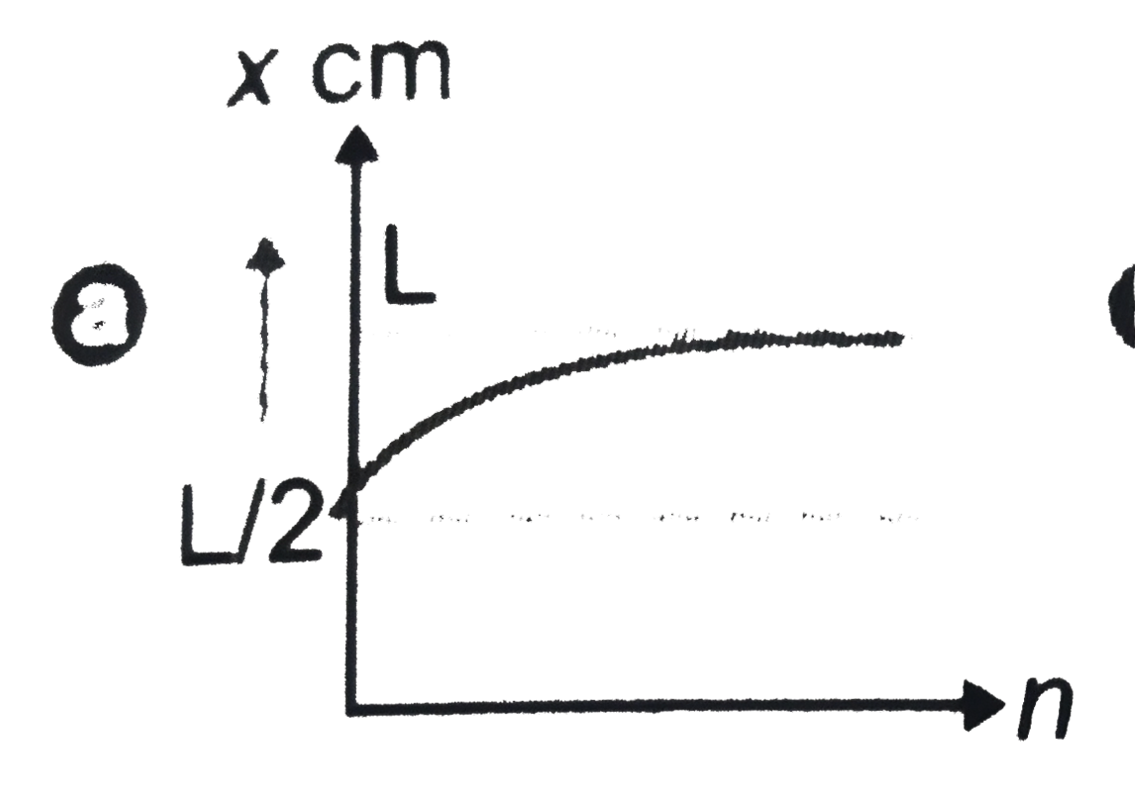
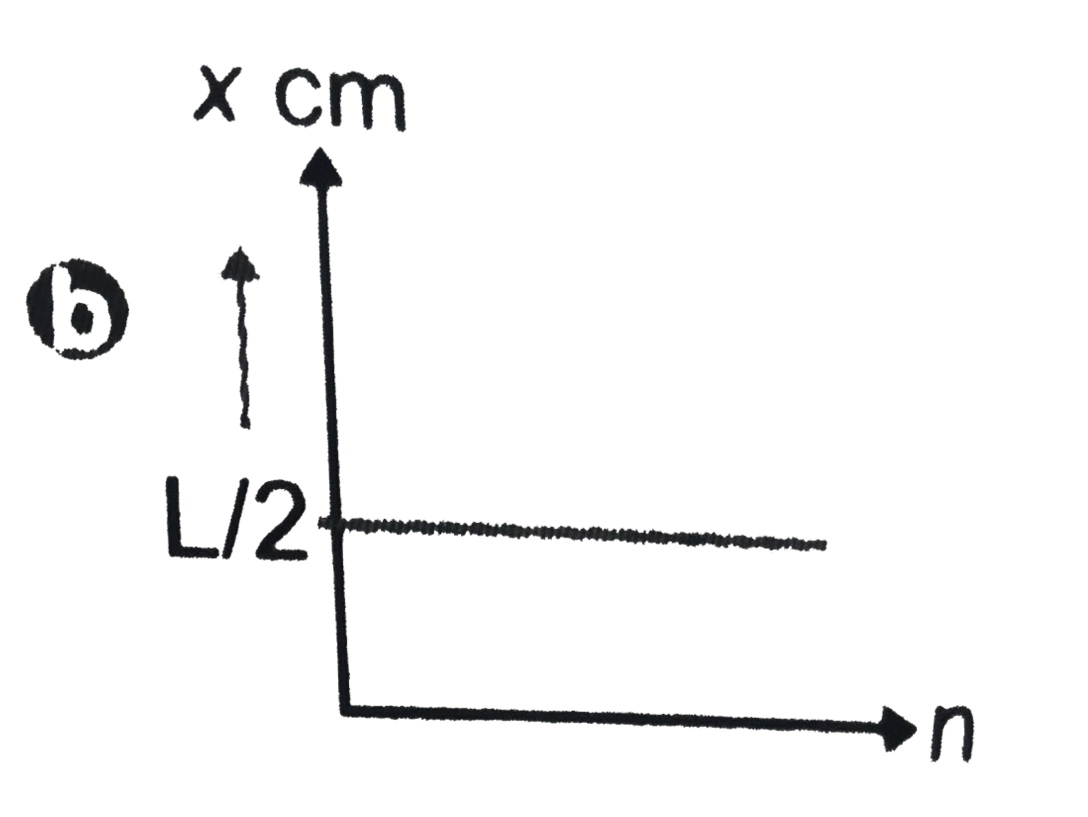
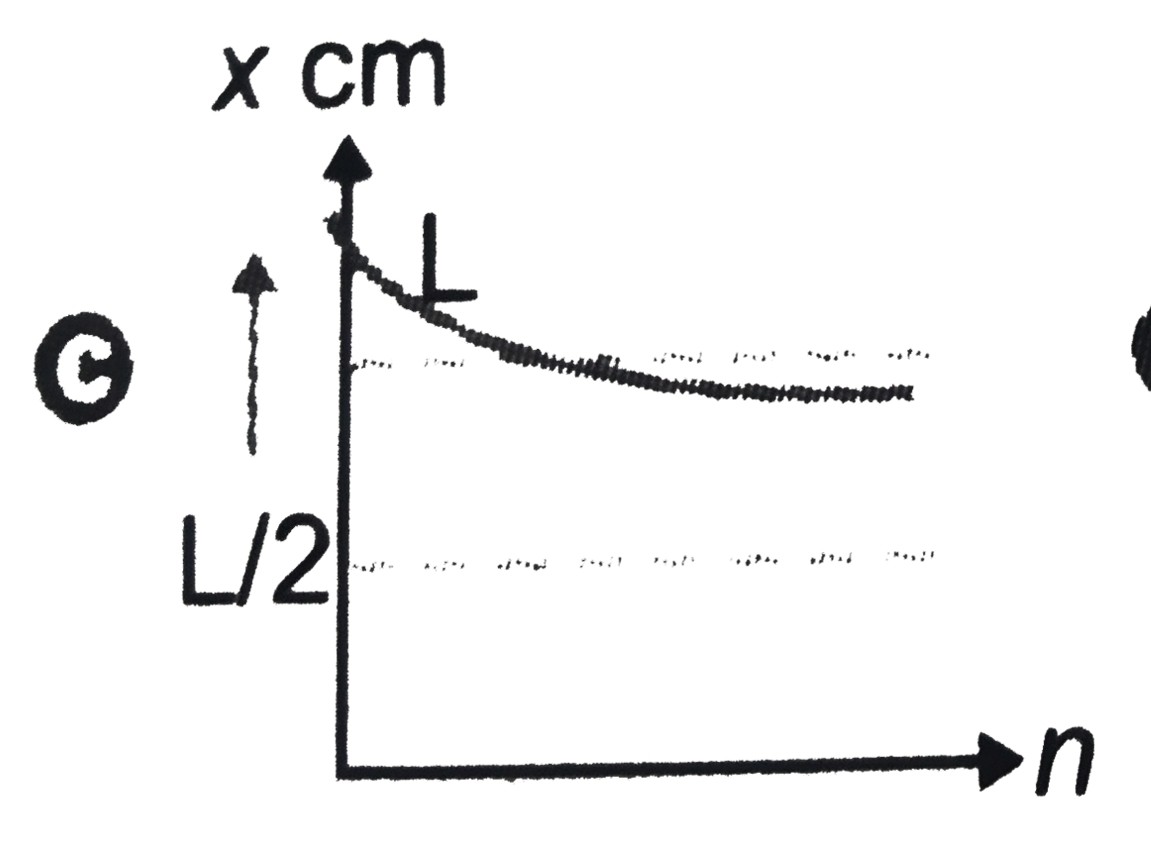
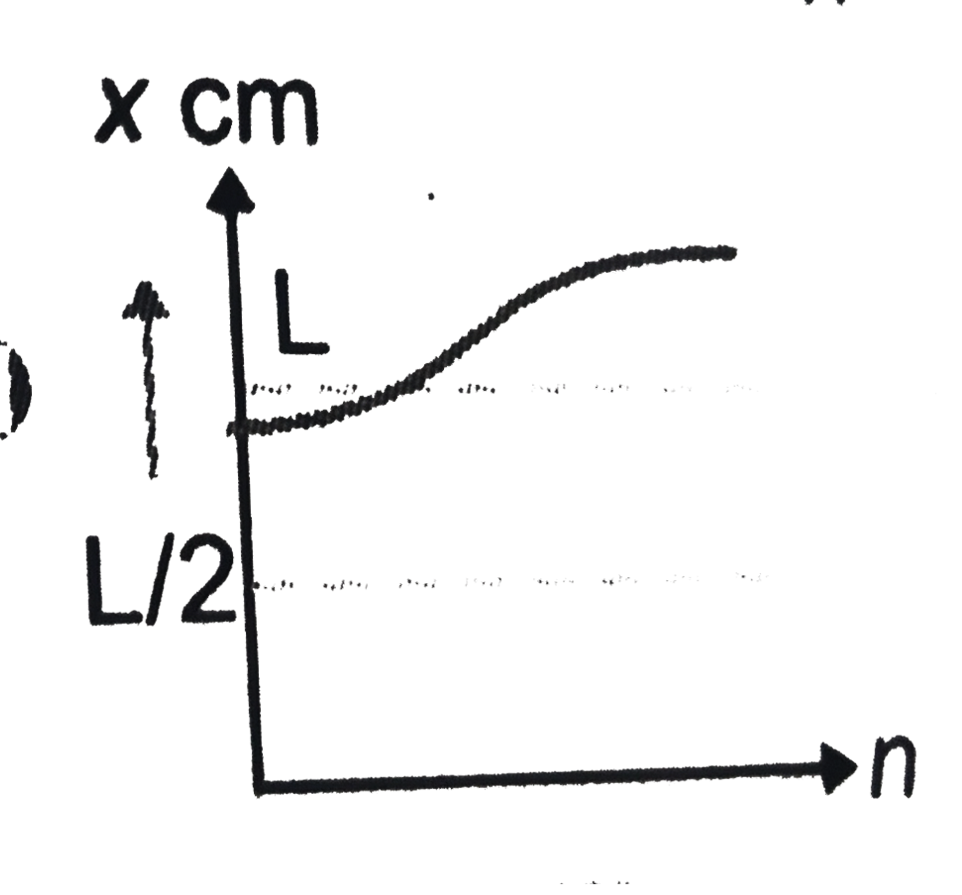
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A thin rod of length 'L' is lying along the x-axis with its ends at x...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of length L is placed along the x-axis between x=0 and x=L . The...
Text Solution
|
- A thin rod of length 6 m is lying along the x-axis with its ends at x=...
Text Solution
|
- L लम्बाई की एक पतली छड़ X-अक्ष के अनुदिश रखी है। उसके सिरे x = 0 तथा x...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of length L is placed along the x-axis between x = 0 and x = L. ...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of length L is placed along the x-axis between x = 0 and x = L. ...
Text Solution
|
- A non–uniform thin rod of length L is placed along x-axis as such its ...
Text Solution
|
- A thin rod of length L is lying along the x-axis with its ends at x = ...
Text Solution
|
- A thin rod length 'L' is lying along the x-axis with its ends at x=0 a...
Text Solution
|