Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
GRAVIATION
PRADEEP|Exercise SOLVED EXAMPLES TYPE H|1 VideosGRAVIATION
PRADEEP|Exercise SOLVED EXAMPLES TYPE I|1 VideosGRAVIATION
PRADEEP|Exercise SOLVED EXAMPLES TYPE G|1 VideosBEHAVIOUR OF PERFECT GAS & KINETIC THEORY
PRADEEP|Exercise Assertion - Reason Type questions|14 VideosKINEMATICS
PRADEEP|Exercise 1 NCERT Comprehension|4 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PRADEEP-GRAVIATION-SOLVED EXAMPLES
- How far from Earth must a body be along a line joining the sun to the ...
Text Solution
|
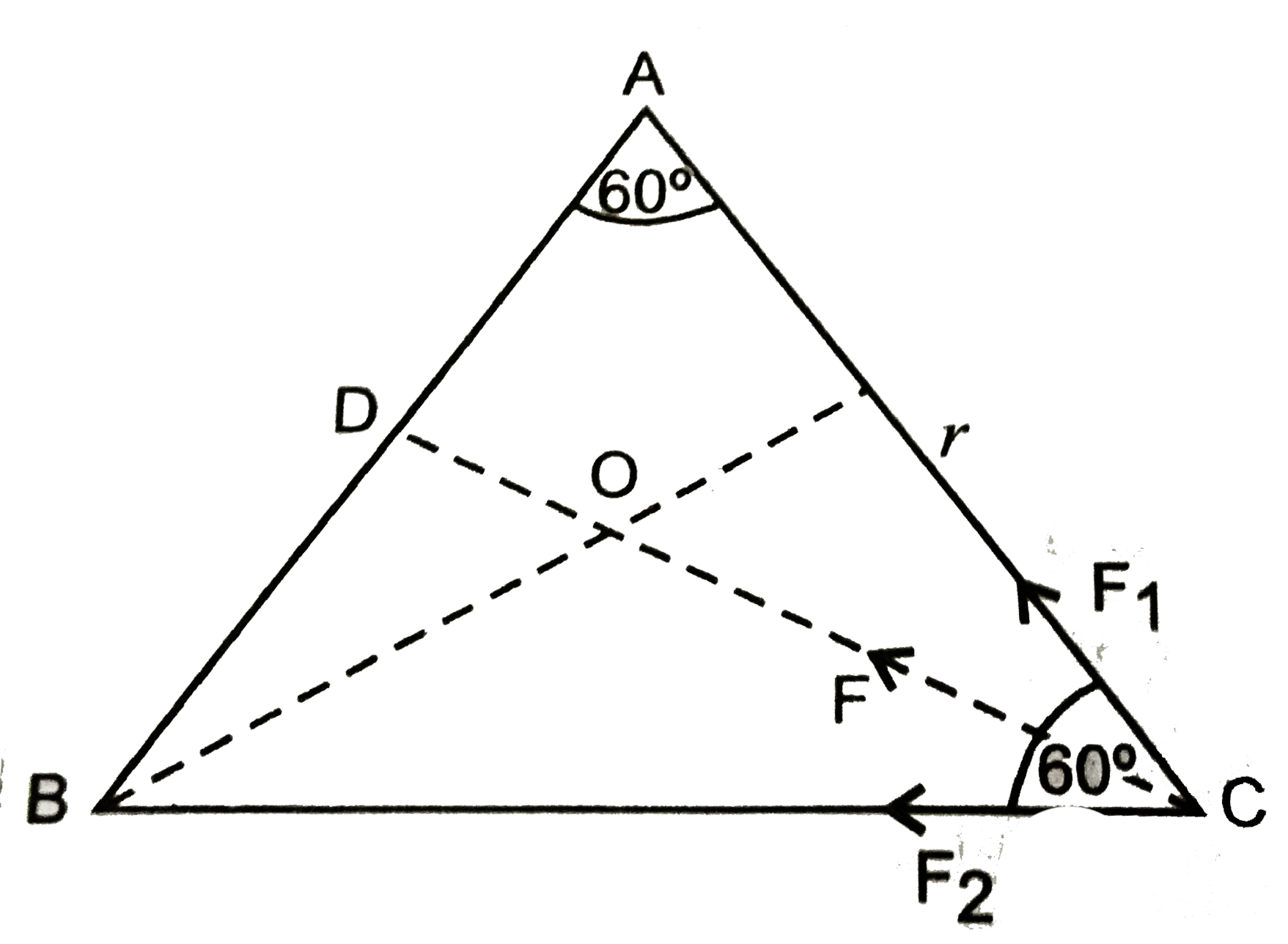
- Three equal masses of m kg each are fixed at the vertices of an equila...
Text Solution
|
- Three identical particles each of mass "m" are arranged at the corner...
Text Solution
|
- Assuming the earth of to be a uniform sphere of radius 6400 kg and den...
Text Solution
|
- If the radius of the earth be increased by a factor of 5, by what fact...
Text Solution
|
- A planet whose size is the same and mass is 4 times as that of Earth, ...
Text Solution
|
- A man can jump 2.0 m high on the earth. Up to what height he can jump ...
Text Solution
|
- If the radius of the Earth shrinks by 2%, mass remaing same, then how ...
Text Solution
|
- Two lead spheres of 20 cm and 2 cm diametre respectively are planet wi...
Text Solution
|
- At what height from the surface of earth will the value of g be reduce...
Text Solution
|
- A body weighs 64 N on the surface of Earth. What is the gravitational ...
Text Solution
|
- Find the percentage decrease in the wight of the body when taken to a ...
Text Solution
|
- A body hanging from a spring stretches it by 2 cm at the earth's surfa...
Text Solution
|
- An object weighs 10 N at north pole of Earth. In a geostationary satel...
Text Solution
|
- At what depth from the surface of earth, the value of acceleration due...
Text Solution
|
- Assuming the Earth to be a sphere of uniform mass density, how much wo...
Text Solution
|
- Find the percentage decrease in the weight of the body when taken 64 k...
Text Solution
|
- Determine the speed with which the earth would have to rotate on its a...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate that imaginary angular velocity of the Earth for which effec...
Text Solution
|
- Suppose Earth is perfect sphere of radius 6.4 xx 10^(6) m. It is rota...
Text Solution
|