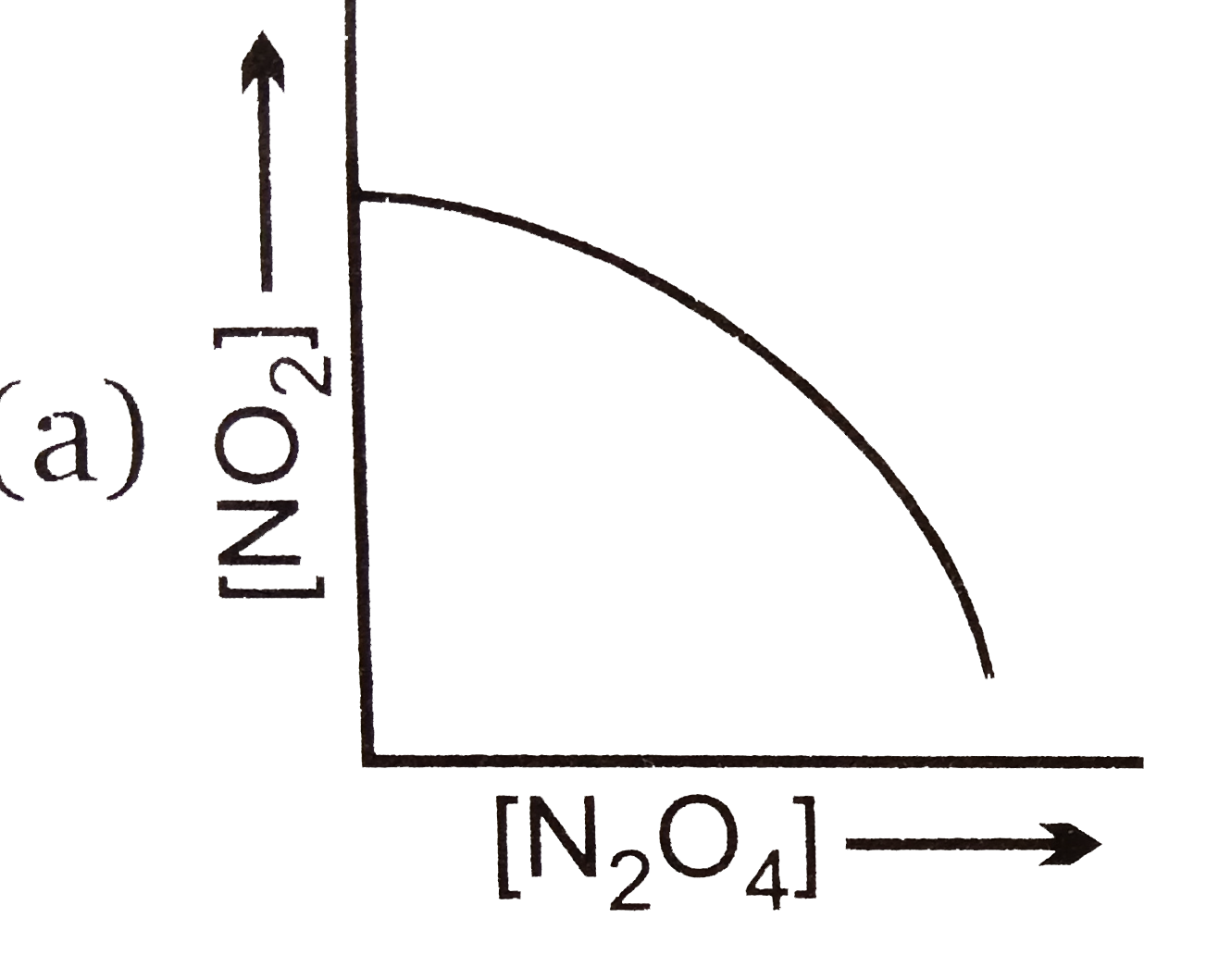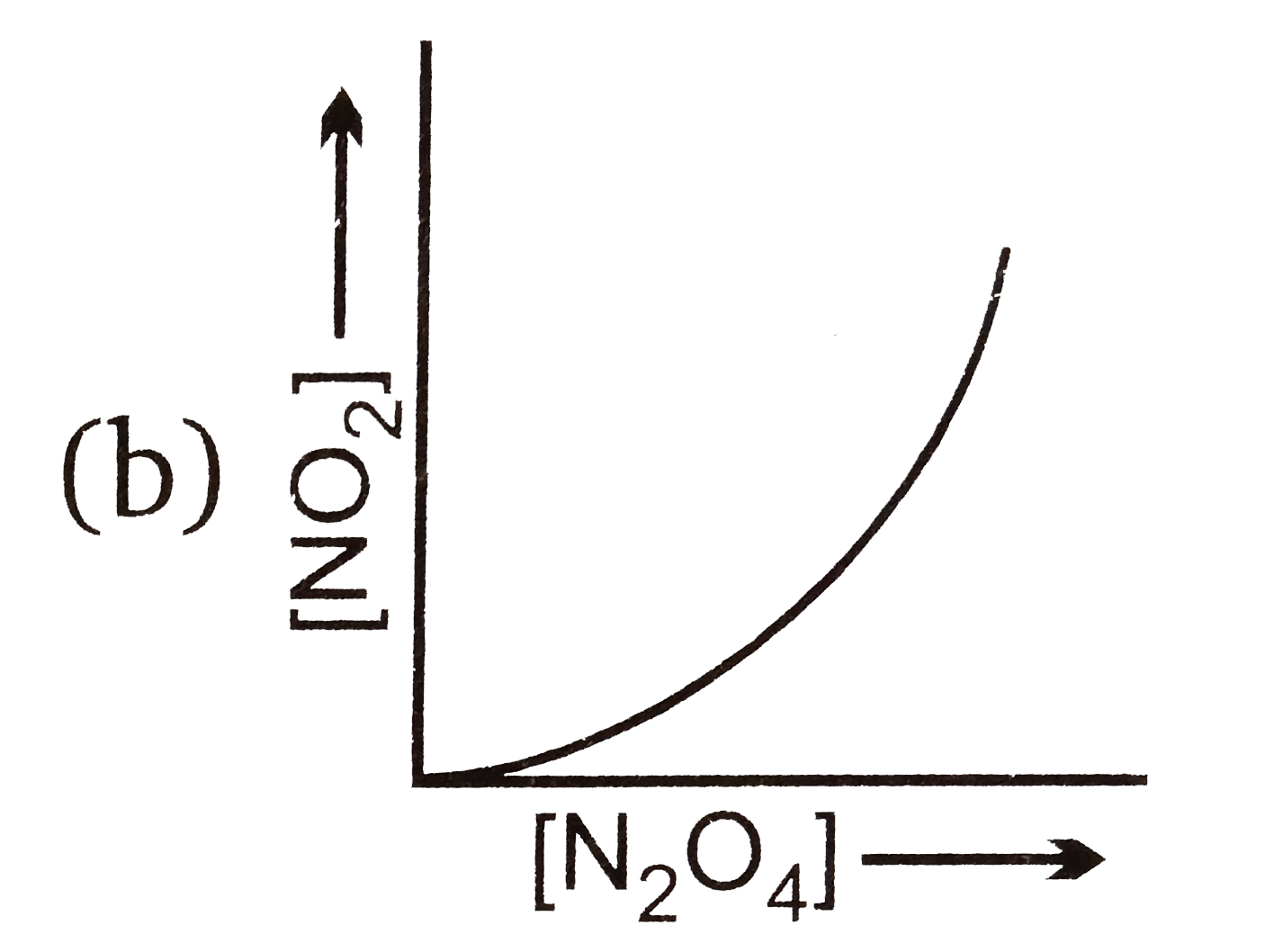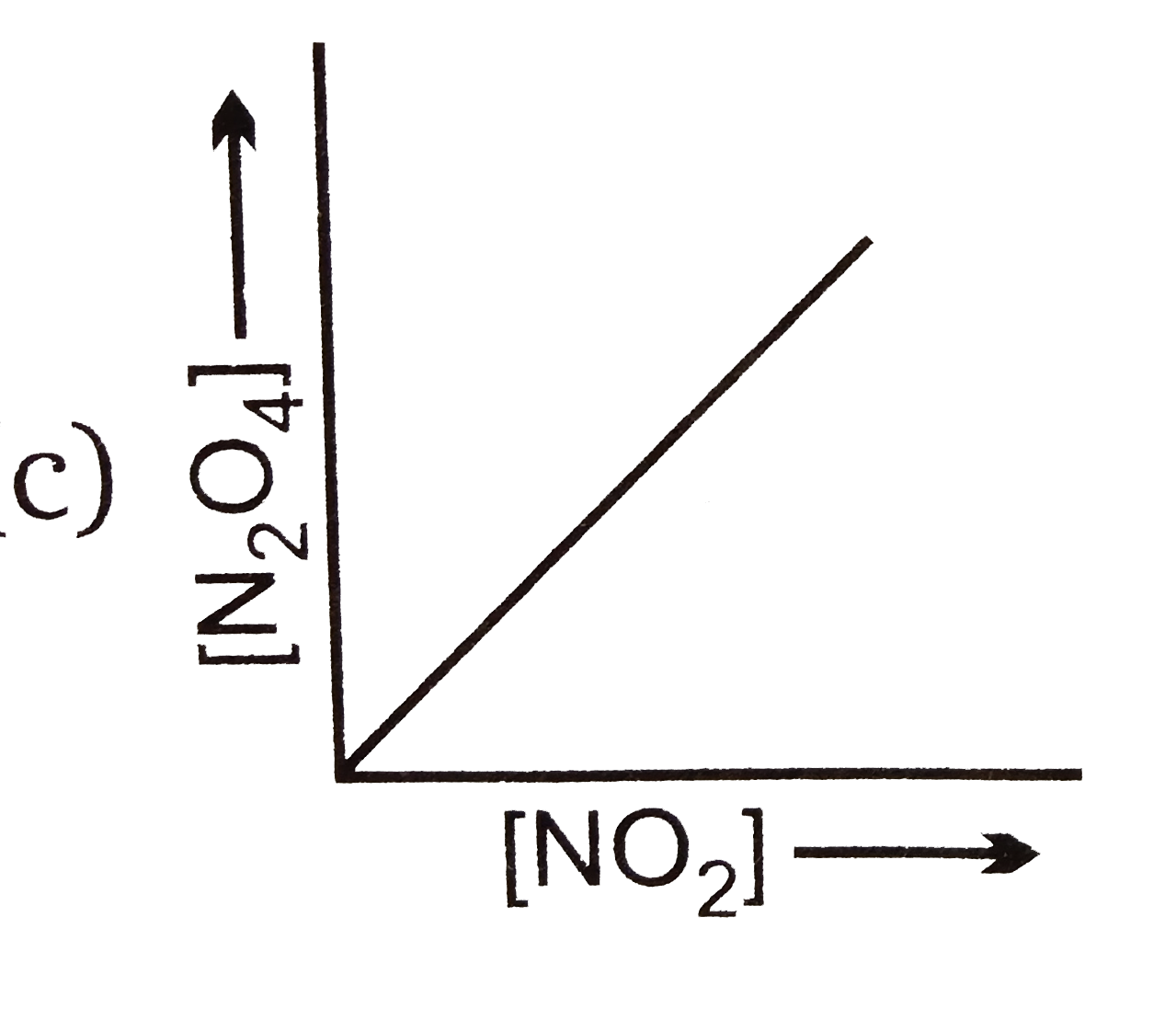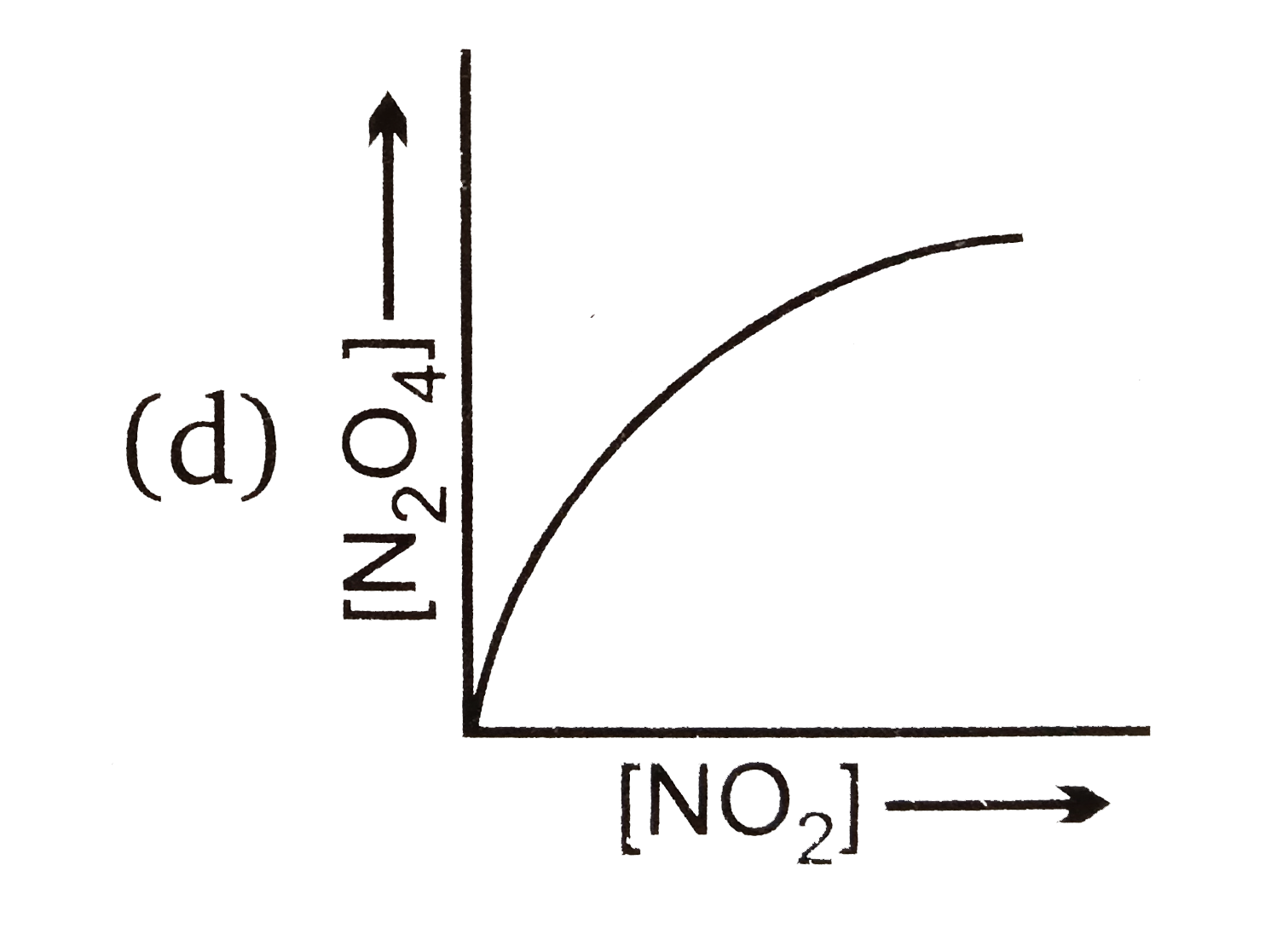A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
P BAHADUR-CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM-Exercise
- If the equilibrium constant for the reaction, N(2)O(4)hArr2NO(2) is K=...
Text Solution
|
- Write equilibrium constant for the each : (a) N(2)O(4(g))hArr2NO(2(g...
Text Solution
|
- The equilibrium constant expression for a gas reaction is : K(c) = (...
Text Solution
|
