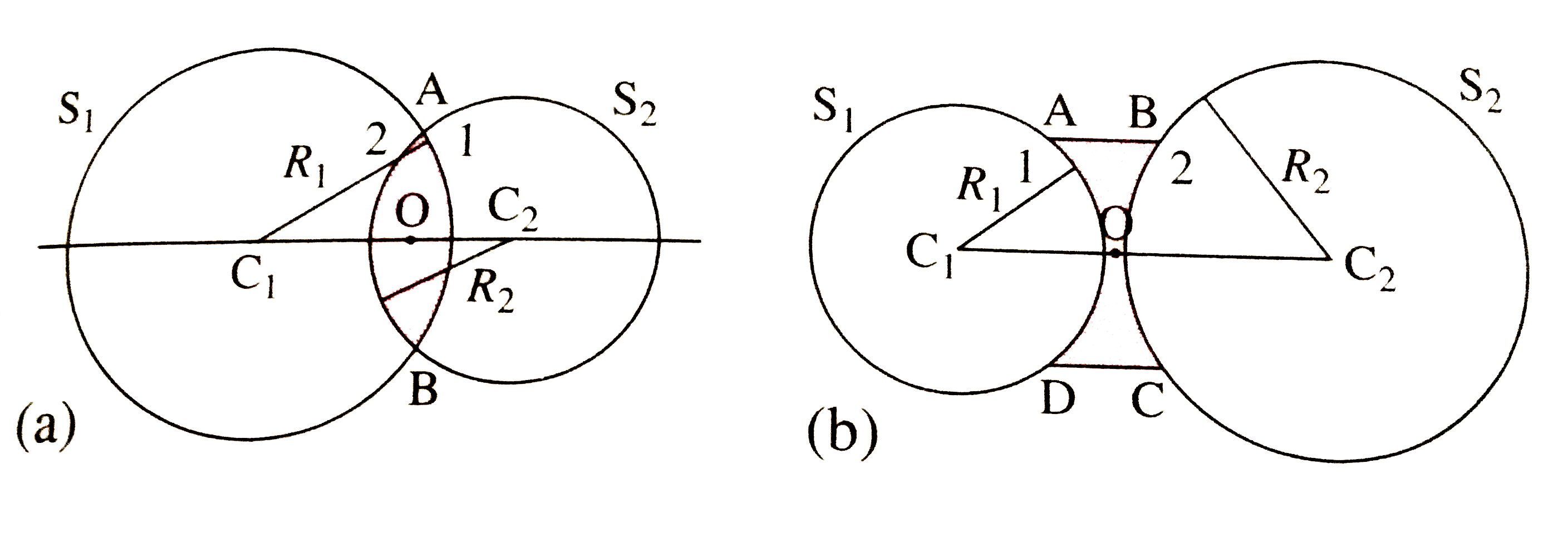Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
LENSES
NAVNEET PUBLICATION - MAHARASHTRA BOARD|Exercise Give scientific reasons|16 VideosLENSES
NAVNEET PUBLICATION - MAHARASHTRA BOARD|Exercise Distinguish between|6 VideosLENSES
NAVNEET PUBLICATION - MAHARASHTRA BOARD|Exercise Answer the following questions in one sentence each :|10 VideosLAWS, RULES, UNITS AND DEFINITIONS
NAVNEET PUBLICATION - MAHARASHTRA BOARD|Exercise Carbon Compounds|18 VideosMAKING CONCEPT DIAGRAMS
NAVNEET PUBLICATION - MAHARASHTRA BOARD|Exercise Cell Biology and Biotechnology|2 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NAVNEET PUBLICATION - MAHARASHTRA BOARD-LENSES-Answer the following questions :
- Draw neat labelled diagrams : Type of lenses.
Text Solution
|
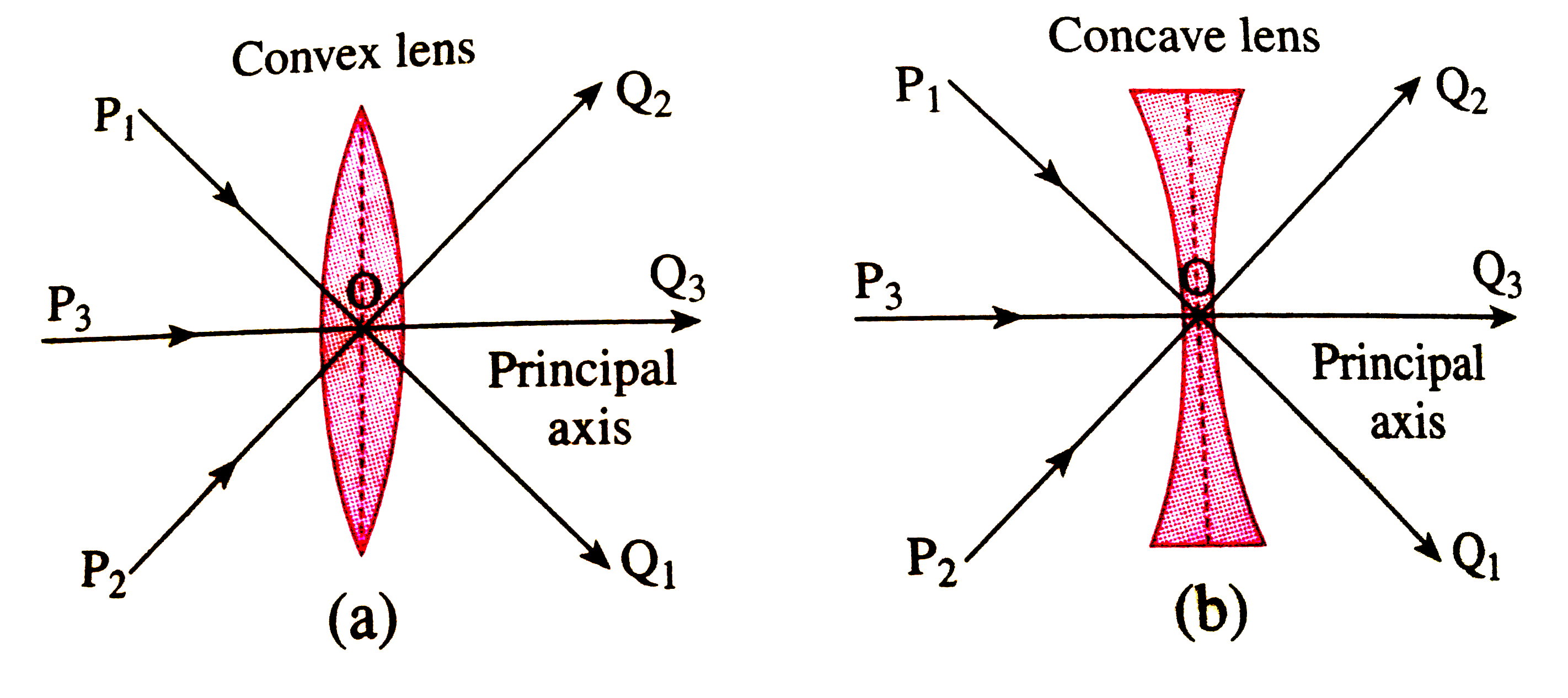
- In general, when a ray of light pasess through a lens, there occurs a ...
Text Solution
|
- With reference to spherical lenses, state the meaning of the following...
Text Solution
|
- State the rules used for drawing ray diagrams for the fomation of an i...
