Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
BEHAVIOUR OF PERFECT GAS & KINETIC THEORY
PRADEEP|Exercise Value Based Questions|15 VideosBEHAVIOUR OF PERFECT GAS & KINETIC THEORY
PRADEEP|Exercise Fill in the blanks|10 VideosBEHAVIOUR OF PERFECT GAS & KINETIC THEORY
PRADEEP|Exercise NCERT questions|13 VideosGRAVIATION
PRADEEP|Exercise Assertion-Reason Type Questions|19 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PRADEEP-BEHAVIOUR OF PERFECT GAS & KINETIC THEORY-Higher order thinking skills questions
- Calculate the mean free path of nitogen at 27^(@)C when pressure is 1....
Text Solution
|
- There is a soap bubble of radius 2.4 xx 10^(-4)m in air cylinder at a ...
Text Solution
|
- A gas has molar heat capacity C = 37.55 J "mole"^(-1)K^(-1), in the pr...
Text Solution
|
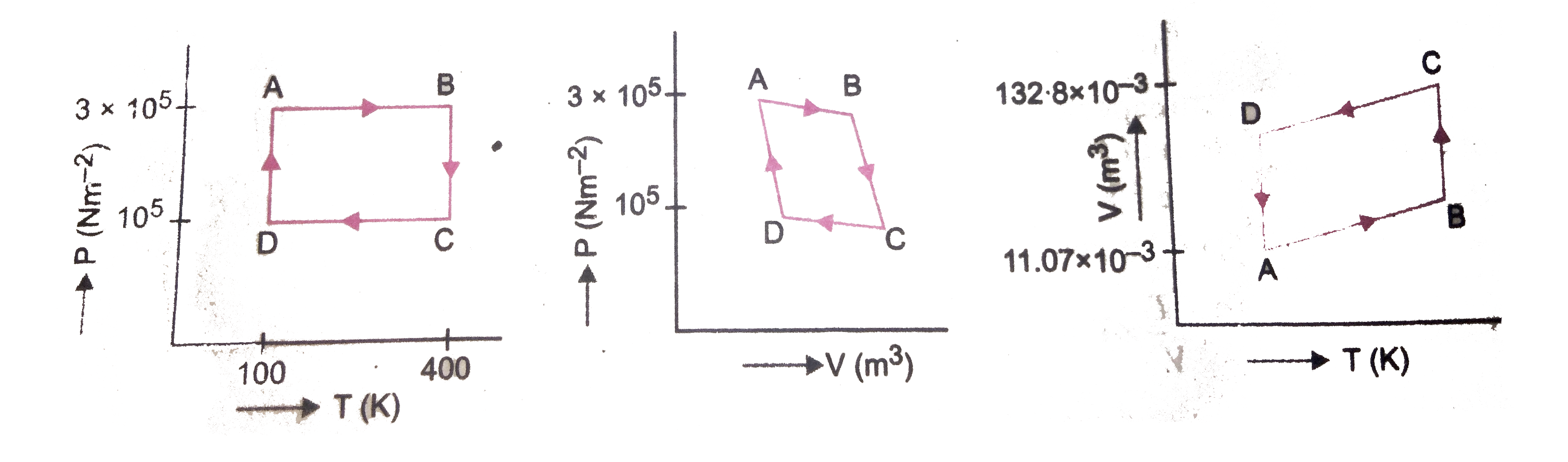
- A moles of a monoatomic ideal gas are at pressure 3xx10^(5)Nm^(-2) and...
Text Solution
|
- A vessel of volume , V = 5.0 litre contains 1.4 g of nitrogen at a tem...
Text Solution
|
- (1//2) mole of helium is contained in a container at STP how much heat...
Text Solution
|
- 8g of oxygen, 14 g of nitrogen and 22 g carbon dioxide are mixed in an...
Text Solution
|
- A nitrogen molecules at teh surface of earth happens to have the rms s...
Text Solution
|
- A vessel is filled with a gas at a pressure of 76 cm of mercury at a c...
Text Solution
|