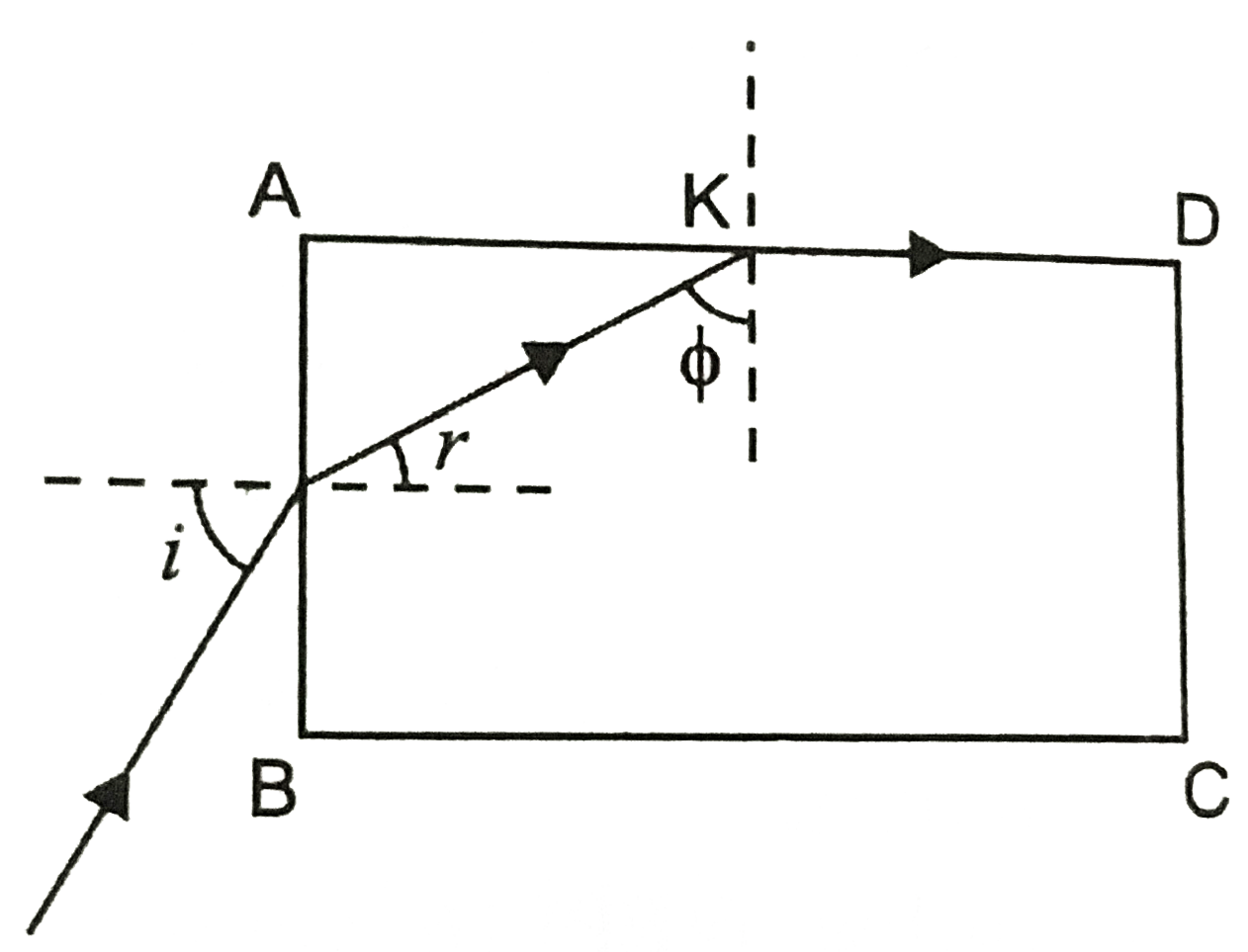
In Fig. we have shown a ray of light incident at `angle i` on face `AB`. It is refracted at `angle r` and falls on face `AD_|_ AC` at `/_phi`. This ray will suffer total internal reflection at `K` and proceed along `KD _|_ AB`, provided
`sin phi ge (1)/(mu)`
`sin (90^(@) - r) ge (1)/(mu)` or `cos r ge (1)/(mu)`
or `1 - cos^(2) le 1 - (1)/(mu^(2)) or sin^(2) le 1 - (1)/(mu^(2))`
According to Snell's law, `sin i = mu sin r :. (1)/(mu^(2))sin^(2)i le - (1)/(mu^(2))`
`sin^(2) i le mu^(2) - 1`
`phi` will be smallest when `i = 90^(@)`
`sin^(2) i = sin^(2) 90^(@) = 1 :. 1 le mu^(2) - 1` or `mu^(2) ge 2 or mu ge sqrt(2)`, which was to be proved.