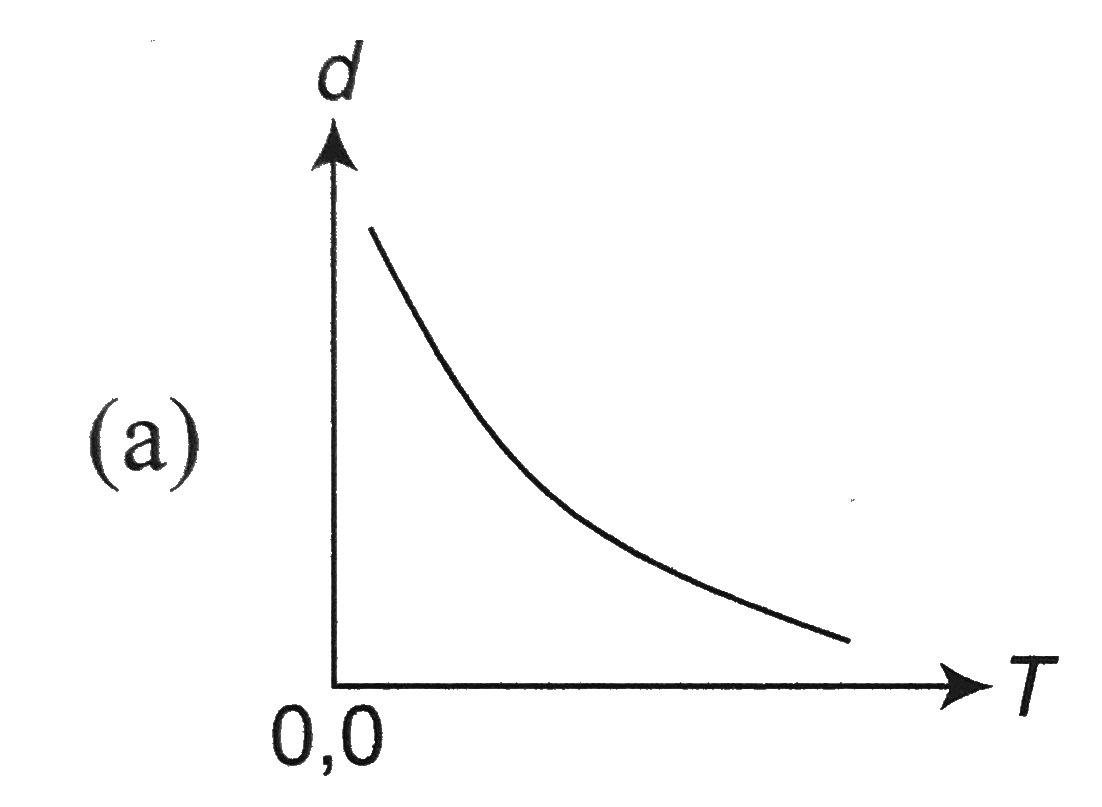
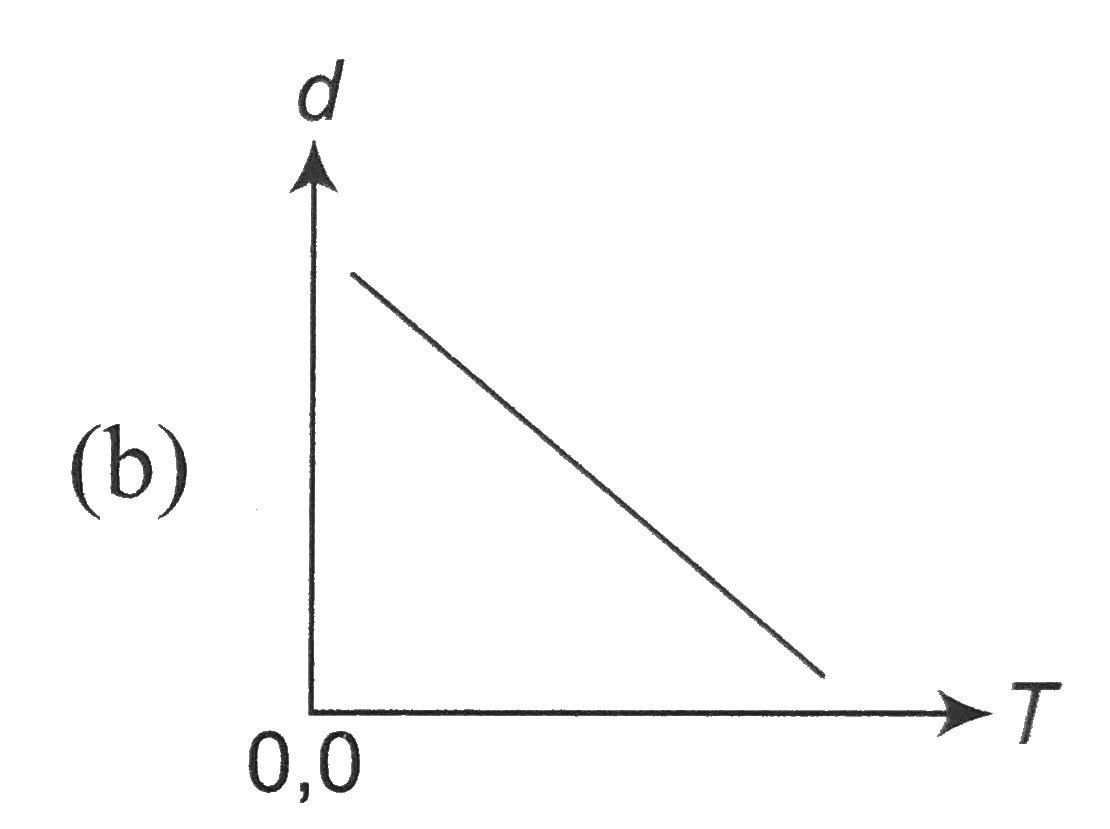
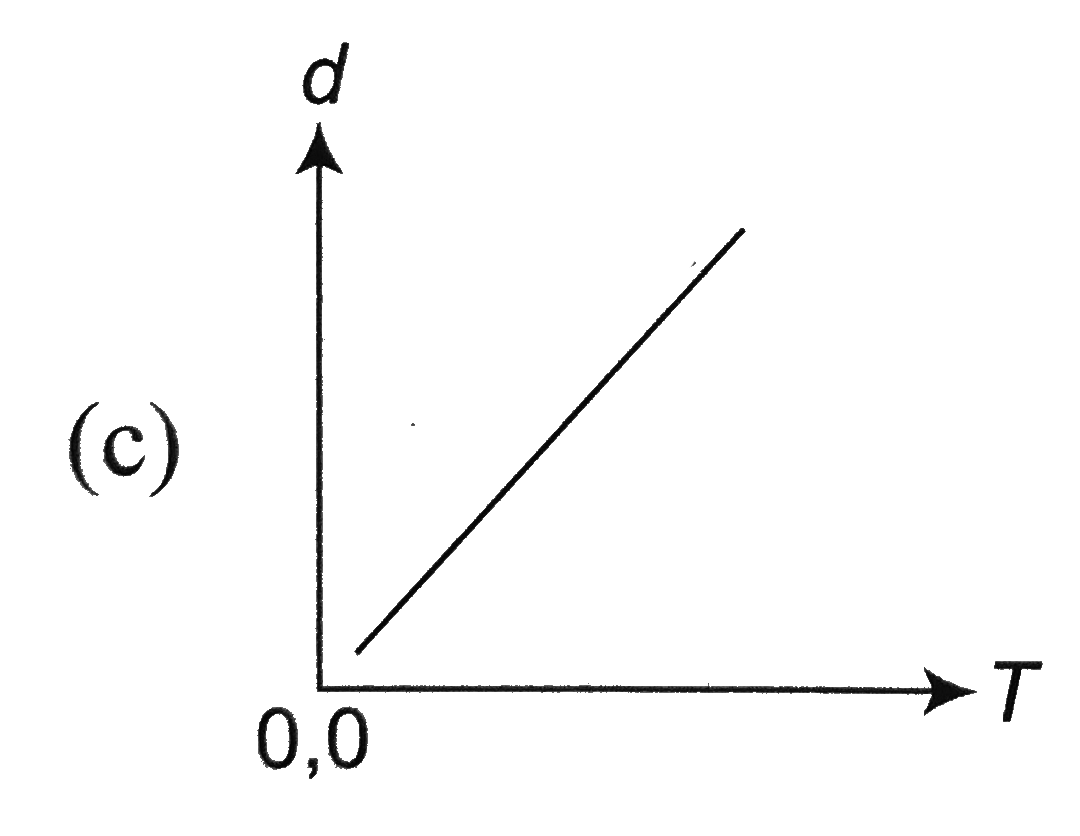
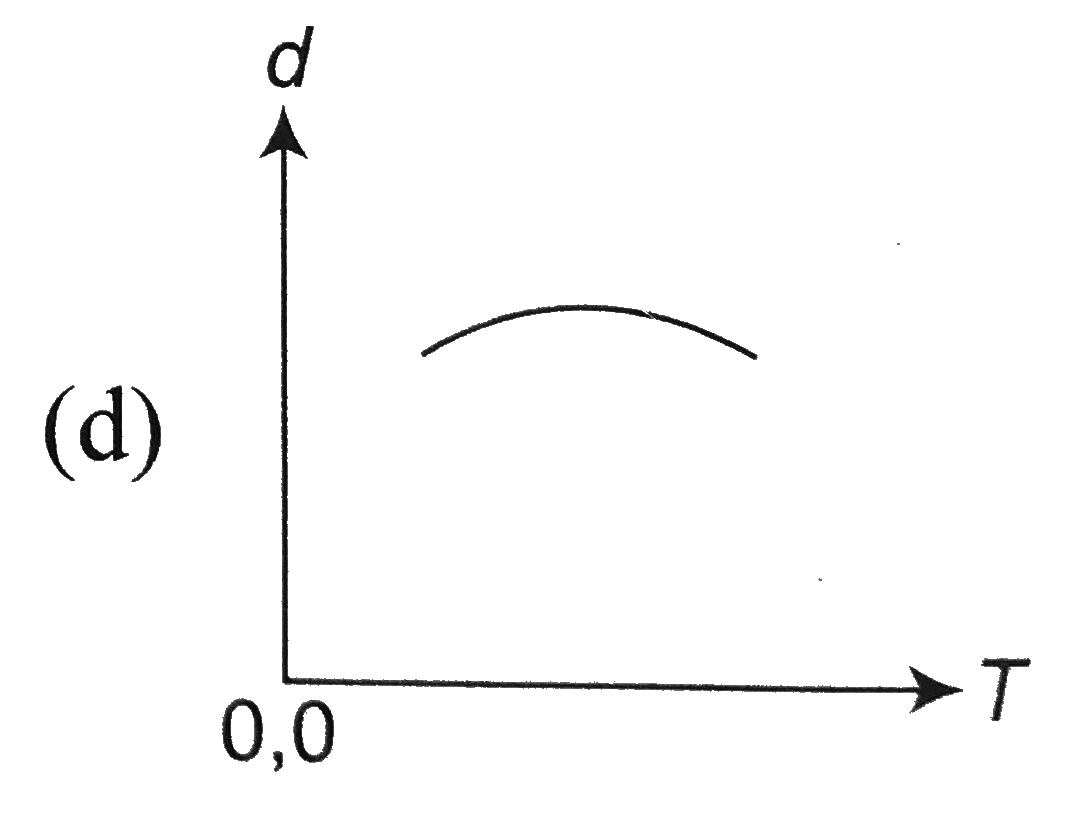
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
KINETIC THEORY OF GASES AND THERMODYNAMICS
A2Z|Exercise First Law Of Thermodynamics , Internal Energy And Work Done|55 VideosKINETIC THEORY OF GASES AND THERMODYNAMICS
A2Z|Exercise Application Of First Law Of Thermodynamics In Different Situations|25 VideosKINETIC THEORY OF GASES AND THERMODYNAMICS
A2Z|Exercise Chapter Test|29 VideosGRAVITATION
A2Z|Exercise Chapter Test|29 VideosMOCK TEST
A2Z|Exercise Motion With Constant Acceleration|15 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
A2Z-KINETIC THEORY OF GASES AND THERMODYNAMICS-Ideal Gas Equation
- A sample of a perfect gas occupies a volume V at a pressure P and obso...
Text Solution
|
