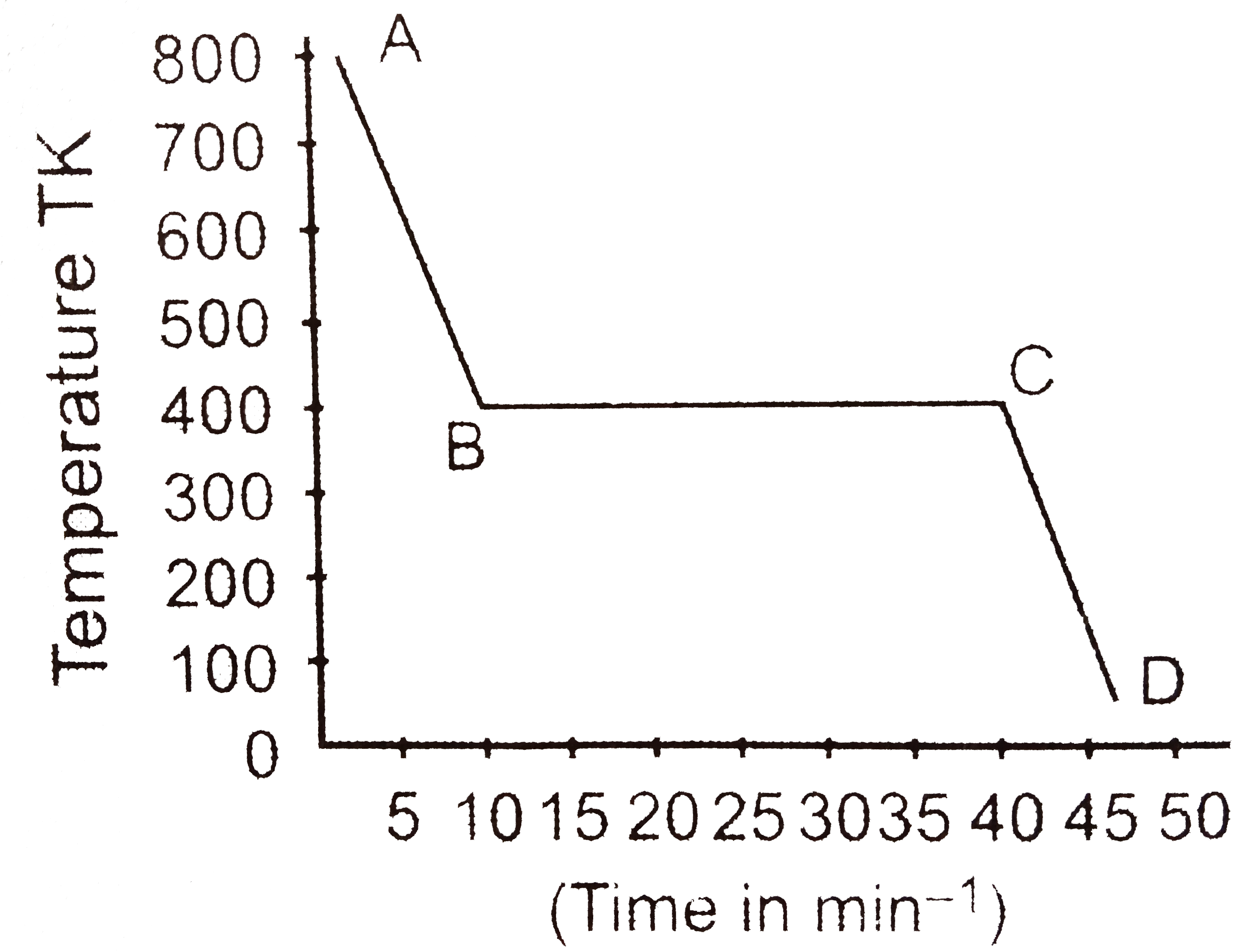A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
P BAHADUR-THERMODYNAMICS-Exercise
- In a given process on an ideal gas, dW=0 and dQ is negative, then for ...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following pairs of a chemical reaction is certain to resu...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of a substance is cooled at the rate of 0.4 kJ min^(-1) as sh...
Text Solution
|
- If a certain mass of gas is made to undergo separately adiabatic and i...
Text Solution
|
- If separate samples of argon, methane, nitrogen and ammonia, all at th...
Text Solution
|
- The maximum entropy of mixing occurs when hexane and heptane are mixed...
Text Solution
|
- Select the correct statements about the following reaction: Fe + HCL...
Text Solution
|
- Select the correct statements for ideal gases: 1. ((delH)/(delT))(P)...
Text Solution
|
- 1mole each of CaCl2, Al4C3, Mg2C3 reacts with excess water in separate...
Text Solution
|
- When a bottle of perfume is opened, odorous molecules mix with air and...
Text Solution
|
- The Gibbs energy change and standard Gibbs energy change for a reactio...
Text Solution
|
- The standard change in Gibbs energy for the reaction: H2O hArr H^+ +OH...
Text Solution
|
- Identify the correct statement for change of Gibbs energy for a system...
Text Solution
|
- A monoatomic gas is suddenly compressed to 1//8 of its original volume...
Text Solution
|
- The enthalpy and entropy change for the reaction, Br(2)(l)+Cl(2)(g)r...
Text Solution
|
- P-V plots for two gases during adiabatic expansion are shown in figure...
Text Solution
|
- For an adiabatic expansion of a perfect gas dP//P is equal to :
Text Solution
|
- The poisson's ratio for O(2) is 1.4. Which of the following are correc...
Text Solution
|
- Which species possesses negative value of specific heat?
Text Solution
|
- In which process net work done is zero ?
Text Solution
|