A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
DY / DX AS A RATE MEASURER AND TANGENTS, NORMALS
ARIHANT MATHS|Exercise Exercise (More Than One Correct Option Type Questions)|15 VideosDY / DX AS A RATE MEASURER AND TANGENTS, NORMALS
ARIHANT MATHS|Exercise Exercise (Statement I And Ii Type Questions)|7 VideosDY / DX AS A RATE MEASURER AND TANGENTS, NORMALS
ARIHANT MATHS|Exercise Exercise For Session 6|4 VideosDIFFERENTIATION
ARIHANT MATHS|Exercise Exercise For Session 10|4 VideosELLIPSE
ARIHANT MATHS|Exercise Exercise (Questions Asked In Previous 13 Years Exam)|27 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ARIHANT MATHS-DY / DX AS A RATE MEASURER AND TANGENTS, NORMALS -Exercise (Single Option Correct Type Questions)
- The graphs y=2x^(3)-4x+2 and y=x^(3)+2x-1 intersect at exacty 3 distin...
Text Solution
|
- In which of the following function Rolle's theorem is applicable ?
Text Solution
|
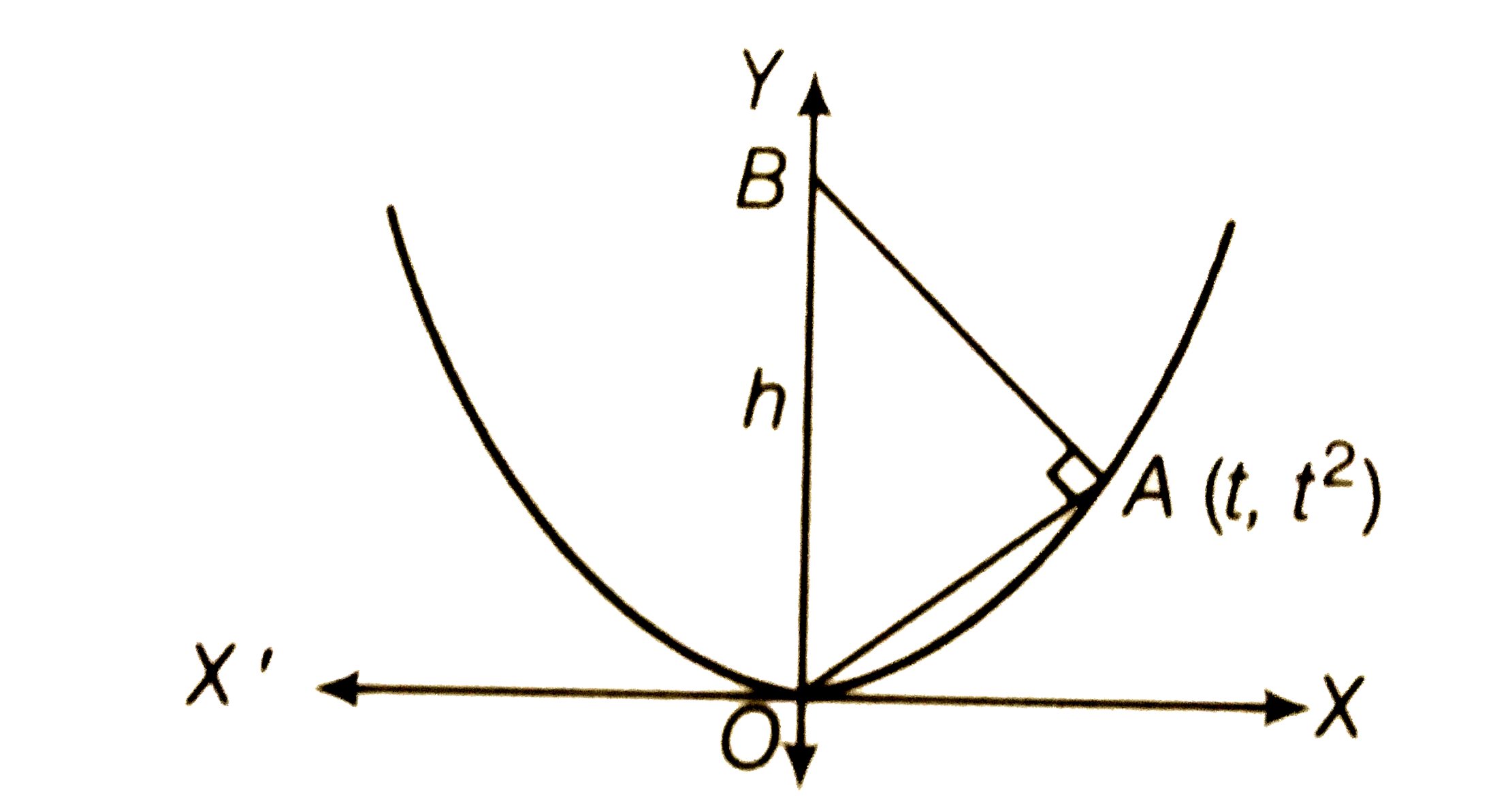
- The figure shows a right triangle with its hypotenuse OB along the Y-a...
Text Solution
|
- Number of positive integral value(s) of 'a' for which the curve y=a^(x...
Text Solution
|
- Given f(x)=4-(1/2-x)^(2/3),g(x)={("tan"[x])/x ,x!=0 1,x=0 h(x)={x},k(...
Text Solution
|
- If the function f(x)=x^(4)+bx^(2)+8x+1 has a horizontal tangent and a...
Text Solution
|
- Coffee is coming out from a conical filter, with height and diameter b...
Text Solution
|
- A horse runs along a circle with a speed of 20k m//h . A lantern is at...
Text Solution
|
- Water runs into an inverted conical tent at the height of the water is...
Text Solution
|
- Let f(x)=x^3-3x^2+2x . If the equation f(x)=k has exactly one posit...
Text Solution
|
- The x-intercept of the tangent at any arbitarary point of the curve (a...
Text Solution
|
- If f(x) is continuous and differentible over [-2, 5] and -4lef'(x)le3 ...
Text Solution
|
- A curve is represented parametrically by the equations x=t+e^(at) and ...
Text Solution
|
- At any two points of the curve represented parametrically by x=a (2 co...
Text Solution
|
- Let F(x)=int(sinx)^(cosx)e^((1+sin^(-1)(t))dt on [0,(pi)/(2)], then
Text Solution
|
- Given f' (1) = 1 and d/(dx) f(2x))=f'(x) AA x > 0. If f' (x) is diff...
Text Solution
|
- Let f(x)a n dg(x) be two functions which are defined and differentiabl...
Text Solution
|
- The range of values of m for which the line y = mx and the curve y=(x)...
Text Solution
|
- Let S be a square with sides of length x. If we approximate the change...
Text Solution
|
- Consider f(x)=int1^x(t+1/t)dt and g(x)=f'(x) If P is a point on the cu...
Text Solution
|