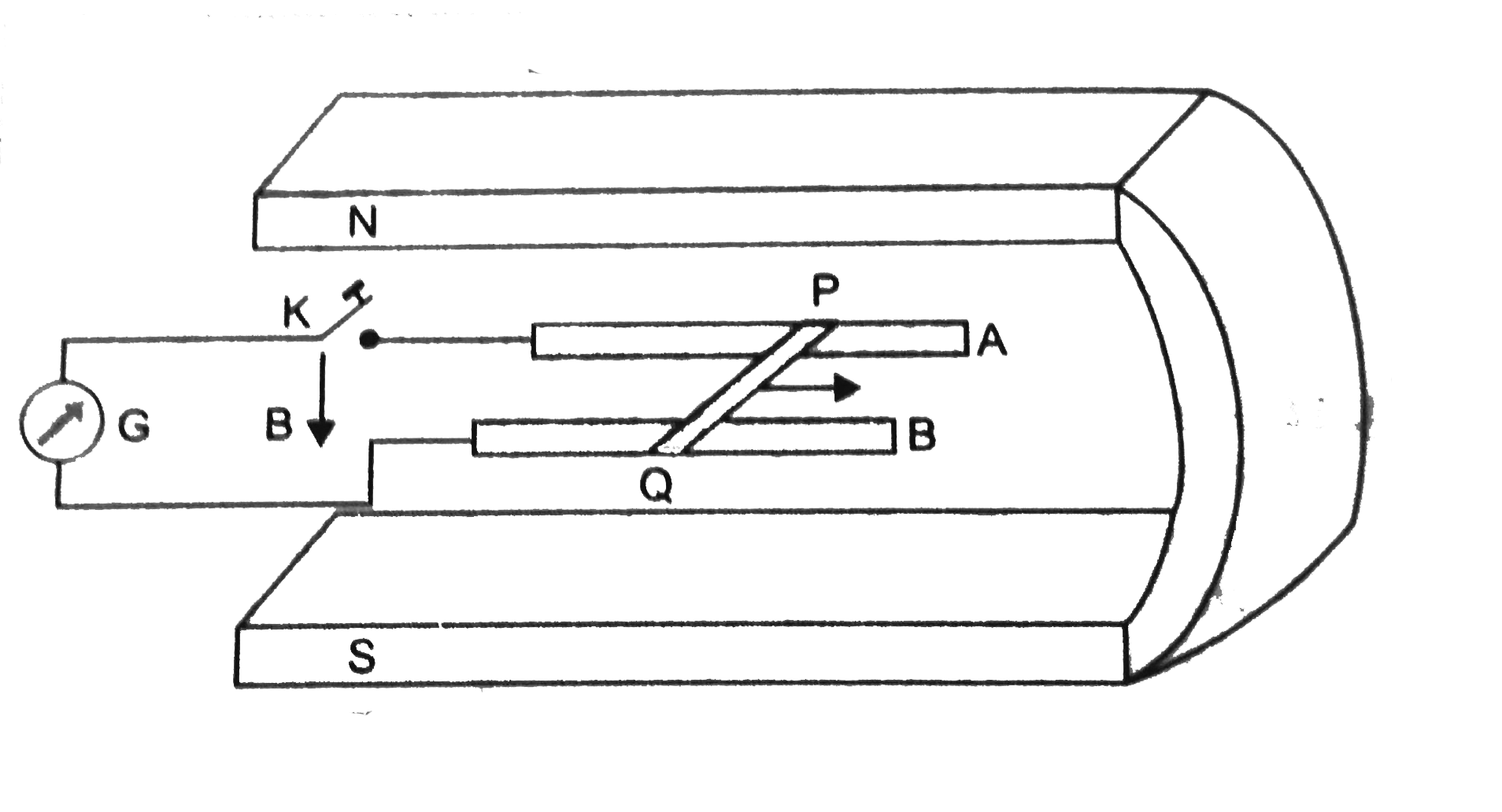
Fig. shows a metal rod PQ resting on the rails A, B and positoned between the poles of a permanent magnet. The rails, the rod and the magnetic field are in three mutually perperdicular directions. A galvanometer connects the rails through a switch K. Length of the rod = 15 cm, B = 0.50 T, resistance of closed loop containing the rod `= 9.0 m Omega` Answer the following questions.
(a) Suppose K is open and the rod moves with a speed of `12 cm//s` in the direction shown, Give the polarity and magnitude of induced e.m.f
(b) Is there on excess charge built up at the ends of rods when K is open ? What if K is closed ?
(c ) With K open and the rod moving uniformly, there is no net force on the electron in the rod PQ even though they do experience magnetic froce due to the motion of the rod Explain.
(d) What is the retarding force on the rod when K is closed?
(e) How much powe s required (by an external agent) to keep the rod moving at the same speed `( = 12 cm//s)` when K is closed. (f) How much power is dissipated as heat in the closed circuit ? What is the source of this power?
(g) What is the induced e.m.f. in the following in the moving rod when the permanent magnet is rotated to a vertical position so that the field is parallel to the rails instead of being perpendicular ?