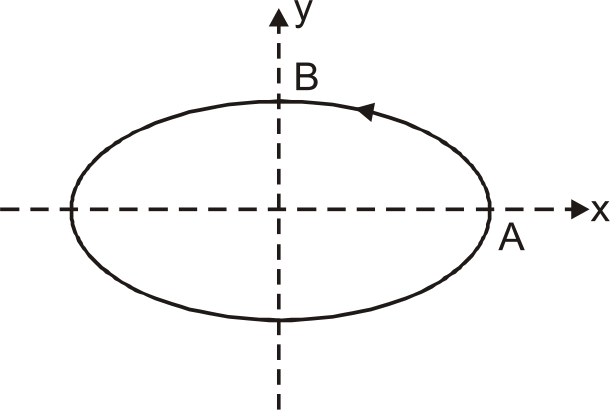
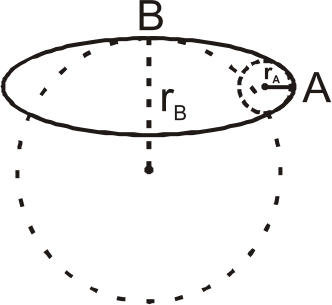
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-REVISION DPP-All Questions
- Power of the only force acting on a particle of mass m=1 kg moving in ...
Text Solution
|
- Sand is falling on a flat car being pulled with constant speed. The ra...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is moving along an elliptical path with constant speed. As ...
Text Solution
|
- A small bead of mass m = 1 kg is free to move on a circular hoop. The ...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of mass m(1) and m(2) (m(1) lt m(2)) are connected with an ...
Text Solution
|
- Three point masses are attached by light inextensible strings of vario...
Text Solution
|
- One end of a light rod of length 1m is attached with a string of lengt...
Text Solution
|
- Particle sticks to wooden loop, If particle reach at the lowest positi...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical blocks A and B of mass m each are connected to each othe...
Text Solution
|
- Three identical particles A, B and C of mass m lie on a smooth horizo...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is attached to an end of a rigid rod. The other end of the ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is moving in a uniform circular motion on a horizontal surf...
Text Solution
|
- The linear momentum of a particle is given by vec(P)=(a sin t hati- ac...
Text Solution
|
- A circular road of radius r is banked for a speed v=40 km/hr. A car of...
Text Solution
|
- A cylinder of radius R is rotating about its horizontal axis with cons...
Text Solution
|
- A gun which fires small balls of mass 20 g is firing 20 balls per seco...
Text Solution
|
- A rocket of total mass 1000kg initially is launched from ground. The g...
Text Solution
|
- AB is a long frictionless horizontal surface. One end of an ideal spri...
Text Solution
|
- In a region, potential energy varies with X as U(x)=30-(x-5)^(2) Joule...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles A and B are revolving with constant angular velocity on ...
Text Solution
|