Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
OSCILLATIONS AND WAVES
PRADEEP|Exercise Multiple Choice Question-I|21 VideosOSCILLATIONS AND WAVES
PRADEEP|Exercise Multiple Choice Question-II|14 VideosOSCILLATIONS AND WAVES
PRADEEP|Exercise Fill In The Blanks|20 VideosMATHEMATICAL TOOLS
PRADEEP|Exercise Fill in the blanks|5 VideosPHYSICAL WORLD AND MEASUREMENT
PRADEEP|Exercise Competiton Focus Jee Medical Entrance|18 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PRADEEP-OSCILLATIONS AND WAVES-PROBLEMS FOR PRACTICE
- Infinite springs with force constants k,2k, 4k and 8k … respectively a...
Text Solution
|
- Two springs of equal lengths and equal cross-sectional area are made o...
Text Solution
|
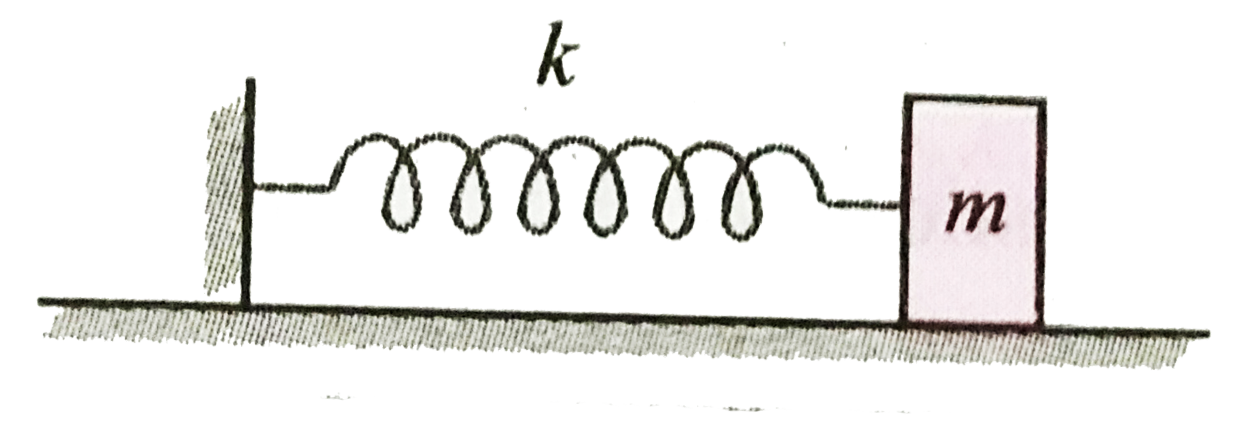
- A spring of constant k=0.5 N//m and an attached mass m oscillates on a...
Text Solution
|
- A force of 1N is required to stretch a spring by 1.5cm. If the spring ...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles A and B of equal masses are suspended from two massless ...
Text Solution
|
- A tray of mass 12 kg is supported by two identical springs as shown in...
Text Solution
|
- A system of springs with their spring constants are as shown in figure...
Text Solution
|
- Three spring are connected to a mass m(=100g) as shown in figure. Give...
Text Solution
|
- Two pendulums of length 90 cm and 100 cm start oscillating in phase. A...
Text Solution
|
- If the acceleration due to gravity on the moon is one-sixth of that on...
Text Solution
|
- If the length of a second's pendulum is increased by 1% , how many sec...
Text Solution
|
- A simple pendulum has time period 2s in air. If the whole arrangement ...
Text Solution
|
- A second's pendulum is taken from a place where g=9.8 ms^(-2) to a pl...
Text Solution
|
- Two pendulums of lengths 200 cm and 220.50 cm start oscillating in pha...
Text Solution
|
- Time period of is simple pendulum of length L is T(1) and the point ti...
Text Solution
|
- A body is dropped in a hole drilled across diameter of the earth. Show...
Text Solution
|
- A cylinderical wooden block of cross-section 15.0 cm^(2) and 250 gram ...
Text Solution
|
- A vertical U-tube of uniform cross-section contains water upto a heigh...
Text Solution
|
- A test tube weighing 10g and external dismeter 2.5cm is floated vertic...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mas 10g is placed in a potential field given by U=(500x^...
Text Solution
|