A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
A2Z-FLUID MECHANICS-Problems Based On Mixed Concepts
- A solid sphere of density eta (gt 1) times lighter than water is suspe...
Text Solution
|
- The verticla water tank, shown has uniform cross section, closed at th...
Text Solution
|
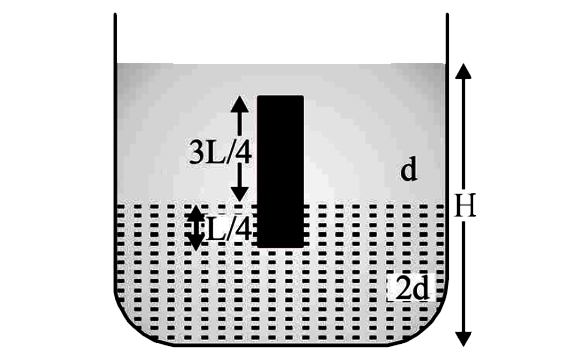
- A homogeneous solid cylinder of length L(LltH/2), cross-sectional area...
Text Solution
|
- A cube made of material having a density of 900 kgm^(-3) floats betwee...
Text Solution
|
- A rectangular bar of soap having density 800kg//m^(3) floats in water ...
Text Solution
|
- We have a vessel in shape of a cuboid partially filled with water. Its...
Text Solution
|
- A concrete sphere of radius R has cavity of radius r which is packed w...
Text Solution
|
- In a wind tunnel experiment the pressure on the upper and lower surfac...
Text Solution
|
- The force acting on a window of area 50cm xx 50cm of a submarine at a ...
Text Solution
|
- Fig, shows a U-tube of uniform cross-sectional area A accelerated with...
Text Solution
|
- A hollow cylinder of mass m made heavy at its bottom is floating verti...
Text Solution
|
- Assume the density of brass weights to be 8 g cm^(-3) and that of air ...
Text Solution
|
- A body floats with one-third of its volume outside water and 3//4 of i...
Text Solution
|
- Two solid pieces, one of gold and the other of silver when immersed co...
Text Solution
|
- Two substances of densities rho(1) and rho(2) are mixed in equal volum...
Text Solution
|
- A metallic sphere with an internal cavity weighs 40 gwt in air and 20 ...
Text Solution
|
- A stream-lined body falls through air from a height h on the surface o...
Text Solution
|
- A plane is in level flight at constant speed and each of the two wings...
Text Solution
|
- An aircraft of mass 4 xx 10^(5)kg with total wing area 500m^(2) in lev...
Text Solution
|
- The two femurs each of cross-sectional area 10 cm^(2) support the uppe...
Text Solution
|