Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
GRAVITATION
NAVNEET PUBLICATION - MAHARASHTRA BOARD|Exercise Give scientific reasons :|3 VideosGRAVITATION
NAVNEET PUBLICATION - MAHARASHTRA BOARD|Exercise Distinguish between :|2 VideosGRAVITATION
NAVNEET PUBLICATION - MAHARASHTRA BOARD|Exercise QUESTIONS & ANSWERS|45 VideosGIVE SCIENTIFIC REASONS
NAVNEET PUBLICATION - MAHARASHTRA BOARD|Exercise CHAPTER 10 : DISASTER MANAGEMENT|2 VideosHEAT
NAVNEET PUBLICATION - MAHARASHTRA BOARD|Exercise NUMERICAL PROBLEMS FOR PRACTICE|12 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NAVNEET PUBLICATION - MAHARASHTRA BOARD-GRAVITATION -Answer the following questions :
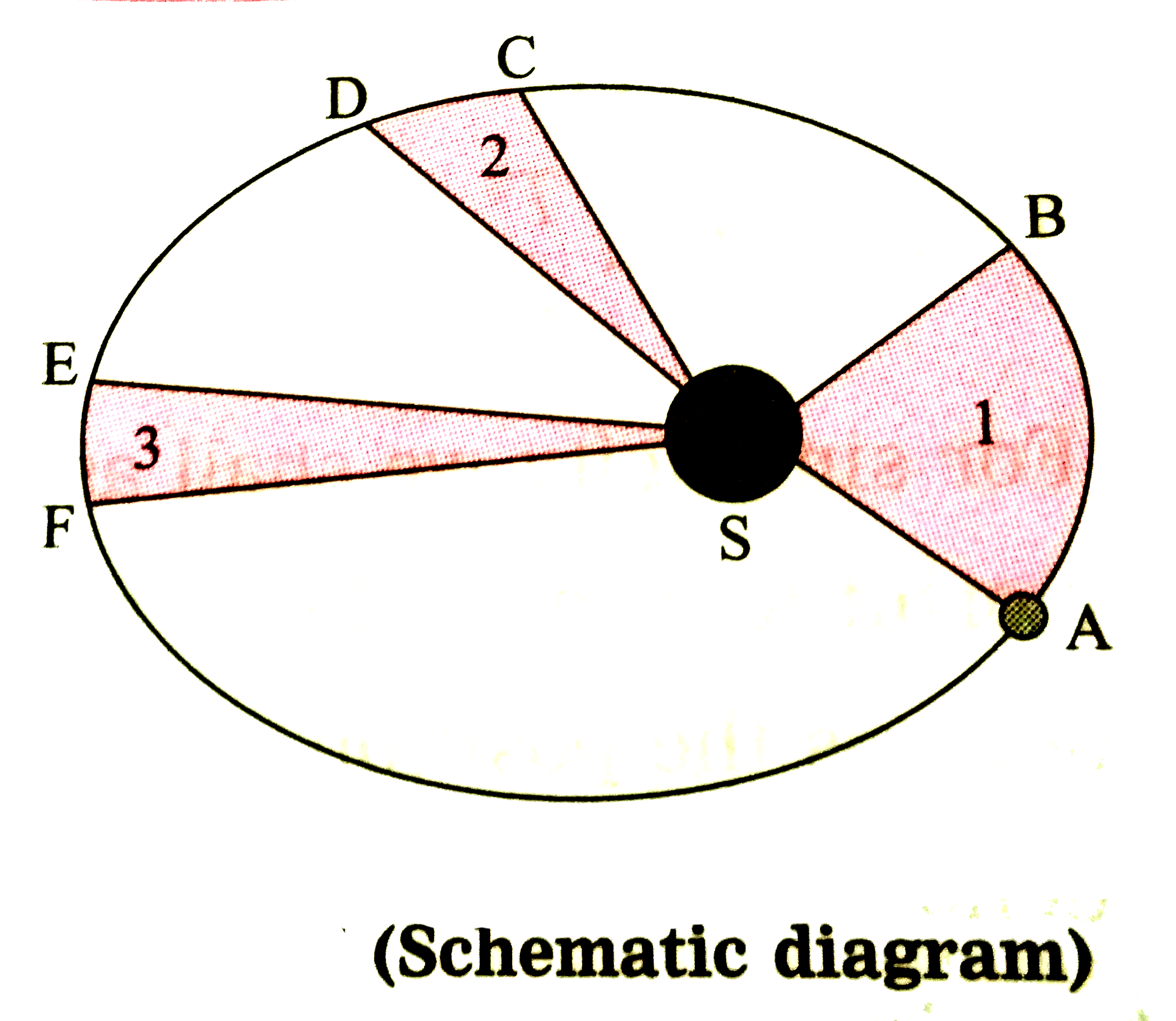
- In the following figure, an orbit of a planet around the Sun (S) has b...
Text Solution
|
- In the following figure, an orbit of a planet around the Sun (S) has b...
Text Solution
|
- In the following figure, an orbit of a planet around the Sun (S) has b...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the term gravitational force. What is gravitation?
Text Solution
|
- Let the period of revolution of a planet at a distance R from a star b...
Text Solution
|
- State Newton's universal law of gravitation. Express it in mathematic...
Text Solution
|
- Why is the constant of gravitation called a universal constant ?
Text Solution
|
- Newton's law of gravitation is called the universal for of gravitation...
Text Solution
|
- If the distance between two bodies is increased by a factor of 5, (i) ...
Text Solution
|
- Determine the SI unit of the universal constant of gravitation from th...
Text Solution
|
- Define G (universal gravitational constant).
Text Solution
|
- State the importance of Newton's universal law of gravitation .
Text Solution
|
- Compare the gravitational force on a body of mass 1 kg due to the eart...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the term the earth's gravitational force. What is the value of...
Text Solution
|
- Write a short note on the earth's gravitational force.
Text Solution
|
- Take two balls of different masses, go to the top of a building, drop ...
Text Solution
|
- Take two similar pages from your notebook. Crumple one paper and allow...
Text Solution
|
- Take a feather and a paper. Allow them to fall to the ground simultane...
Text Solution
|
- What is the acceleration Due to Gravity?
Text Solution
|
- What is meant by 'free fall' hence define acceleration due to gravity.
Text Solution
|