- The equilibrium constant of the reaction , SO(3(g))hArrSO(2(g))+(1)/...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the equilibrium constant for the reaction, H(2(g))+CO(2(g)...
Text Solution
|
- For the reactions, N(2(g))+3H(2(g))hArr2NH(3(g)). At 400 K, K(p)=41 at...
Text Solution
|
- Find out the value of K(c) for each of the following equilibrium from ...
Text Solution
|
- The rate of reversible reaction (change in concentration per second): ...
Text Solution
|
- Write a stoichiometric equation for the reaction between A(2) and C wh...
Text Solution
|
- In which case does the reaction go farthest to completion: K=1 K, K=10...
Text Solution
|
- The equilibrium constant K(c) for A((g))hArrB((g)) is 1.1. Which gas h...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the value of equilibrium constant K(p) for the reaction: O...
Text Solution
|
- Equilibrium constant, K(c) for the reaction, N(2(g))+3H(2(g))hArr2NH...
Text Solution
|
- The ester , ethyl acetate is formed by the reaction of ethanol and ace...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following equations for cell reaction: A+BhArrC+D ….(1)...
Text Solution
|
- For the gasesous reaction, 2NO(2)hArrN(2)O(4), calculate DeltaG^(@) an...
Text Solution
|
- DeltaG^(@) for (1)/(2)N(2)+(3)/(2)H(2)hArrNH(3) is -16.5 kJ mol^(-1) a...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the values of DeltaE^(@) and DeltaH^(@) for the reaction: ...
Text Solution
|
- For the reaction at 298 K: A((g))+B((g))hArrD((g))+C((g)) DeltaH^(...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the value of equilibrium constant for the reaction: A((g))...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the pressure for CO(2) at equilibrium if DeltaG^(@)=31.1kcal...
Text Solution
|