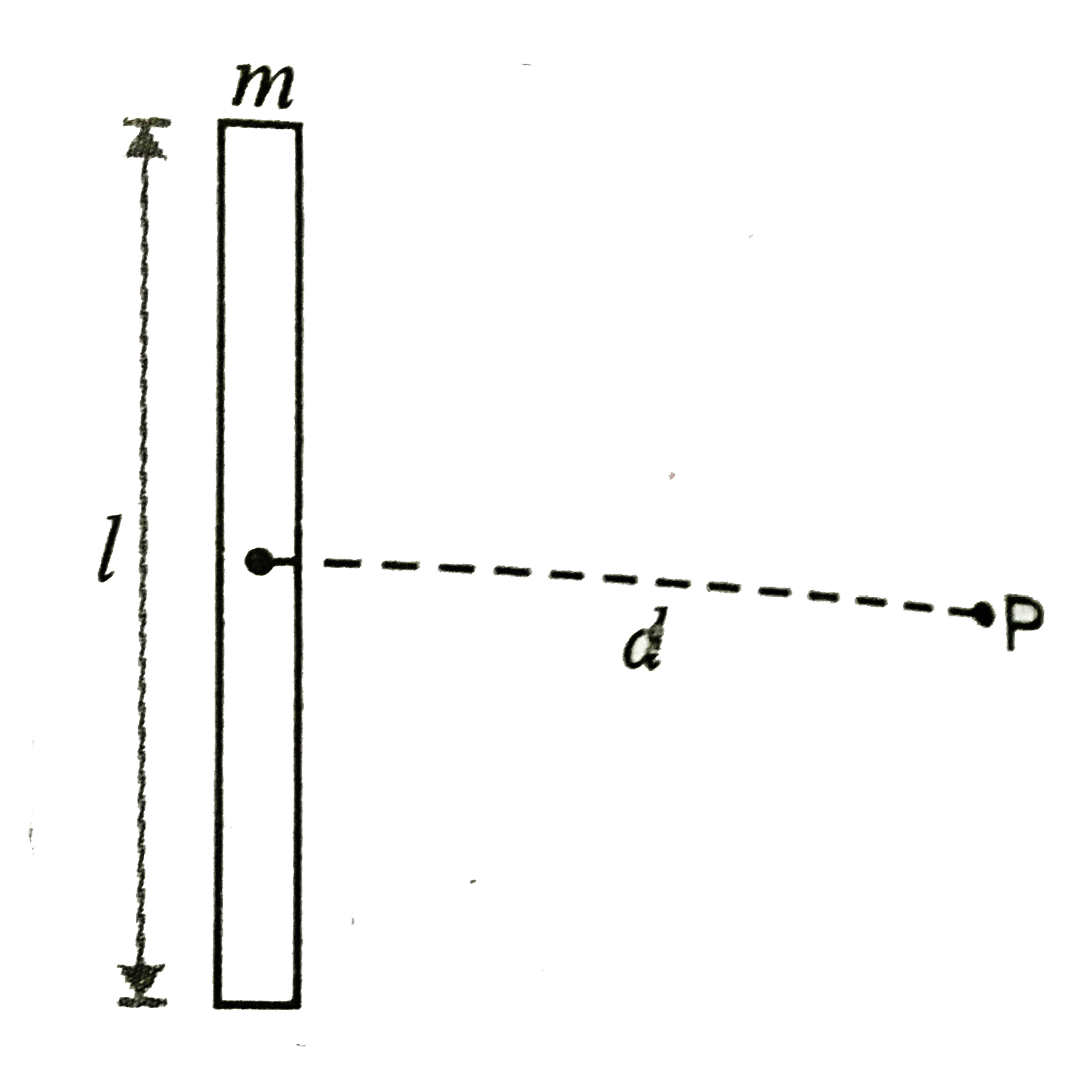
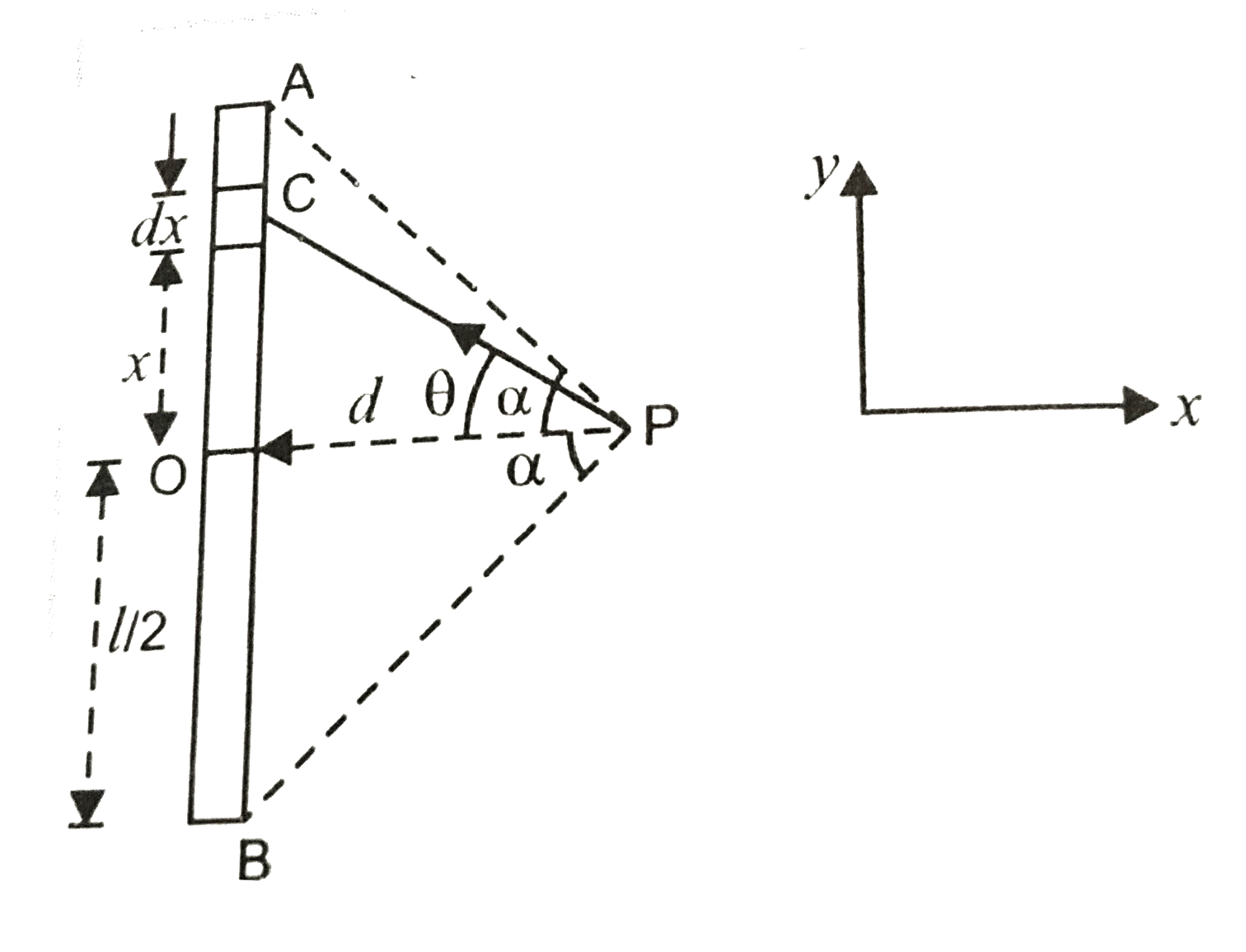
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A uniform rod of mass m and length l is taken. Find the gravitational ...
Text Solution
|
- Derive an expression fro the gravitational field due to a unifrom rod ...
Text Solution
|
- A mass m is at a distance a from one end of a uniform rod of length l ...
Text Solution
|
- Find the electric field at a point P on the perpendicular bisector of ...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rod of mass m and length l is taken. Find the gravitational ...
Text Solution
|
- Find the gravitational potential energy of system consisting of unifor...
Text Solution
|
- Find the gravitational potential energy of a system consisting of a un...
Text Solution
|
- L लंबाई एवं M द्रव्यमान वाले एक समरूप छड के कारण इसके लंब अर्द्...
Text Solution
|
- Find : (i)Electric field intensity due to an infinitely long uniformly...
Text Solution
|