Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
GRAVIATION
PRADEEP|Exercise SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS II.|1 VideosGRAVIATION
PRADEEP|Exercise SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS III.|1 VideosGRAVIATION
PRADEEP|Exercise SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS I.|1 VideosBEHAVIOUR OF PERFECT GAS & KINETIC THEORY
PRADEEP|Exercise Assertion - Reason Type questions|14 VideosKINEMATICS
PRADEEP|Exercise 1 NCERT Comprehension|4 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PRADEEP-GRAVIATION-SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
- An artificial satellite is moving in a circular orbit around the earth...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : An astronaut in an orbiting space station above the earth ...
Text Solution
|
- There is no atomosphere on moon because
Text Solution
|
- The garvitational force exerted by the sun on the Moon is greater than...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : On satellites we feel weightlessness. Moon is also a satel...
Text Solution
|
- What do you understand by gravity and acceleration due to gravity. Est...
Text Solution
|
- Explain how the knowledge of g helps us to find (i) mass of earth an...
Text Solution
|
- Explain gravitational potential at a point and gravitational potential...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: The ratio of intertial mass to gravitational mass is equal ...
Text Solution
|
- PRINCIPLE OF LAUNCHING A SATELLITE
Text Solution
|
- What do you underestand by orbital velocity ? Derive an expression for...
Text Solution
|
- What do you understand by geostationary and polar satellite ? Discuss ...
Text Solution
|
- What do you undersatnd by 'Escape velocity' ? Derive an expression for...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the reason of weightlessness inside a satellite.
Text Solution
|
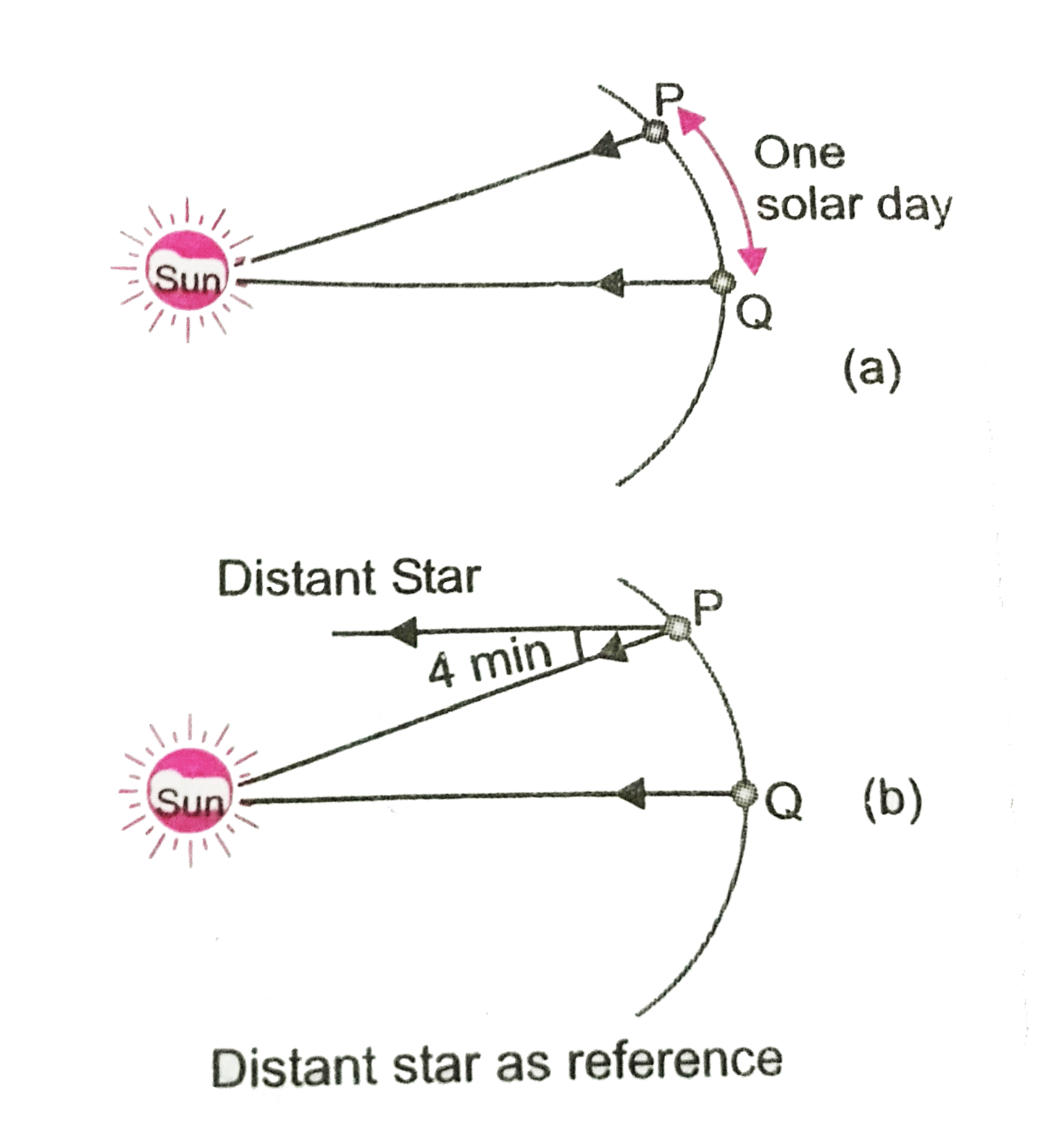
- The difference in the lengths of a mean solar day and a sidereal day i...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical heavy sphers are separated by a distance 10 times their ...
Text Solution
|
- Show the nature of the following graph for a satellite orbiting the ea...
Text Solution
|
- Shown are several cuves (fig. (a), (b), (c), (d), (e), (f)]. Explain w...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass 'm' is raised to a height h = R from the surface of...
Text Solution
|
- A mass m is placed at P a distance h along the normal through the cent...
Text Solution
|