Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
THERMODYNAMICS
PRADEEP|Exercise Higher order thinking skills|9 VideosTHERMODYNAMICS
PRADEEP|Exercise Value based Questions|4 VideosTHERMODYNAMICS
PRADEEP|Exercise Short answer questions(NCERT)|6 VideosSYSTEMS OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION
PRADEEP|Exercise Assertion- Reason Type questions|20 VideosWORK, ENERGY AND POWER
PRADEEP|Exercise Assertion-Reason Type Questions|24 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PRADEEP-THERMODYNAMICS-Long answer questions(NCERT)
- Consider a P-V diagram in which the path followed by one mole of perfe...
Text Solution
|
- A cycle followed by an engine (made of one mole of perfect gas in a cy...
Text Solution
|
- A cycle followed by an engine (made of one mole of an ideal gas in a c...
Text Solution
|
- Consider that an ideal gas (n mol es) is expanding in a process given ...
Text Solution
|
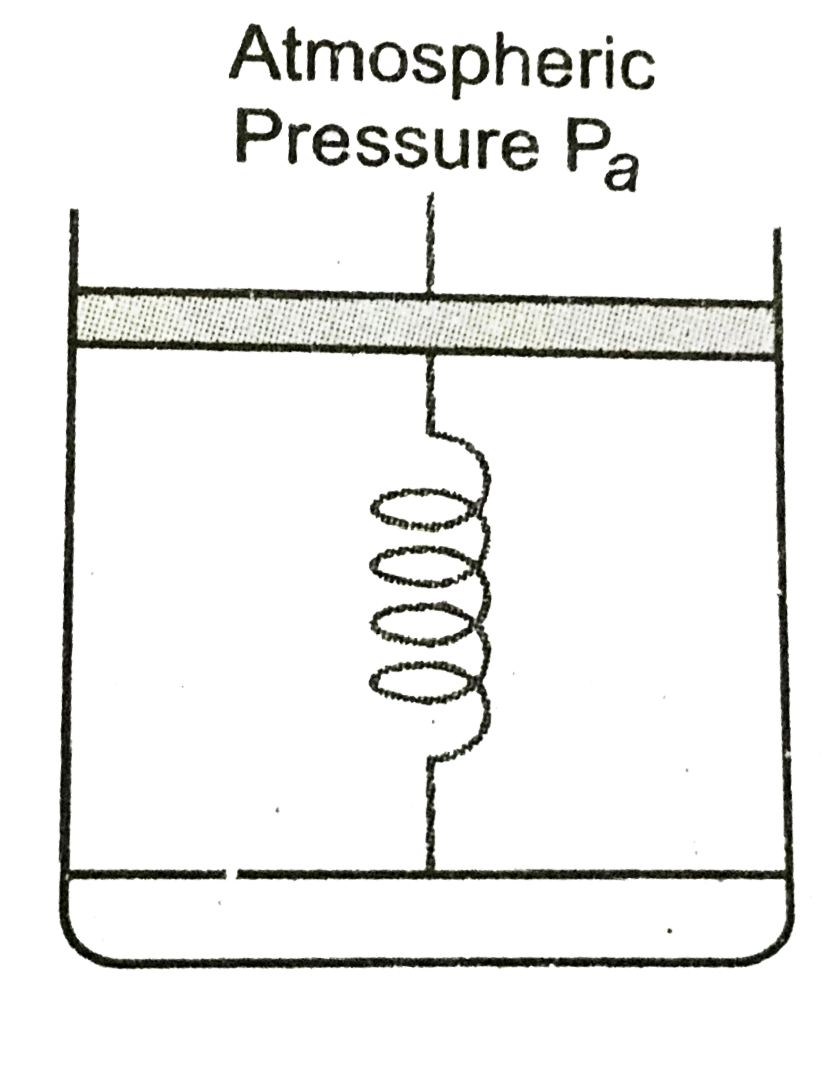
- Consider one mole of a perfect gas in a cyclinder of unit cross sectio...
Text Solution
|