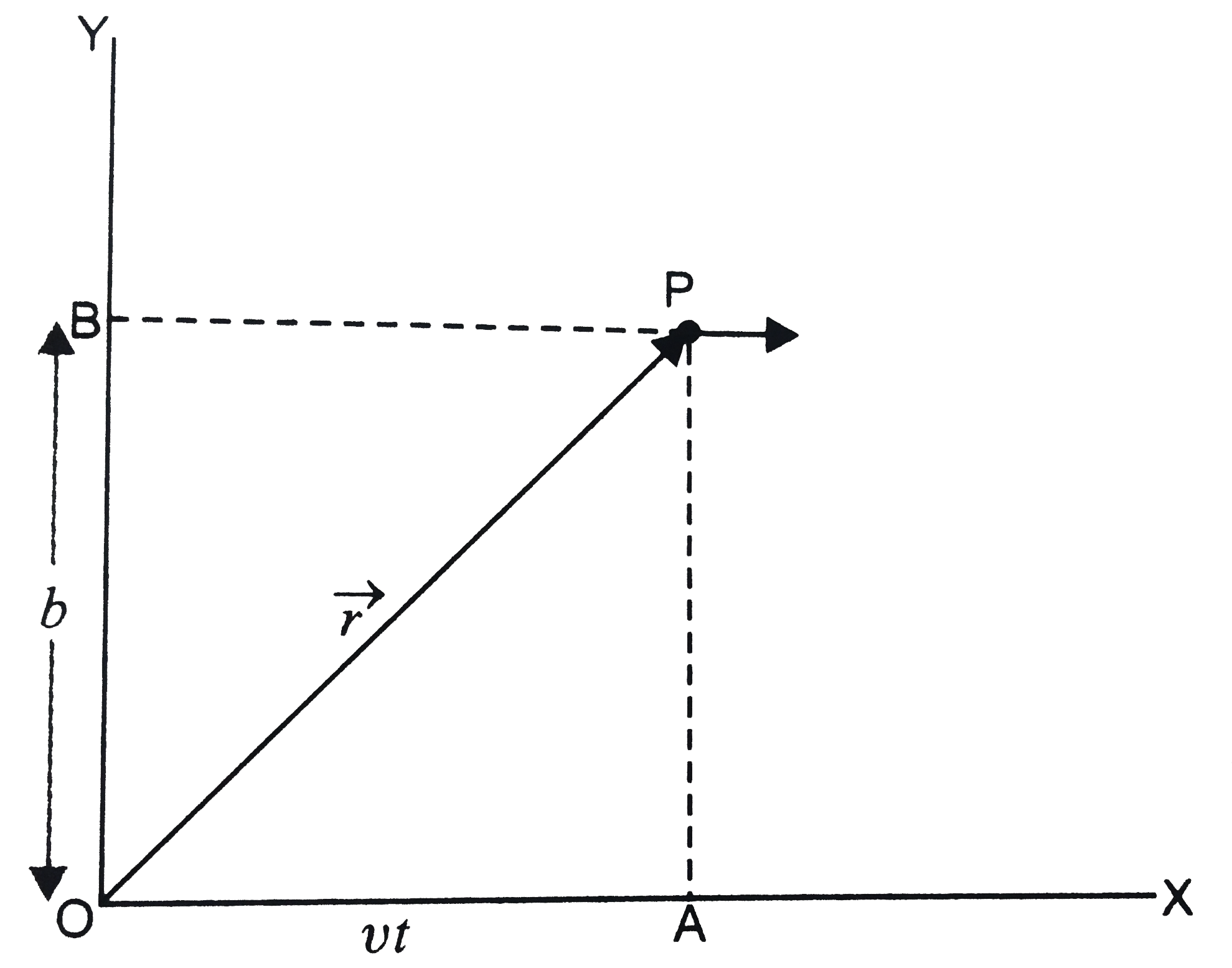
- A particle is moving along a stright line parallel to x-axis with cons...
Text Solution
|
- A particle performing uniform circular motion has angular frequency is...
Text Solution
|
- Does the moment of inertia of abody change with the speed of rotation...
Text Solution
|
- What is the advantage of a flywheel ?
Text Solution
|
- Why spokes are provided in a bicycle wheel ?
Text Solution
|
- The moment of inertia of a soild sphere about a tangent is (5)/(3)mr^(...
Text Solution
|
- Find radius of gyration of a rod of length l and mass m about an axis ...
Text Solution
|
- For a given mass and size, moment of inertia of a soild disc is smalle...
Text Solution
|
- In a fly wheel, most of the mass is concentrated at the rim ? Explain ...
Text Solution
|
- Two satellites of equal masses, which can be considered as particles a...
Text Solution
|
- How will you distinguish between a hard boiled egg and a raw egg by s...
Text Solution
|
- If earth were to shrink suddenly, what would happen to the length of t...
Text Solution
|
- If two circular disks of the weight and thickness are made from metals...
Text Solution
|
- The moments of inertia of two rotating bodies A and B are I(A) and I(B...
Text Solution
|
- If polar ice caps melt, then the time duration of one day
Text Solution
|
- If no external torque acts on a body, will its angular velocity remain...
Text Solution
|
- How does an ice-skater, a ballet dancer or an acrobat take advantage o...
Text Solution
|
- Explain why the speed of a whirl wind in a tornado is alarmingly high ...
Text Solution
|