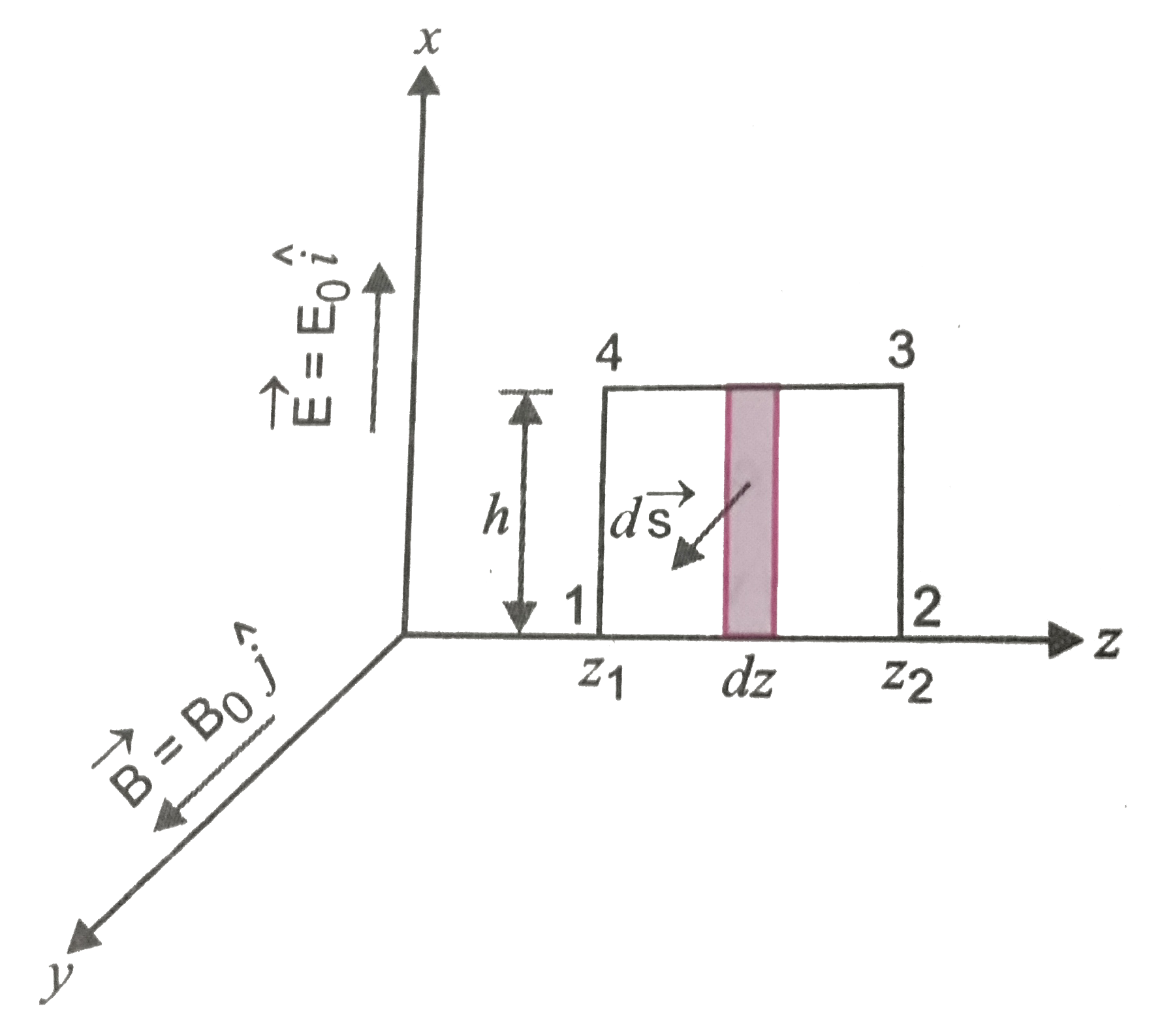
(i) During the propagation of e.m. wave along z-axis, let electric field vector `vecE` be along x-
axis and magnetic field vector `vecB` be along y-axis i.e., `vecE=E_0hati and vecB=B_0hatj`. Line
integral of `vecE` over the closed rectangular, path 1234 in x-z plane is
`oint vecE.vec(dl)=int_1^2vecE.vec(dl)+int_2^3vecE.vec(dl)+int_3^4vecE.vec(dl)+int_4^1vecE.vec(dl)`
`=int_1^2Edl cos 90^@+int_2^3Edl cos 0^@+int_3^4Edl cos 90^@+int_4^1Edl cos 180^@`
`=0+E_(z_2)h+0-E_(z_1)h=E_(z_2)-E_(z_1)=E_0h[sin (kz_2-omegat)-sin (kz_1-omegat)]......(i)`
(ii) For evaluting `ointvecB.vec(dl)` over the surface bounded by
loop1234, let us consider a rectangle 1234 be made of small
strips. One small strip of area ds=h dz is shown in fig.