Text Solution
|
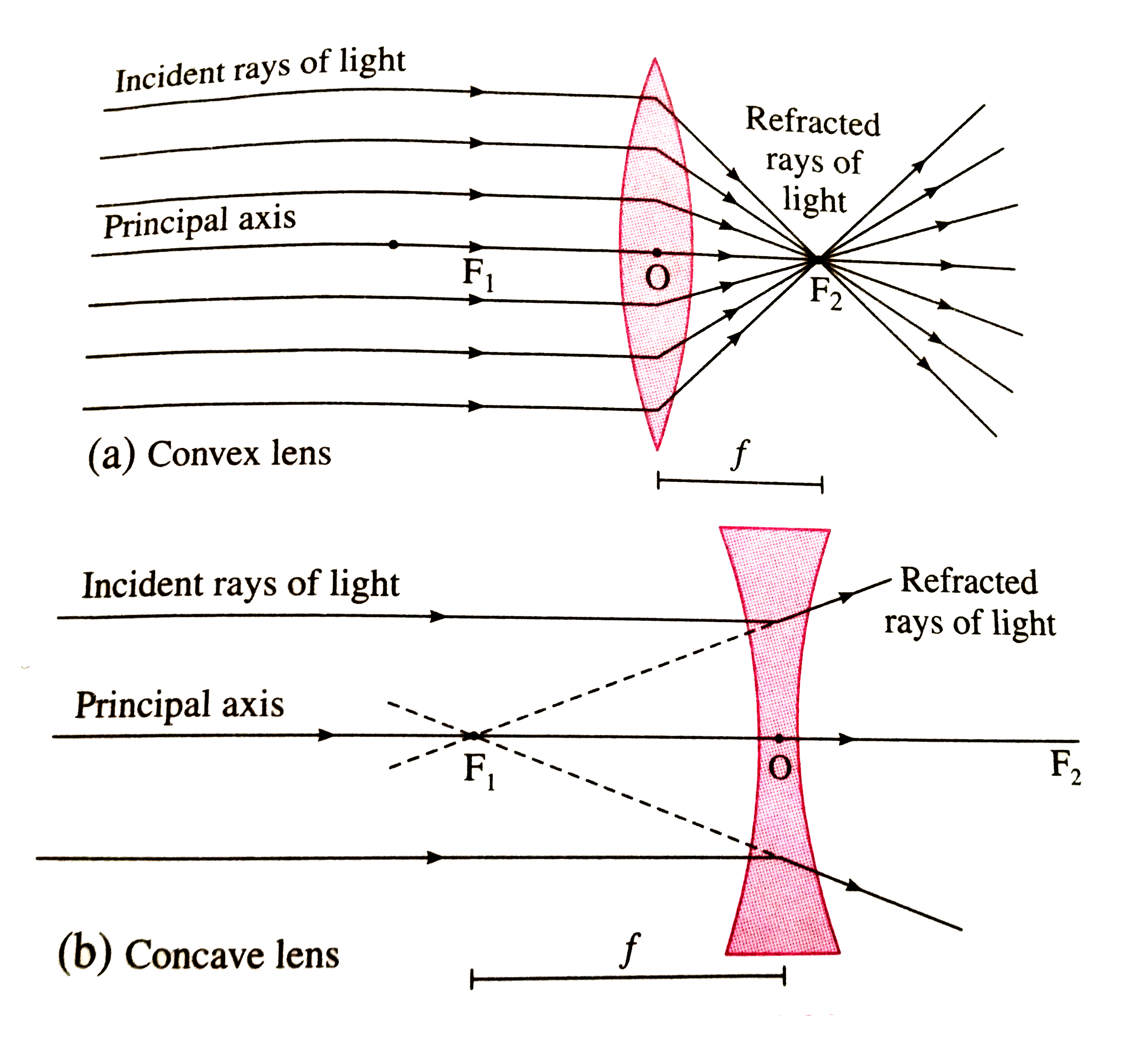
- In the case of a convex lens, show the path of the refraction ray when...
Text Solution
|
- Draw neat and well labelled ray diagrams for image formation by a conv...
Text Solution
|
- Draw neat and well labelled ray diagrams for image formation by a conv...
Text Solution
|
- Draw neat and well labelled ray diagrams for image formation by a conv...
Text Solution
|
- Draw neat and well labelled ray diagrams for image formation by a conv...
Text Solution
|
- Draw neat and well labelled ray diagrams for image formation by a conv...
Text Solution
|
- Draw neat and well labelled ray diagrams for image formation by a conv...
Text Solution
|
- Observe the following figure and complete the table :
Text Solution
|
- At which position will you keep an object in front of a convex lens to...
Text Solution
|
- At which position will you keep an object in front of a convex lens to...
Text Solution
|
- State the rules used fro drawing ray diagrams for the formation of an ...
Text Solution
|
- State the characteristics of an image formed by a concave lens.
Text Solution
|
- In the case of image formation by a concave lens , what can you say a...
Text Solution
|
- Draw a ray diagram to show image formation by a concave lens.
Text Solution
|
- State the Cartesian sign convention for refraction of light (image for...
Text Solution
|
- What is a lens formula ? State it.
Text Solution
|