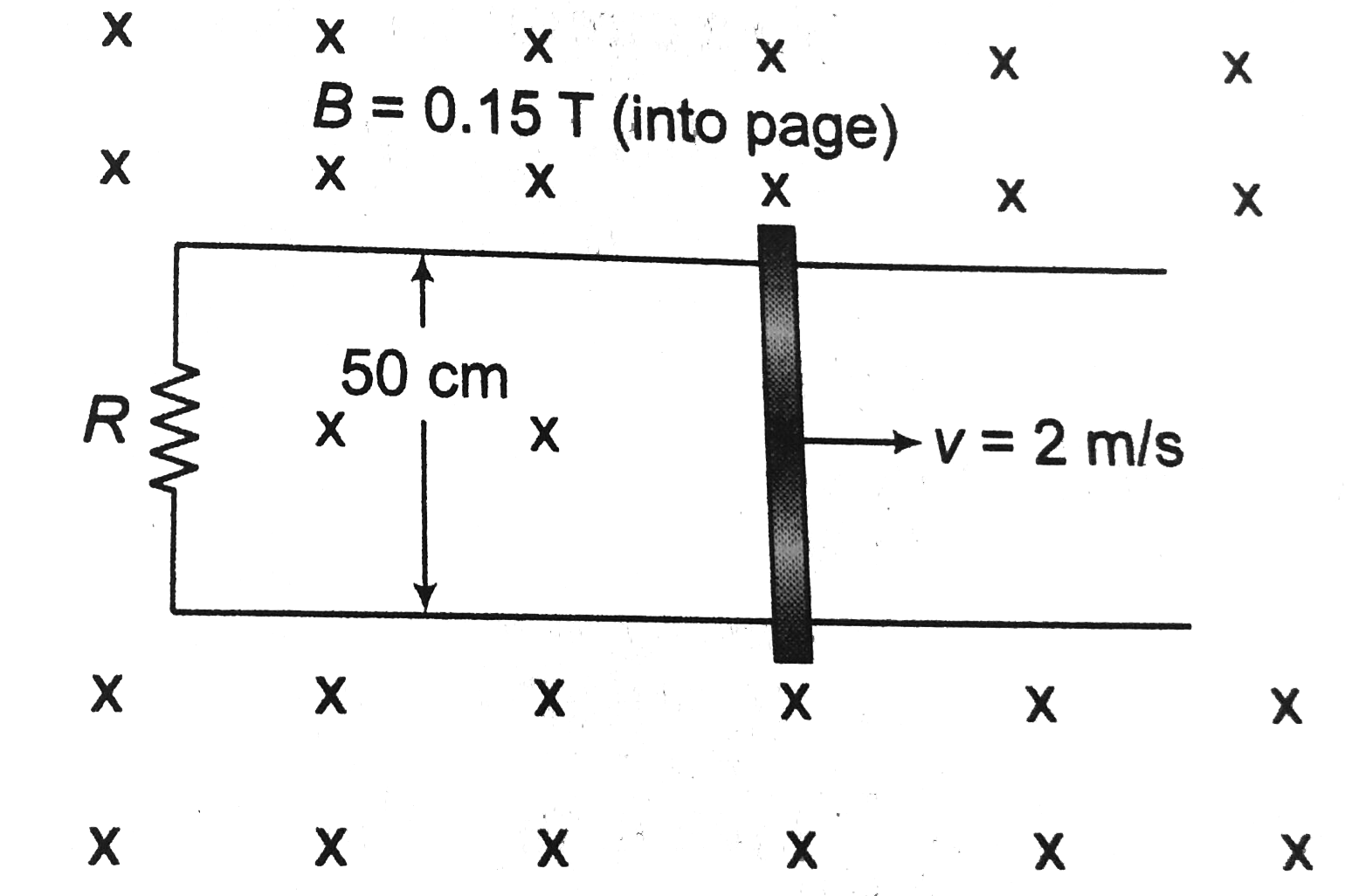A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
A2Z|Exercise Inductor Circuits|31 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
A2Z|Exercise Applications Of Emi|58 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
A2Z|Exercise Section D - Chapter End Test|30 VideosELECTRIC POTENTIAL & CAPACITANCE
A2Z|Exercise Section D - Chapter End Test|29 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES AND COMMUNICATION SYSTEM
A2Z|Exercise Section D - Chapter End Test|30 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
A2Z-ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION-Motional And Rotational Emf
- A conducting rod of length 2l is rotating with constant angular speed ...
Text Solution
|
- A wire cd of length l and mass m is sliding without friction on conduc...
Text Solution
|
- As shown in figure, a metal rod completes the circuit. The circuit are...
Text Solution
|
- A thin semicircular conducting ring of radius R is falling with its pl...
Text Solution
|
- At a plane the value of horizontal component of the eart's magnetic fi...
Text Solution
|
- One conducting U tube can slide inside another as shown in figure, mai...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the situation shown in the figure. The wire Ab is sliding on ...
Text Solution
|
- A square metallic wire loop of side 0.1 m and resistance of 1W is move...
Text Solution
|
- A conductor ABOCD moves along its bisector with a velocity of 1 m//s t...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting rod of length L=0.1 m is moving with a uniform sped v=0.2...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting rod AC of length 4l is rotated about point O in a uniform...
Text Solution
|
- A rectangular loop is being pulled at a constant speed v, through a re...
Text Solution
|
- The figure shows four wire loops, with edge length of either L or 2L. ...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of length l rotates with a small but uniform angular velocity om...
Text Solution
|
- Two circular coils can be arranged in any of the three situation shown...
Text Solution
|
- The back e.m.f. induced in a coil, when current change from 1 ampere t...
Text Solution
|
- An e.m.f. of 5 "volt" is produced by a self-inductance, when the curre...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the energy stored in an inductor of inductance 50 mH when a ...
Text Solution
|
- The current passing through a choke coil of 5 henry is decreasing at t...
Text Solution
|
- Average energy stored in a pure inductance L when current i flows thro...
Text Solution
|