`oint_("Surface bounded by strips 1234")vecB.vec(ds)=oint Bds cos0^@=oint B ds`
`=int_(z_1)^(z_2)B_0sin (kz_2-omegat)hdz`
`=-(B_0h)/k[cos (kz_2-omegat)-cos(kz_1-omegat).....(ii)`
(iii) Given, `oint vecE.vec (dl)=-(dphi_B)/(dt)=-d/(dt) oint vecB.vec(ds)`
Puting the values from (i) and (ii), we get,
`E_0h[sin (kz_2-omegat)-sin (kz_1-omegat)]`
`=-d/(dt)[-(B_0h)/k{cos (kz_2-omegat)-cos(kz_1-omegat)}]`
`=(B_0h)/k omega[sin (kz_2-omegat)-sin(kz_1-omegat)}]`
or `E_0=(B_0omega)/k=B_0c ( :' omega/k=c) or E_0//B_0=c`
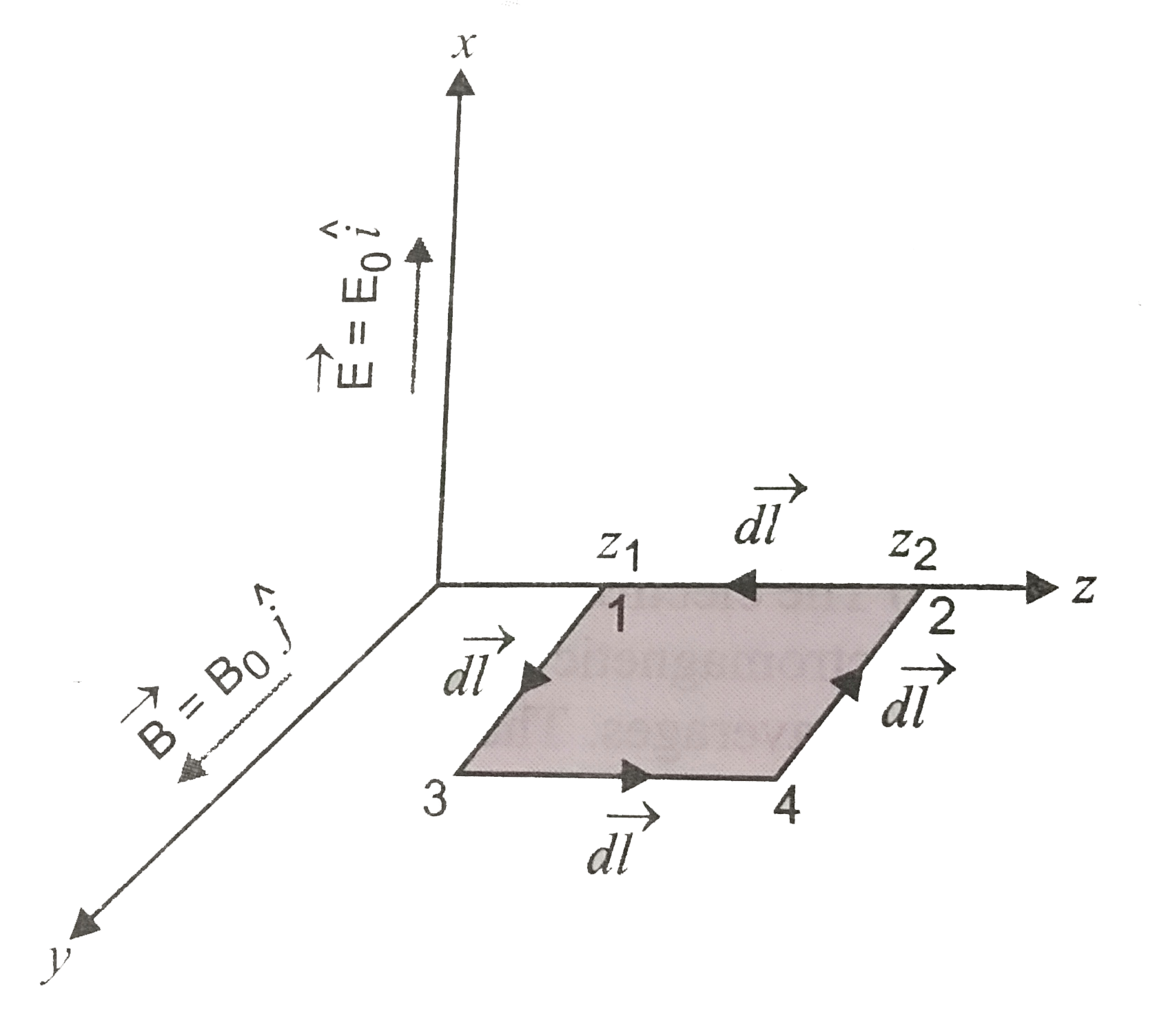
(iv) For evaluting `oint vecB.vec(dl)`, let us consider a loop 1342
