Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
SYSTEMS OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION
PRADEEP|Exercise SOLVED EXAMPLES TYPE E|1 VideosSYSTEMS OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION
PRADEEP|Exercise ADVANCED PROBLEMS FOR COMPETITIONS|20 VideosSYSTEMS OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION
PRADEEP|Exercise SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS II.|2 VideosRAY OPTICS
PRADEEP|Exercise Problem For Practice(a)|25 VideosTHERMODYNAMICS
PRADEEP|Exercise Assertion- Reason Type Questions|19 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PRADEEP-SYSTEMS OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION-LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS
- Obtain a expression for torque in polar co-ordinates.
Text Solution
|
- Explain the concept of angular momentum and obtain an expression for i...
Text Solution
|
- Discuss the physical meaning of angular momentum.
Text Solution
|
- Briefly explain equilibrium of a rigid body. When is a body said to be...
Text Solution
|
- Obtain an expression for kinetic energy of rotation of a body. Hence d...
Text Solution
|
- Establish a relation between torque and moment of inertia of a rigid b...
Text Solution
|
- Establish a relation between angular momentum and moment of inertia of...
Text Solution
|
- State and explain the principle of conservation of angular momentum. G...
Text Solution
|
- State and prove theorem of parallel axes.
Text Solution
|
- State and prove theorem of perpendicular axes.
Text Solution
|
- Derive an expression for moment of inertia of a thin circular ring abo...
Text Solution
|
- Obtain an expression for moment of inertia of a uniform circular disc ...
Text Solution
|
- Discuss rolling without slipping of a cylinder down a rough inclined p...
Text Solution
|
- Draw analogy between rotational motion and translational motion.
Text Solution
|
- Find the centre of mass of a unifrom (a) half-disc,(b) quarter-disc.
Text Solution
|
- Two discs of moments of inertia I(1) and I(2) about their respective a...
Text Solution
|
- A disc of radius R is rotating with an angular speed omega(0) about a ...
Text Solution
|
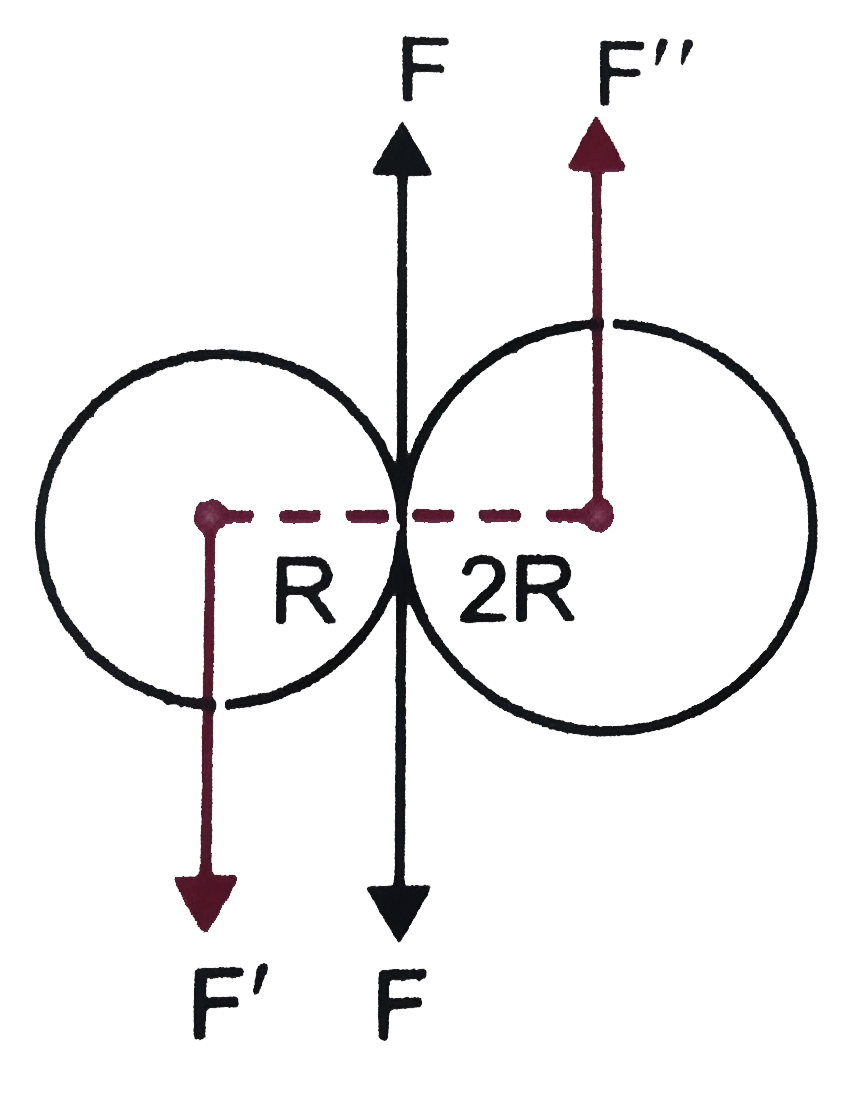
- Two cylindrical hollow drums of radii R and 2R, and of a commom height...
Text Solution
|
- A unifrom square plate S (side c) and a unifrom rectangular plate R(si...
Text Solution
|
- A unifrom disc of radius R, is resting on a table on its rim. The coef...
Text Solution
|