A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
DIFFERENTIATION
ARIHANT MATHS|Exercise Exercise (Statement I And Ii Type Questions)|10 VideosDIFFERENTIATION
ARIHANT MATHS|Exercise Exercise (Passage Based Questions)|16 VideosDIFFERENTIATION
ARIHANT MATHS|Exercise Exercise For Session 10|4 VideosDIFFERENTIAL EQUATION
ARIHANT MATHS|Exercise Exercise (Questions Asked In Previous 13 Years Exam)|26 VideosDY / DX AS A RATE MEASURER AND TANGENTS, NORMALS
ARIHANT MATHS|Exercise Exercise (Questions Asked In Previous 13 Years Exam)|7 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ARIHANT MATHS-DIFFERENTIATION -Exercise (More Than One Correct Option Type Questions)
- If x=e^(y+e^(y^(+..."to"00))),xgt0,"then"(dy)/(dx)
Text Solution
|
- Let g be the inverse function of f and f'(x)=(x^(10))/(1+x^(2)). If g(...
Text Solution
|
- If f and g are the function whose graphs are as shown, let u(x)=f(g(x)...
Text Solution
|
- f'(x) = g(x) and g'(x) =-f(x) for all real x and f(5)=2=f'(5) then f^2...
Text Solution
|
- if f(x) = x +x^2/1! + x^3/3! +---+ x^n/n! then f(0) + f'(0) + f''(0) ...
Text Solution
|
- If y=(f(0)f(0)f)(x)andf(0)=0,f'(0)=2 then y'(0) is equal to
Text Solution
|
- If y^2=P(x) is a polynomial of degree 3, then 2(d/(dx))(y^2dot(d^2y)/(...
Text Solution
|
- If y=f(x)andx=g(y) are inverse functions of each other, then
Text Solution
|
- If y is a function of x then (d^2y)/(dx^2)+y \ dy/dx=0. If x is a func...
Text Solution
|
- Leg g(x)=ln(f(x)), whre f(x) is a twice differentiable positive functi...
Text Solution
|
- If the function f(x)=x^(3)+e^(x//2)andg(x)=f^(-1)(x), then the value ...
Text Solution
|
- If f(theta) = sin(tan^(-1)(sintheta/sqrt(cos2theta))), where -pi/4 lt ...
Text Solution
|
- If y=log(sinx)(tanx), then (dy)/ (dx) at x=(1)/(4) is equal to
Text Solution
|
- If y=sum(r=1)^(x) tan^(-1)((1)/(1+r+r^(2))), then (dy)/(dx) is equal t...
Text Solution
|
- If y=(sin^(-1)(sinalphasinx)/(1-cosalphasinx)), then y'(0) is equal to
Text Solution
|
- If f(x)=cot^(-1)((x^(x)-x^(-x))/(2)) then f'(1) equals
Text Solution
|
- The function f(x)=e^x+x , being differentiable and one-to-one, has a d...
Text Solution
|
- If f^(x)=-f(x) and g(x)=f^(prime)(x) and F(x)=(f(x/2))^2+(g(x/2))^2 an...
Text Solution
|
- If x=sectheta-costhetaandy=sec^(n)theta-cos^(n)theta, then (x^(2)+4 )(...
Text Solution
|
- If x=f(t)cost-f^(prime)(t)sint and y=f(t)sint+f^(prime)(t)cost , then ...
Text Solution
|
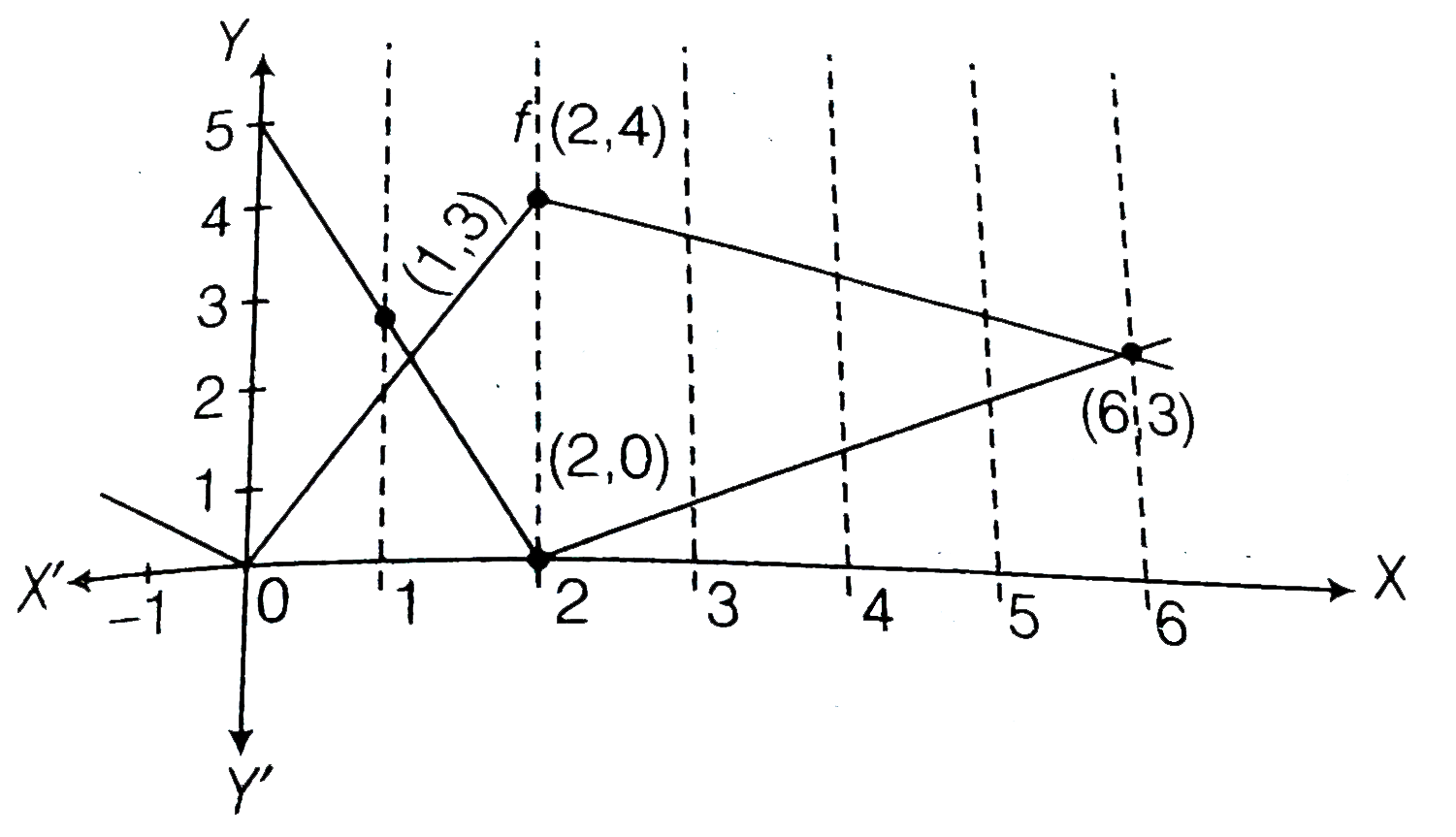 Then the value of `u'(1)+w'(1)` is
Then the value of `u'(1)+w'(1)` is