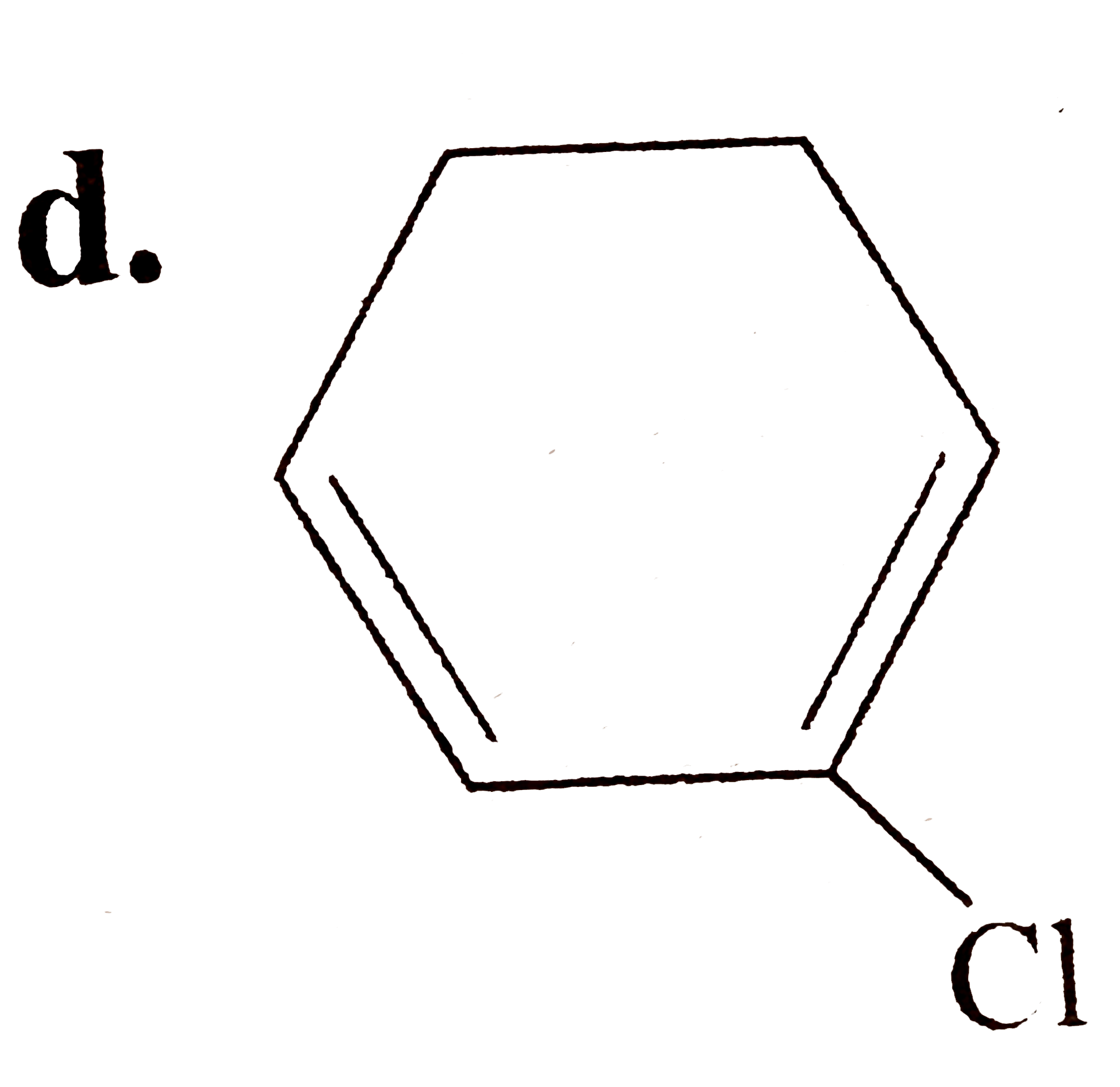
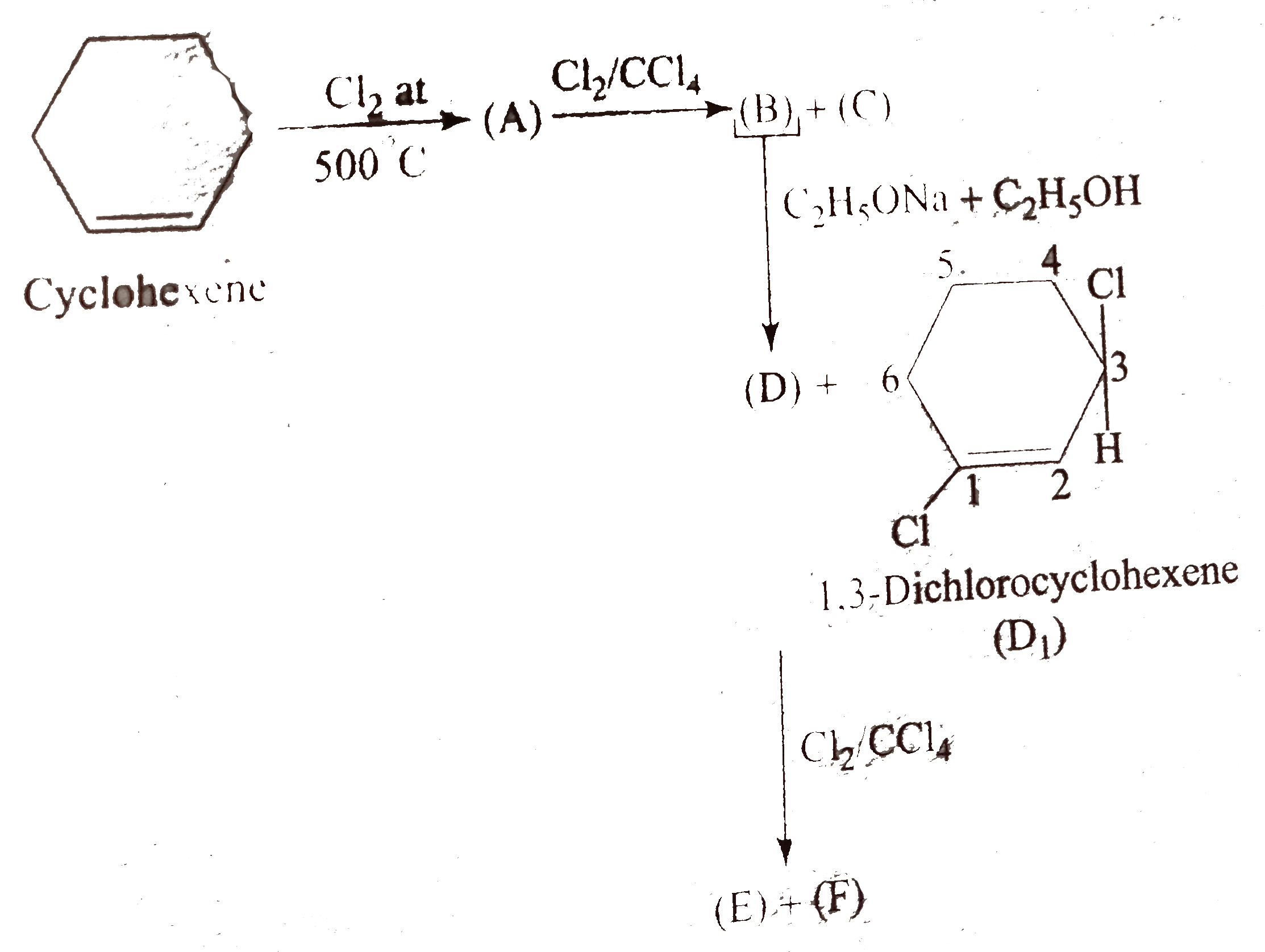A
B
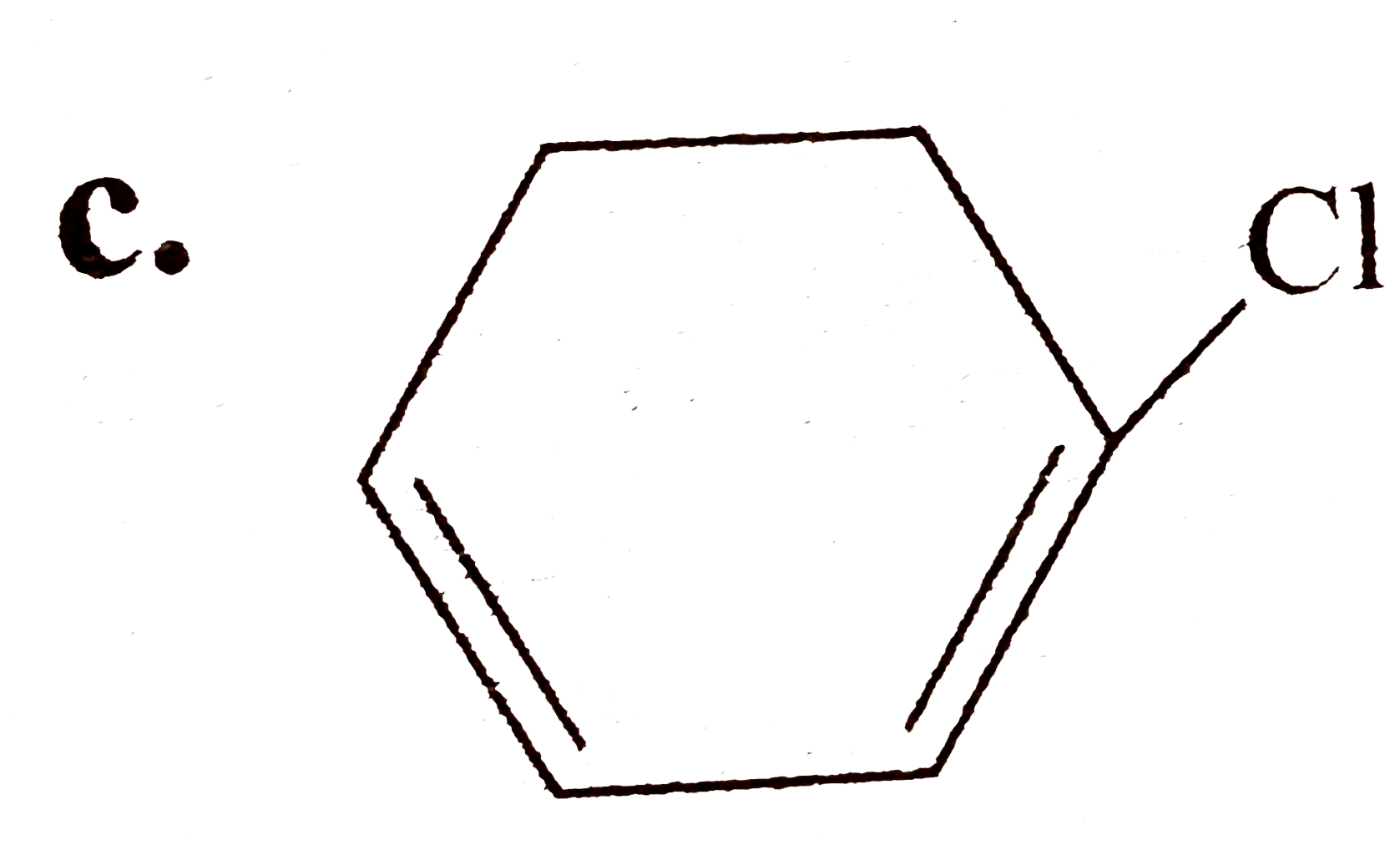
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ALKENES AND ALKADIENES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Multiple Correct Answer Type|41 VideosALKENES AND ALKADIENES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Single Correct Answer Type|62 VideosALKENES AND ALKADIENES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise EXERCISES|29 VideosALKANES AND CYCLOALKANES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Archives|13 VideosALKYNES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Exercises (Archives - Analytical and Desriptive Type)|4 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY-ALKENES AND ALKADIENES-linked Comprehension Type
