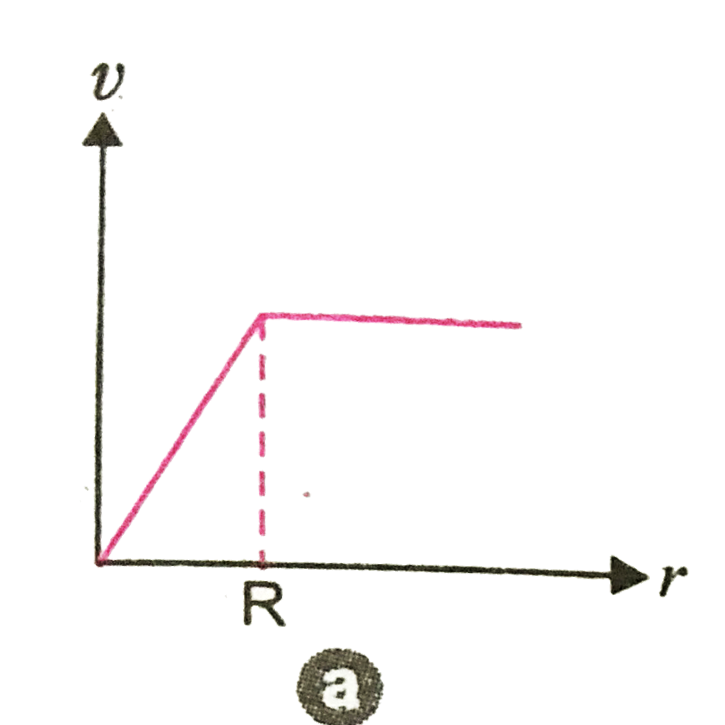
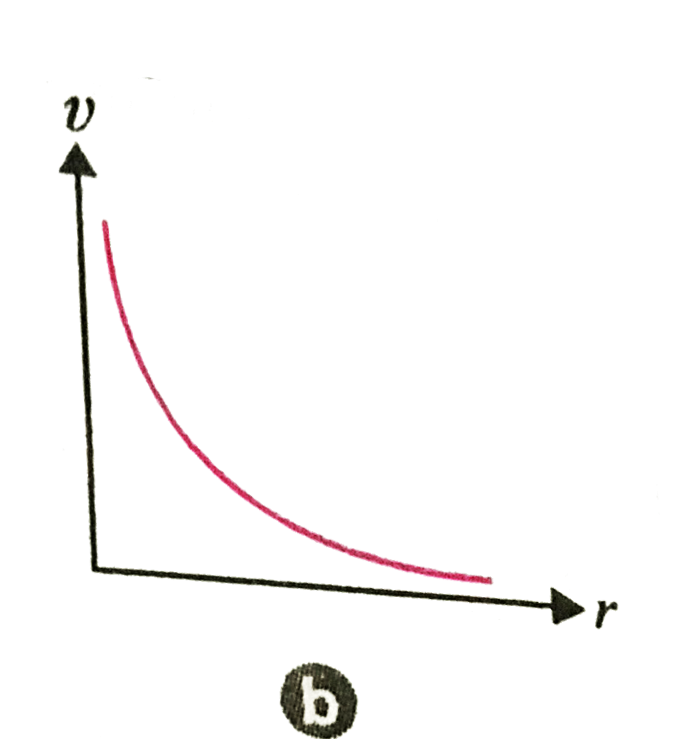
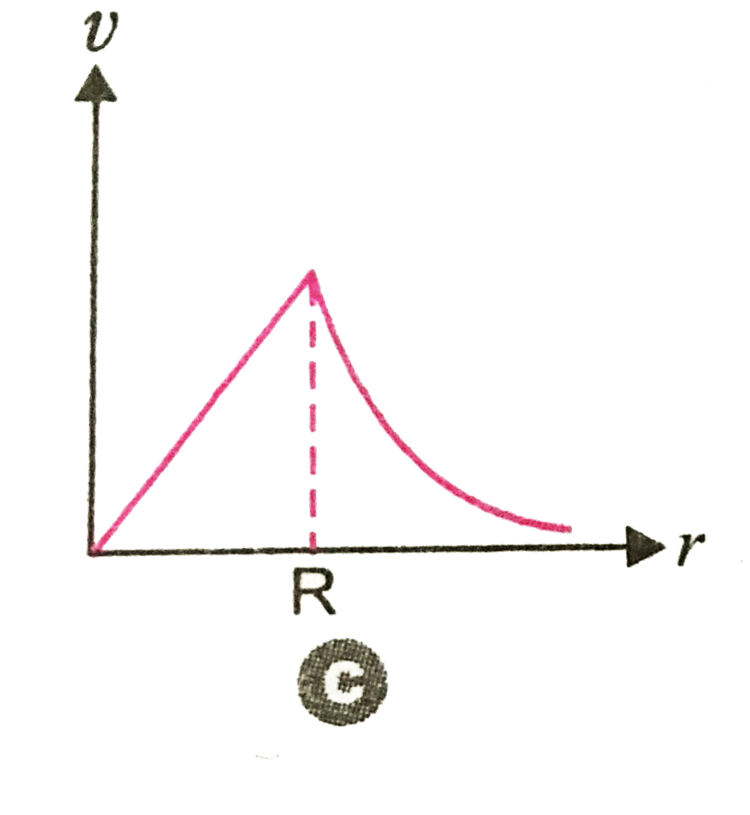
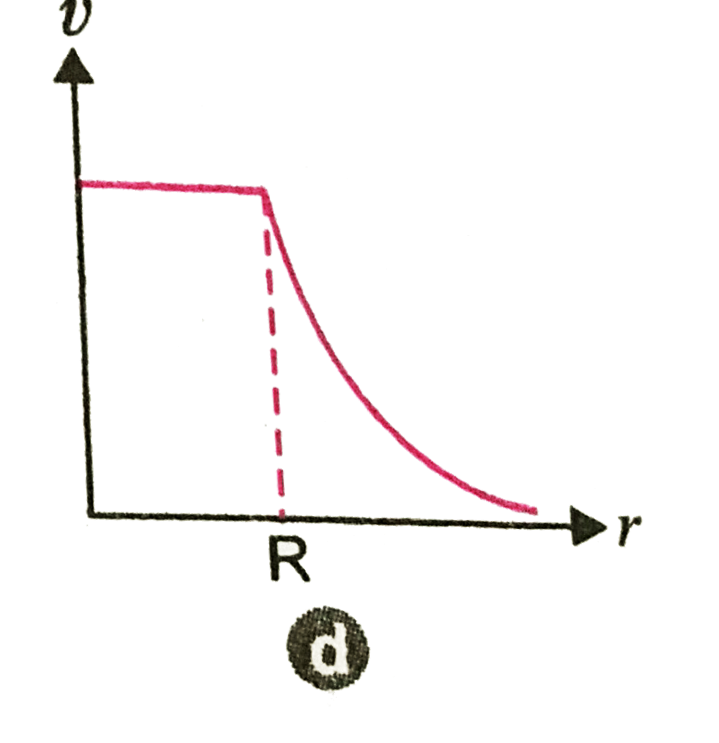
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A spherically symmetric gravitational system of particles has a mass d...
Text Solution
|
- A spherically symmetric gravitational system of particles has a mass d...
Text Solution
|
- एक गोलाकार सममित (symmetrical) गुरुत्वीय के समूह का द्रव्यमान घनत...
Text Solution
|
- The volume charge density in a spherical ball of radius R varies with ...
Text Solution
|
- Mass density of sphere having radius R varies as rho = rho0(1-r^2/R^2)...
Text Solution
|
- एक परीक्षण कण, द्रव्यमान घनत्व rho(r )=(K)/(r^(2)) से उत्पन्न गुरुत्वी...
Text Solution
|
- Charge density of a sphere of radius R is rho = rho0/r where r is dist...
Text Solution
|
- Mass density of sphere having radius R varies as rho = rho0(1-r^2/R^2)...
Text Solution
|
- Charge density of a sphere of radius R is rho = rho0/r where r is dist...
Text Solution
|