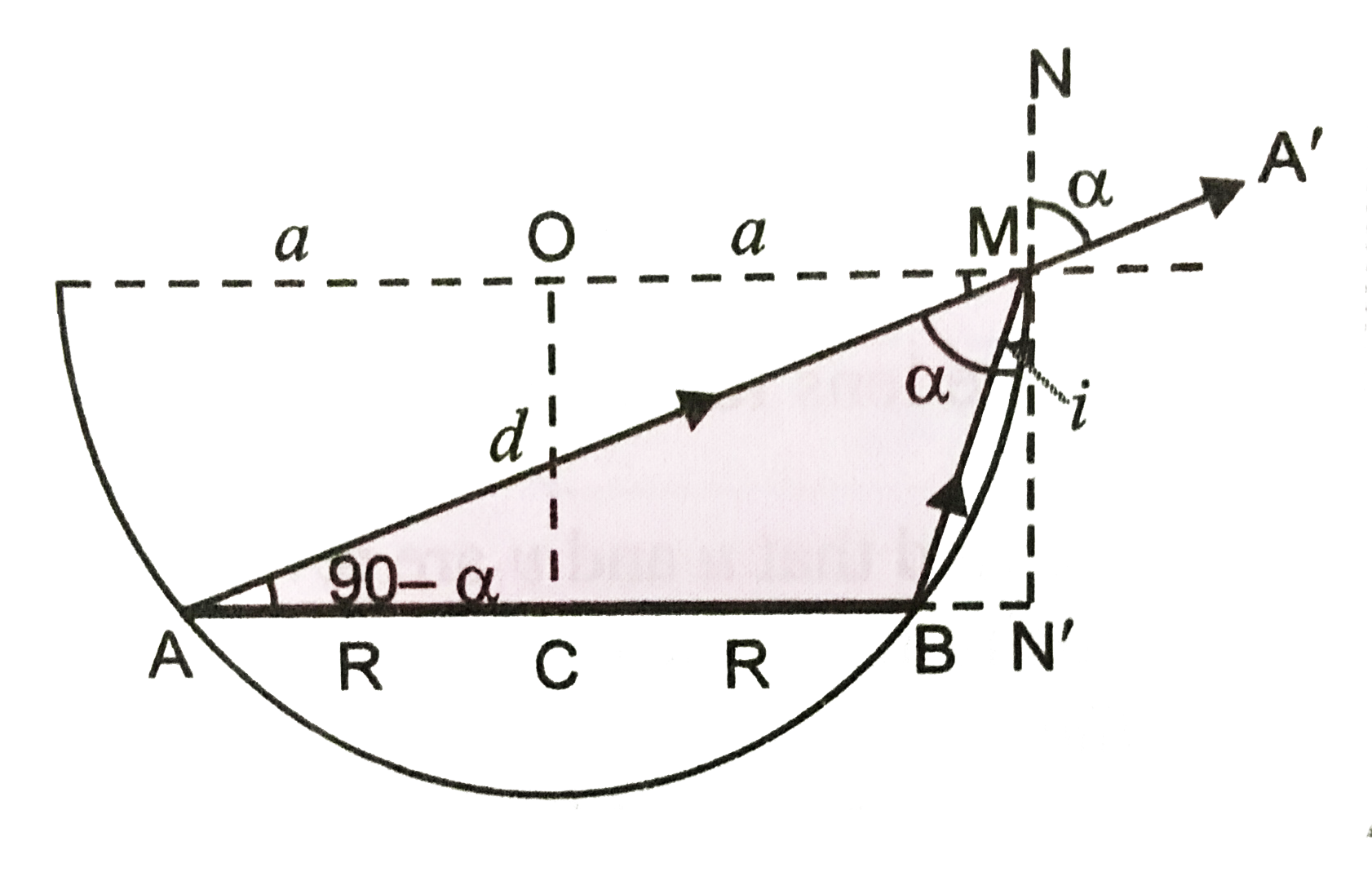
In Fig. we have shwon an opaque hemispherical bowl of raduis a with centre `O`.
A circular disc of radius `R` with centre `C` is placed co-axially and horizontally inside the bowl. We have to calculate `OC = d`.
AMA' is the direction of incident ray before liquid is filled in the bowl.
When liquid of refractive index `mu` is filled in the bowl, the near edge `B` of the disc just becomes visible. Here, `BM` is the incident ray, which is refracted along `MA'`.
`NN"` is normal to the horizontal surface of liquid in the bowl. `i` is the angle of incidence and `r = alpha` is the angle of refraction.
As refraction occurs at `M` in going from denser to rarer medium, therefore, according to Snell's law
`(1)/(mu) = (sin i)/(sin r) = (sin i)/( sin alpha)` ...(i)
Now, `sin i = (BN')/(BM) = (a - R)/(sqrt(d^(2) + (a - R)^(2))) and sin alpha = cos (90 - alpha) = (AN')/(AM) = (a + R)/(sqrt(d^(2) + (a + R)^(2)))`
Putting in (i), we get
`(1)/(mu) = (a - R)/(sqrt(d^(2) + (a - R)^(2))) xx sqrt(d^(2) + (a + R)^(2))/(a + R) or mu xx (a - R)sqrt(d^(2) + (a + R)^(2)) = (a + R) sqrt(d^(2) + (a - R)^(2))`
On simplifying, we get `d = (mu(a^(2) - R^(2)))/(sqrt(a + r)^(2) - mu (a - R)^(2))`