- (A) is :
Text Solution
|
- (B) and (C) , respectively, are :
Text Solution
|
- (D) is :
Text Solution
|
- (E) and (F), respectively, are :
Text Solution
|
- Why does not (C) gives (D) or (D(1)) on treatment with alcoholic KOH ...
Text Solution
|
- Compound (B) is :
Text Solution
|
- Compound (C) is :
Text Solution
|
- Compound (D) is :
Text Solution
|
- Compound (E) is :
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is true regarding the hydroboration oxidation o...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following are true regarding hydroboration of alkene ?( M...
Text Solution
|
- Which is the wrong statement about oxymercuration - demercuration ?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the wrong statement in the Diels - Alder reaction (A) with (B...
Text Solution
|
- In the reaction of (A) to form (E) and (F), which statement is wrong ?
Text Solution
|
- Which statement is wrong ?
Text Solution
|
- Stabilities of alkanes can be compared by converting these compounds t...
Text Solution
|
- Stabilities of alkanes can be compared by converting these compounds t...
Text Solution
|
- Stabilities of alkanes can be compared by converting these compounds t...
Text Solution
|
- Stabilities of alkanes can be compared by converting these compounds t...
Text Solution
|
- Stabilities of alkanes can be compared by converting these compounds t...
Text Solution
|