- In order to increase the volume of a gas to 3 times at constant pressu...
Text Solution
|
- At a constant pressure, of the following graphs that one which represe...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows the pressure P versus volume V graphs for a certains mass...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows graphs of pressure vs density for an ideal gas at two tem...
Text Solution
|
- Suppose ideal gas equation follows VP^(3) = constant. Initial temperat...
Text Solution
|
- Two spherical vessel of equal volume are connected by a n arrow tube. ...
Text Solution
|
- Pressure versus temperature graphs of an ideal gas are as shown in fig...
Text Solution
|
- Density vs volume graph is shown in the figure. Find corresponding pre...
Text Solution
|
- The initial temperature of a gas is 100^(@)C. The gas is contained in ...
Text Solution
|
- A closed hollow insulated cylinder is filled with gas at 0^(@)C and al...
Text Solution
|
- The air tight and smooth piston of a cylindrical vessel are connected ...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas has a volume of 3 V at 2 atmosphere pressure. Keeping the...
Text Solution
|
- The volume of a given mass of a gas at 27^(@)C, 1 atm is 100 cc. What ...
Text Solution
|
- A vessel of volume 1660 cm^(3) contains 0.1 "mole" of oxygen and 0.2 "...
Text Solution
|
- One litre of helium gas at a pressure 76 cm. Of Hg and temperature 27^...
Text Solution
|
- A constant pressure V(1) and V(2) are the volumes of a given mass of a...
Text Solution
|
- In which of these diagrams, the density of an ideal gas remains consta...
Text Solution
|
- V = k((P)/(T))^(0.33) where k is constant. It is an,
Text Solution
|
- The densities at points A and B are rho(0) and (3 rho(0))/(2). Find th...
Text Solution
|