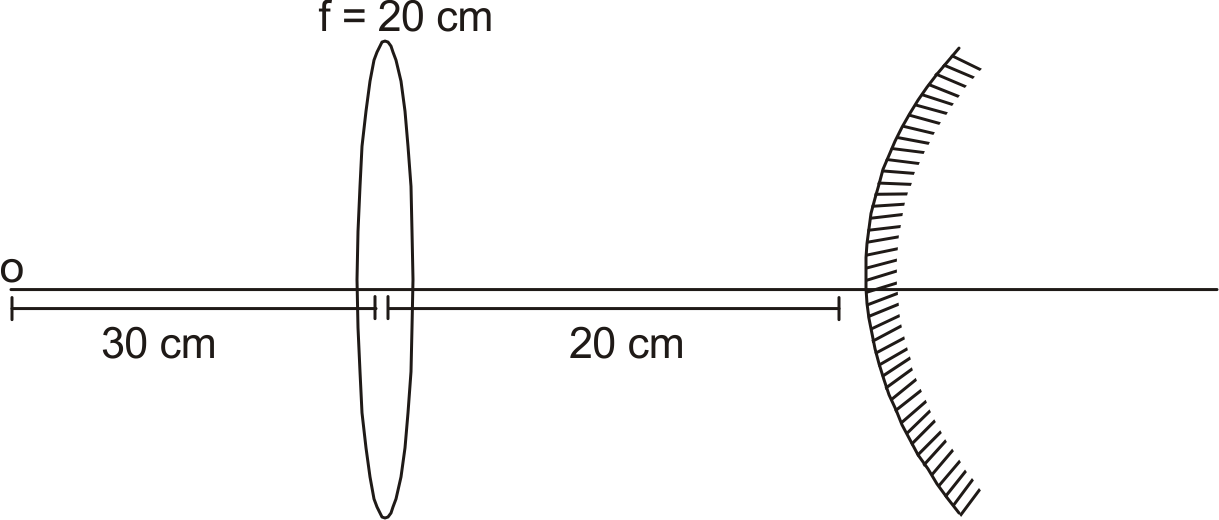
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-REVISION DPP-All Questions
- Consider a solid sphere of density rho and radius 4R. Centre of the sp...
Text Solution
|
- The lens shown is equiconvex having refractive Index. 1.5. In the situ...
Text Solution
|
- The electric field intensity at the center of a uniformly charged hemi...
Text Solution
|
- A thin converging lens forms a real image of an object located far awa...
Text Solution
|
- A point object P is moving towards left with speed 5 mm/sec parallel t...
Text Solution
|
- Monochromatic light rays parallel to x-axis strike a convex lens AB of...
Text Solution
|
- Two point charges having charge +Q, –q and mass M, m respectively are ...
Text Solution
|
- At distance 'r' from a point charge, the ratio (U)/(V^(2)) (where 'U' ...
Text Solution
|
- A cylindrical portion of radius r is removed from a solid sphere of ra...
Text Solution
|
- Two satellites revolve around the ‘Sun’ as shown in the figure. First ...
Text Solution
|
- A small area is removed from a uniform spherical shell of mass M and r...
Text Solution
|
- A meteorite approaching a planet of mass M (in the straight line passi...
Text Solution
|
- Two converging lenses have focal length f1 and f2 (f1gtgtf2 ). The o...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown an infinitely long wire of uniform linear charge d...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a spherical planet rotating about its axis. The velocity of a...
Text Solution
|
- The figure shows two equal, positive charges, each of magnitude 50 muC...
Text Solution
|
- Orbital velocity of a satellite in its orbit (around earth) of radius ...
Text Solution
|
- A solid spherical planet of mass 2m and radius 'R' has a very small tu...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown A & B are two charged particles having charges q a...
Text Solution
|
- A light ray enters into a medium whose refractive index varies along t...
Text Solution
|