Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ALKENES AND ALKADIENES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise EXERCISES|29 VideosALKENES AND ALKADIENES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise linked Comprehension Type|38 VideosALKENES AND ALKADIENES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Single correct Answer|14 VideosALKANES AND CYCLOALKANES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Archives|13 VideosALKYNES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Exercises (Archives - Analytical and Desriptive Type)|4 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY-ALKENES AND ALKADIENES-SOLVED Example
- Write the monomer of the following polymer : a. P.M.M.A. ,b. H.D.P....
Text Solution
|
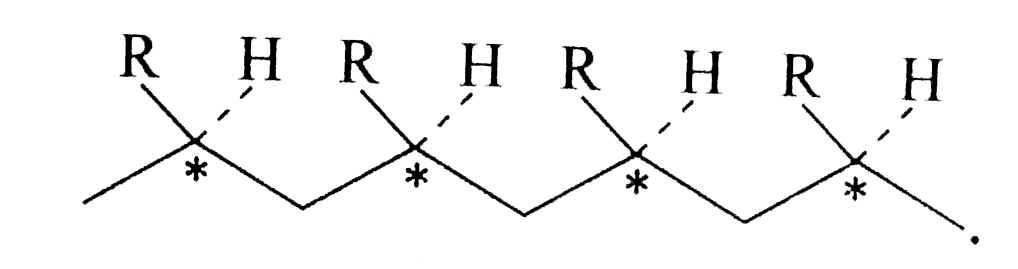
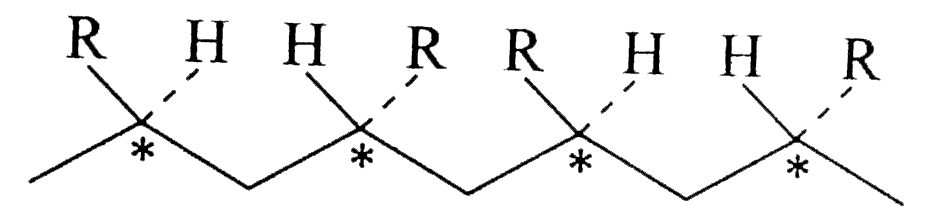
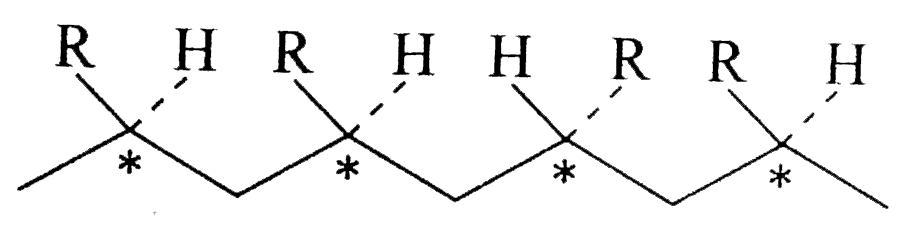
- Which of the polymer (s) in Example is // are optically active or chir...
Text Solution
|
- Based on the arrangement of branching of [(R)-(Ph), in case of styron ...
Text Solution
|
- Convert the following :
Text Solution
|
- Identify compound (A).
Text Solution
|
- Identify compound (A) and (B).
Text Solution
|
- Identify compounds (A) and (B) Acetic acid + Propanoic acid + ...
Text Solution
|
- a. Write the products of the reductive and oxidative ozonolyses of mes...
Text Solution
|
- a. Identify compound (A) in the following reactions. Compound (A)ove...
Text Solution
|
- Give the product of the following with : a. O(3)//Zn-CH(3)COOH ,b. ...
Text Solution
|
- Write the structural lformulae for the compounds that yields the follo...
Text Solution
|
- Give the product obtained from the oxidation of the following compound...
Text Solution
|
- Complete the following reaction
Text Solution
|
- Comlete the following reaction : Also write the mechanism of th...
Text Solution
|
- Give all the structural isomers ( excloding stereoisomers and allenes ...
Text Solution
|
- Complete the following reaction : Also write the mechanism of the...
Text Solution
|
- Write all the resonating structures of : Which of these carbons ...
Text Solution
|
- Conver : Which product is kinetically favoured and which product...
Text Solution
|
- Give the name and structure of the lowest molecular mass cumulative po...
Text Solution
|
- Complete the following reaction
Text Solution
|