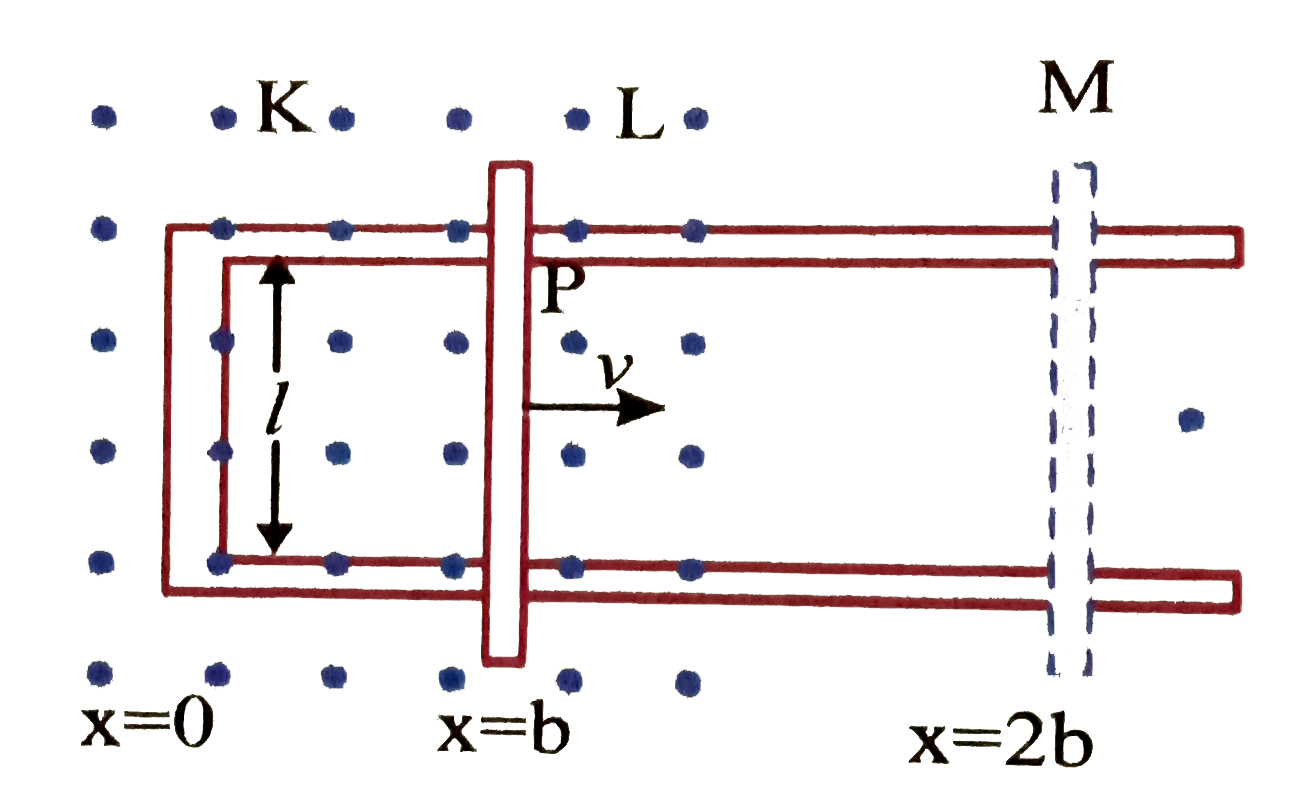
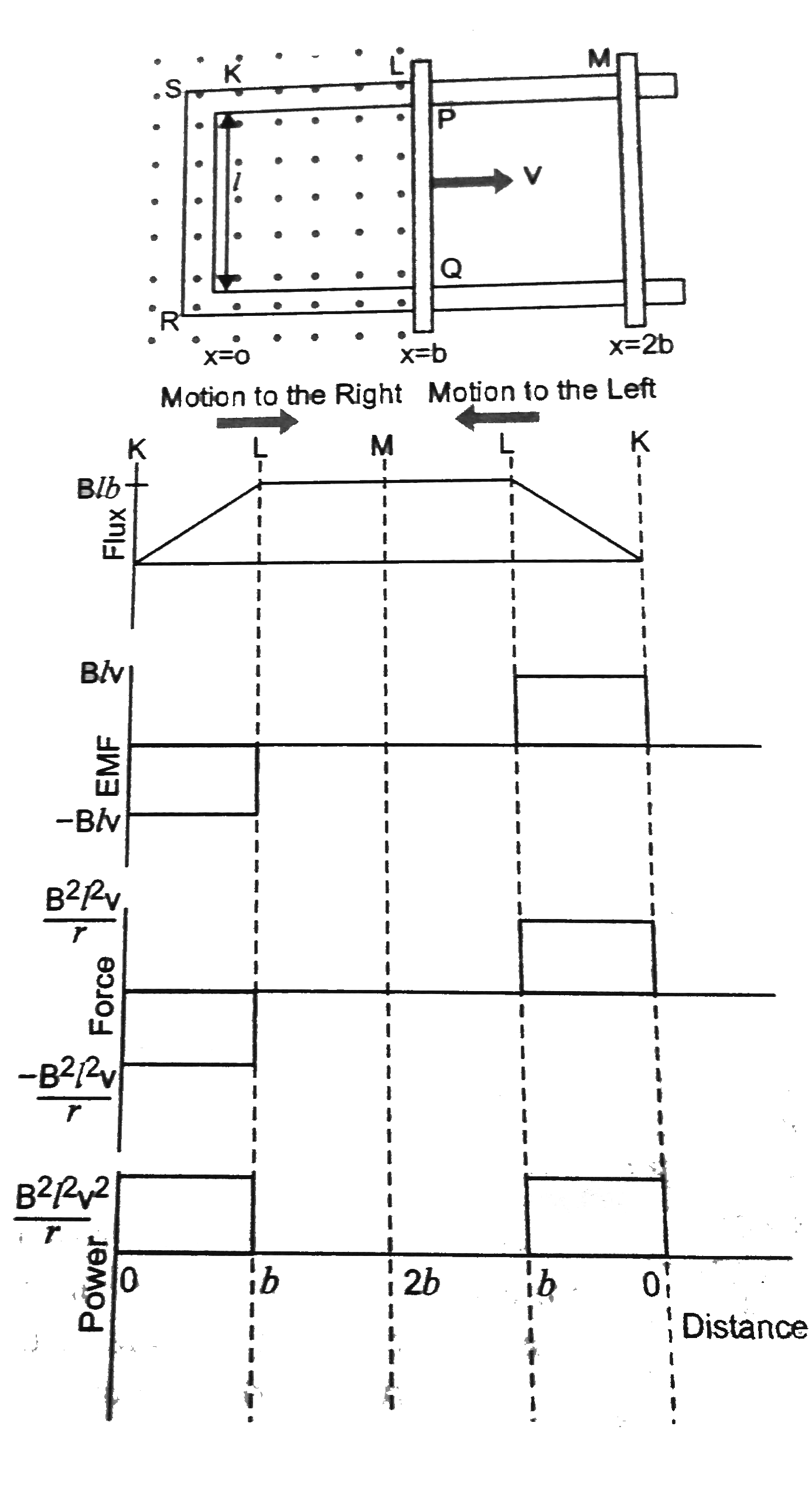
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION & ALTERNATING CURRENT
PRADEEP|Exercise Solved Examples (b)|1 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION & ALTERNATING CURRENT
PRADEEP|Exercise Short Answer Qusetions|2 VideosDUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER
PRADEEP|Exercise Exercise|191 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES
PRADEEP|Exercise II Focus multiple choice question|5 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems