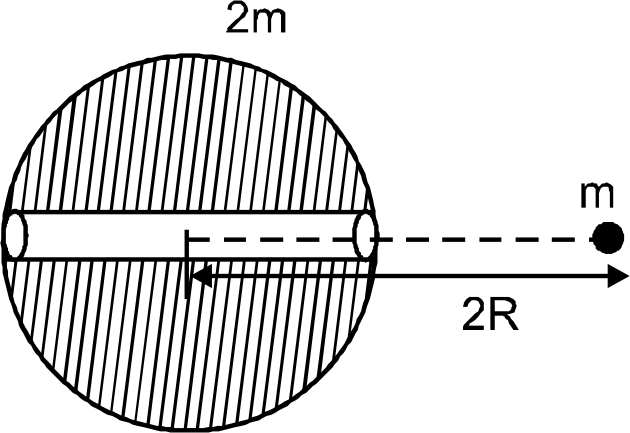
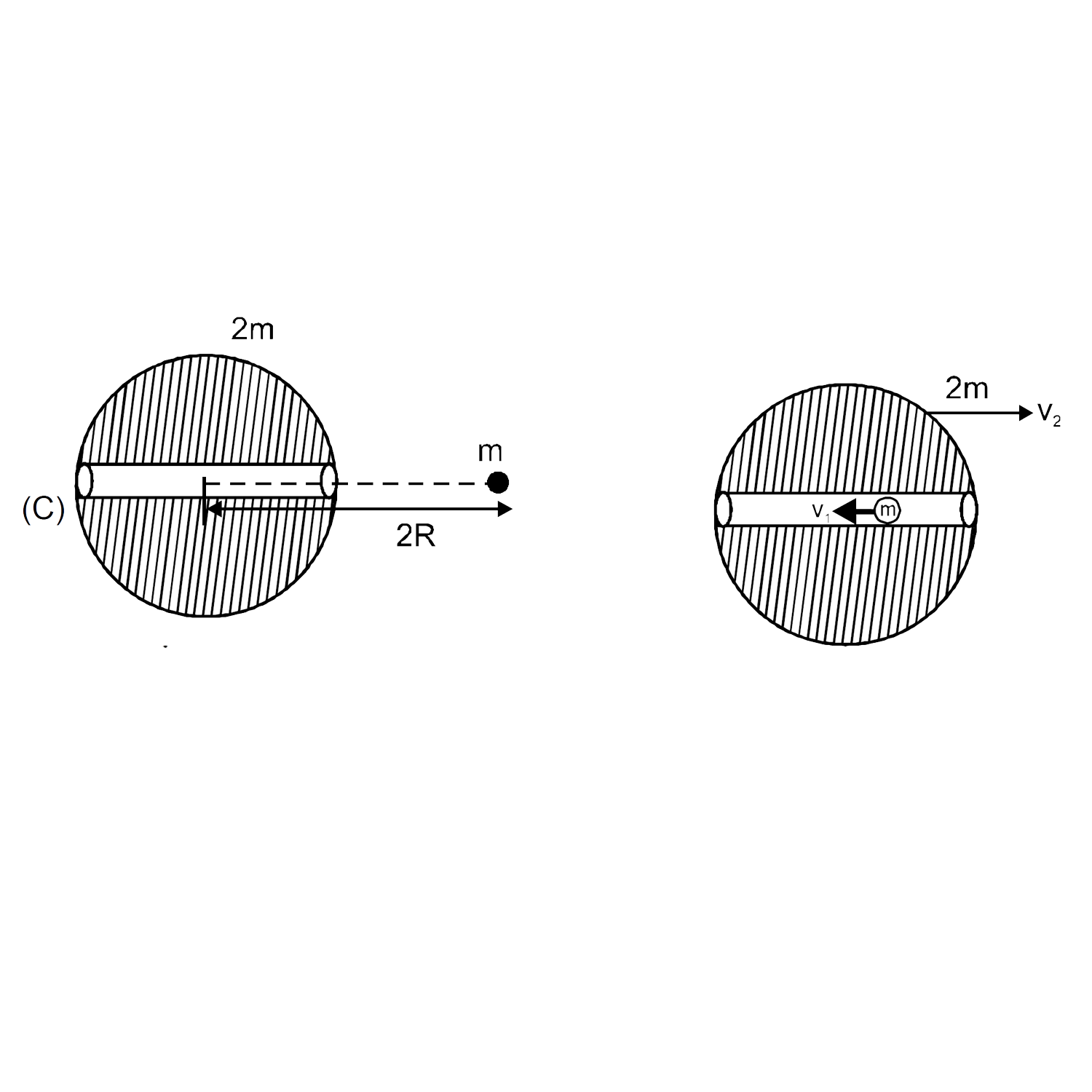
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-REVISION DPP-All Questions
- The figure shows two equal, positive charges, each of magnitude 50 muC...
Text Solution
|
- Orbital velocity of a satellite in its orbit (around earth) of radius ...
Text Solution
|
- A solid spherical planet of mass 2m and radius 'R' has a very small tu...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown A & B are two charged particles having charges q a...
Text Solution
|
- A light ray enters into a medium whose refractive index varies along t...
Text Solution
|
- A charge 'q' is placed on the diagonal AP of a cube at a distance (AP)...
Text Solution
|
- Two infinite parallel,non- conducting sheets carry equal positive char...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown there is a hollow hemisphere of radius 'R'. It has...
Text Solution
|
- A cavity of radius r is present inside a fixed solid dielectric sphere...
Text Solution
|
- A planet revolves about the sun in an elliptical orbit of semi-major a...
Text Solution
|
- A light ray parallel to the principal axis is incident (as shown in th...
Text Solution
|
- A satellite is orbiting around the earth in a circular orbit and in th...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform thin rod of mass m and length R is placed normally on surfac...
Text Solution
|
- Two persons A and B wear glasses of optical powers (in air) P1 = + 2 D...
Text Solution
|
- The final image of the object O shown in the figure is formed at poi...
Text Solution
|
- The density of the core a planet is rho(1) and that of the outer shell...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows an irregular block of material of refractive indec sqrt(2...
Text Solution
|
- The curve of angle of incidence versus angle of deviaton wshown has be...
Text Solution
|
- The curve of angle of incidence versus angle of deviaton wshown has be...
Text Solution
|
- There are two nonconducting spheres having uniform volume charge densi...
Text Solution
|