A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-REVISION DPP-All Questions
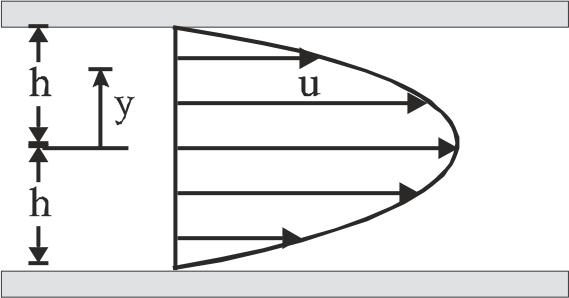
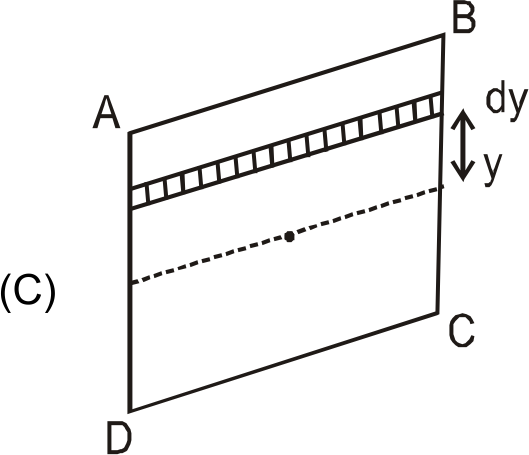
- The velocity distribution for the flow of a Newtonian fluid between tw...
Text Solution
|
- The velocity distribution for the flow of a Newtonian fluid between tw...
Text Solution
|
- The velocity distribution for the flow of a Newtonian fluid between tw...
Text Solution
|
- A rod is formed by joining two cylinders each having a length l and cr...
Text Solution
|
- A cubical block of mass m and surface area 6A is placed on a thick lay...
Text Solution
|
- A very large metal plate carries a charge of Q=-1C. The work function ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following statements: (i) Nuclear fission is normally fol...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass 'm' is projected from ground with velocity u making...
Text Solution
|
- Light of wavelength 400nm is incident continuously on a Cesium ball. (...
Text Solution
|
- In a photoelectric experiment, with light of wavelength lambda, the fa...
Text Solution
|
- The radionuclide .^(238)U decays by emitting an alpha particle. .^(238...
Text Solution
|
- The energy that should be added to an electron, to reduce its de-Brogl...
Text Solution
|
- X-rays of high penetrating power are called hard X-ray. Hard X-rays ha...
Text Solution
|
- The voltage applied to an X-ray tube is 18 kV. The maximum mass of pht...
Text Solution
|
- In a photoelectric experiment, the frequency and intensity of a light ...
Text Solution
|
- n a sample of radioactive nuclide
Text Solution
|
- In a radioactive reactor, radionuclide X are being injected at a rate ...
Text Solution
|
- Radius of a nucleus is given by the relation R = R(0)A^(1//3) where R...
Text Solution
|
- Three samples of a radioactive substance have activity in a ratio 2 : ...
Text Solution
|
- The only source of energy in a particular star is the fusion reaction ...
Text Solution
|