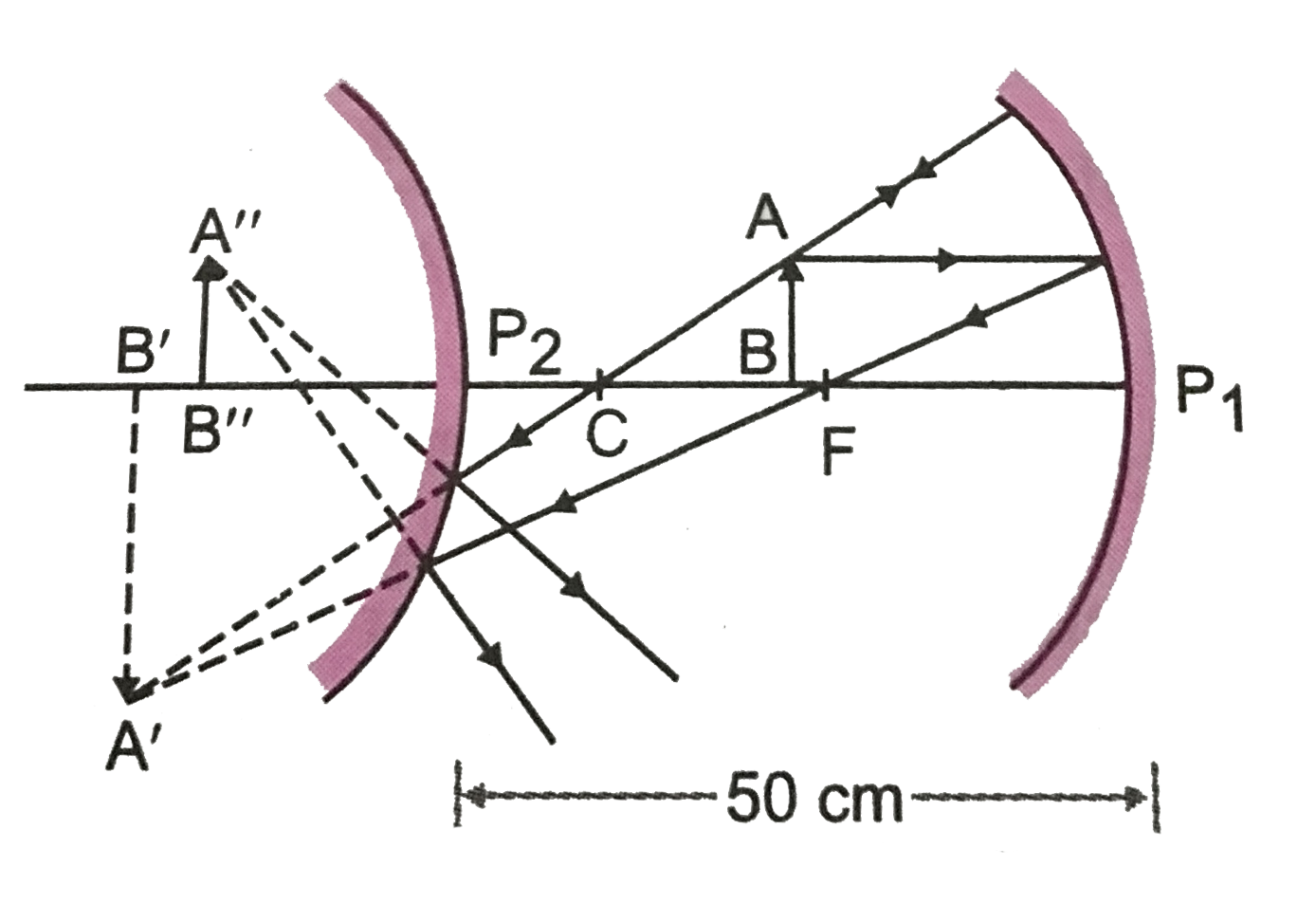
The course of rays for image formation is shown in Fig.
(i) For concave mirror :
`f_(1) = -25 cm`.
`(1)/(v_(1)) = (1)/(f_(1)) - (1)/(u_(1)) = (1)/(-20) + (1)/(25) = -(1)/(100)`
`v_(1) = -100 cm`
As `v_(1)` is negative, image `A'B'` formed by concave mirror is real, formed in front of concave mirror such that `P_(1)B' = 100 cm`.
(ii) For convex mirror : `A'B'` acts as a virtual object
`u_(2) = P_(2)B' = P_(1)B' - P_(1)P_(2) = 100 - 50 = 50 cm`,
`f_(2) = (R_(2))/(2) = (30)/(2) = 15 cm`
`(1)/(v_(2)) = (1)/(f_(2)) - (1)/(u_(2)) = (1)/(15) - (1)/(50) = (7)/(150)`
`:. v_(2) = (150)/(7) = 21.43 cm`
As `v_(2)` is positive, final image `A"B"` is virtual and is fromed behind the convex mirror, such that `P_(2)B" = 21.43 cm`.