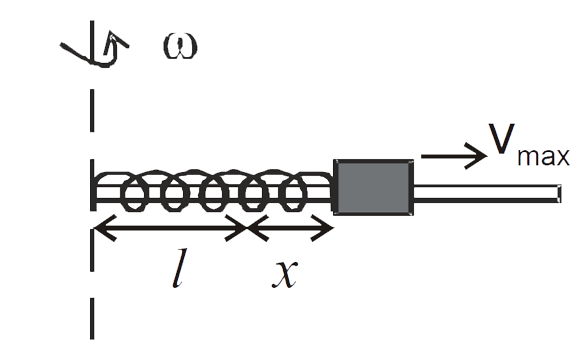
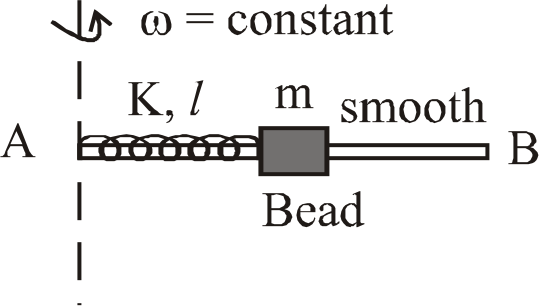A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-REVISION DPP-All Questions
- Suppose the earth was covered by an oceam of uniform depth h,(hltltR) ...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of an ideal monatomic gas has initial temperature T(0), is ma...
Text Solution
|
- AB is a light rigid rod. Which is rotating about a vertical axis passi...
Text Solution
|
- Three projecties are thrown all with same speed u but at different ang...
Text Solution
|
- The figure shown the velocity as a function of the time for an object ...
Text Solution
|
- In an isobaric process (lambda is adiabatic exponent of the gas)
Text Solution
|
- Ina moving coil galvanometer, a coil of area pi cm^(2) and 10 windings...
Text Solution
|
- A gas consisting of rigid diatomic molecules (degrees of freedom r = 5...
Text Solution
|
- The degree of freedom per molecule for a gas is 6. At constant pressur...
Text Solution
|
- 5 moles of nitrogen gas are enclosed in an adiabatic cylindrical vesse...
Text Solution
|
- At the middle of the mercury barometer tube there is a little column o...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of an ideal gas (y=1.4) at 500K, is filled in an adiabatic cy...
Text Solution
|
- The current density bar(J) inside a long, solid cylindrical wire of ra...
Text Solution
|
- The basic idea of Quantum Mechanics is that motion in any system is qu...
Text Solution
|
- The basic idea of Quantum Mechanics is that motion in any system is qu...
Text Solution
|
- The basic idea of Quantum Mechanics is that motion in any system is qu...
Text Solution
|
- The fixed non-conducting cylinder shown in figure has a noconducting h...
Text Solution
|
- The fixed non-conducting cylinder shown in figure has a noconducting h...
Text Solution
|
- The fixed non-conducting cylinder shown in figure has a noconducting h...
Text Solution
|
- Sand is droped vetically downward at the constant rate mu kg//s on a c...
Text Solution
|