in y-z plane as shown in fig.
`oint vecB.vec(dl)=oint_1^3vecB.vec(dl)+oint_3^4vecB.vec(dl)+oint_4^2vecB.vec(dl)+oint_2^1vecB.vec(dl)`
`int_1^3Bdl cos0^@+int_3^4Bdl cos90^@+int_4^2Bdl cos180^@+int_2^1Bdl cos90^@=int_1^3Bdl +0-int_4^2Bdl +0`
`=B_(z_1)h-B_(z_2)h=h(B_(z_1)-B_(z_2))=B_0h [sin (kz_1-omegat)-sin(kz_2-omegat)]....(iii)`
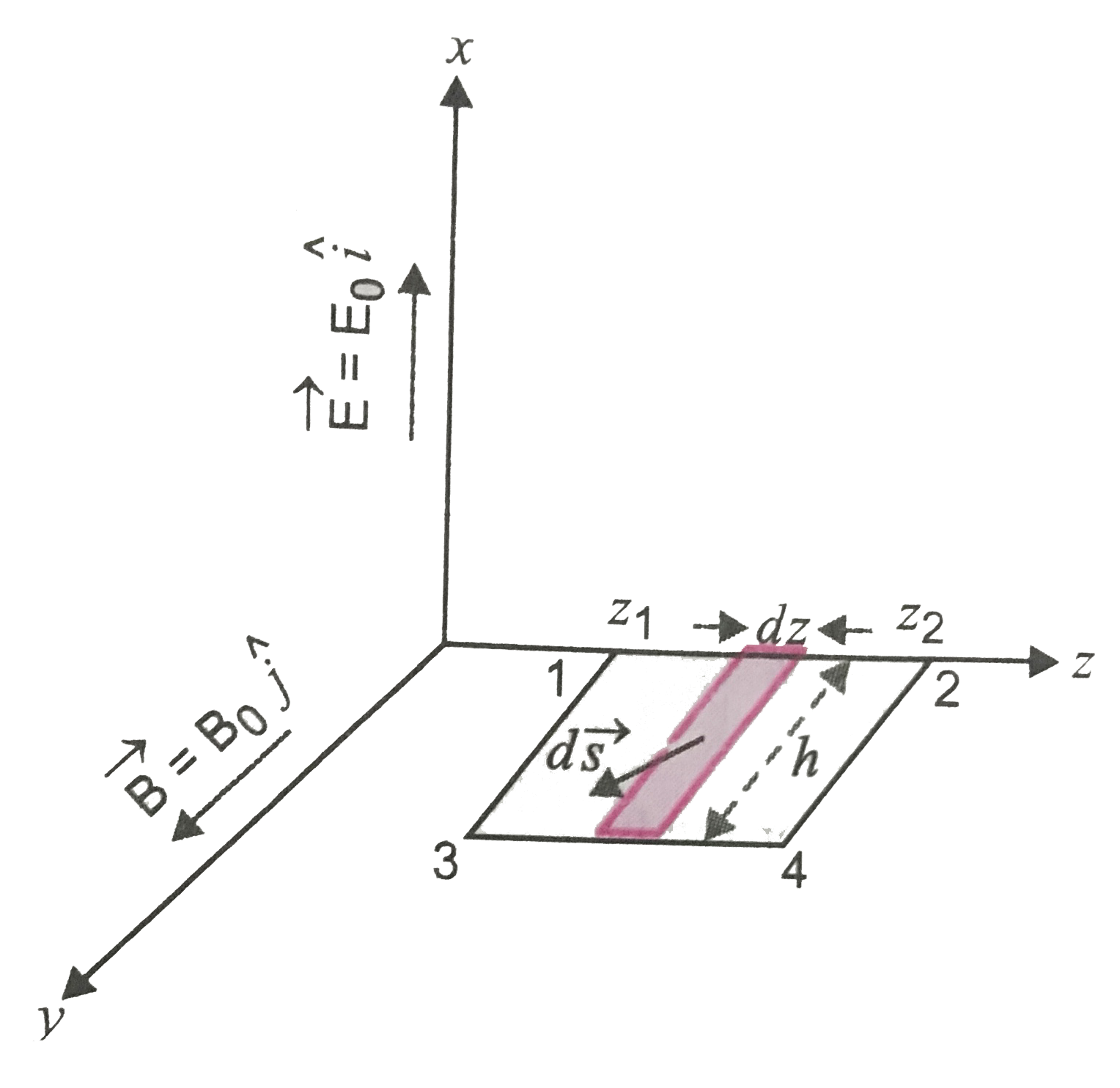
To evalute `phi_E=oint vecE.vec(ds)`, let us consider the rectangle
1342 to be made up of strips, each of area ds=hdz. fig.
`phi_E=oint vecE.vec(ds)=ointEdscos0^@=ointEds`
`int_(z_1)^(z_2) E_0sin (kz_1-omegat)hdz`
`=-(E_0h)/k[cos (kz_2-omegat)-cos(kz_1-omegat)]`
`:. (dphi_E)/(dt)=(E_0homega)/k[sin (kz_1-omegat)-sin(kz_2-omegat)....(iv)`
In the relation, `ointvecB.vec(dl)=mu_0[1+epsilon_0(dphi_E)/(dt)]`
I is the conduction current. The value of I=0 (in vacuum) `:. oint vecB.vec(dl)=mu_0epsilon_0(dphi_E)/(dt)`
Putting values form (iii) and (iv), we get
`B_0h[sin (kz_1-omegat)-sin(kz_2-omegat)]=mu_in_0 (E_0h omega)/k [sin (kz_1-omegat)-sin(kz_2-omegat)]`
or `B_0h=mu_0in_0E_0h omega/k or (E_0)/(B_0) omega/k=1/(mu_0in_0) [as (E_0)/(B_0) =c and omega=ck]`
`:. c (ck)/k=1/(mu_0in_0) or c^2=1/(mu_0in_0) or c=1/(sqrt(mu_0in_0))`