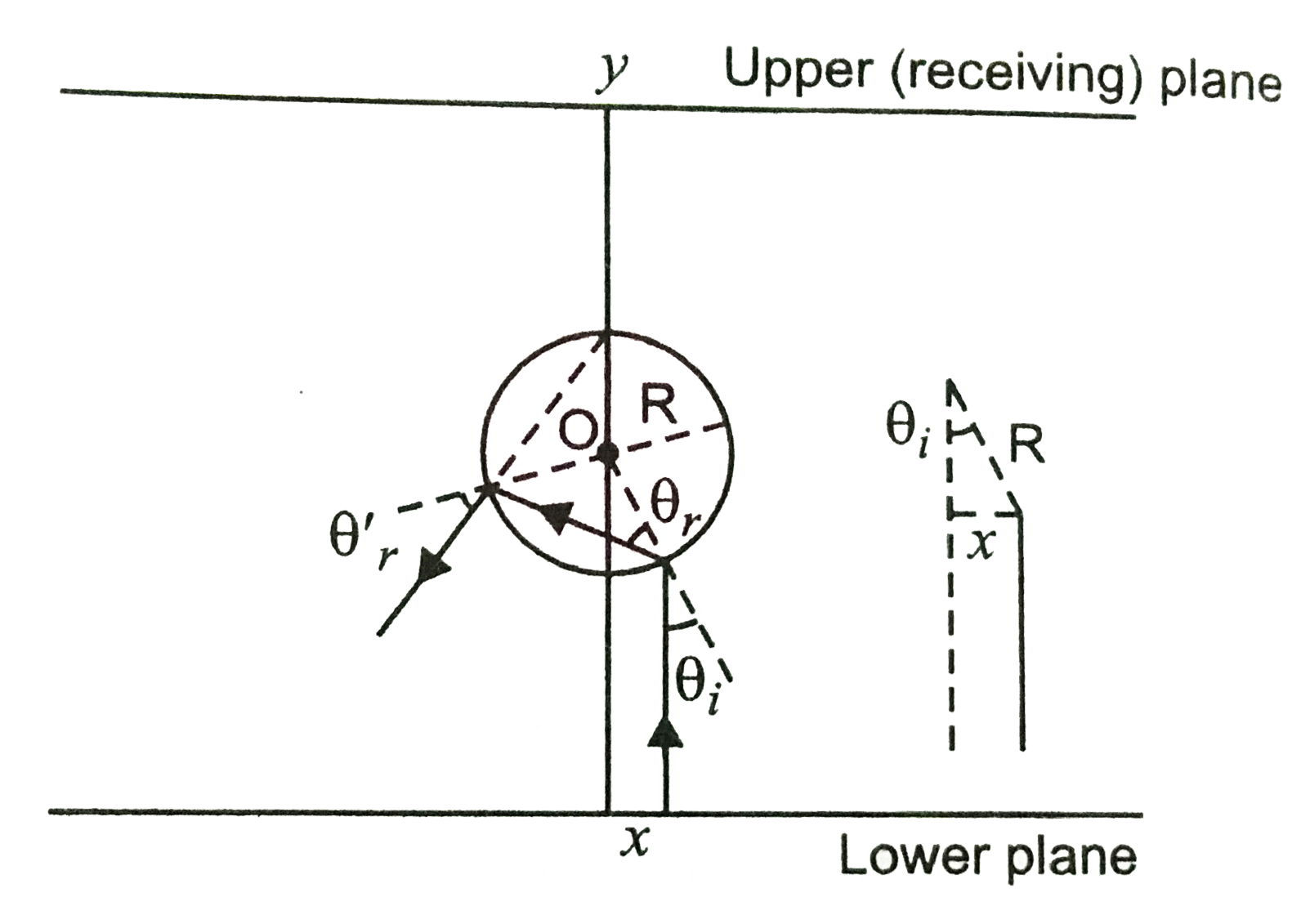The set up described in the question is shown in Fig. The full line circle represents cross ssection of infintely long cylinder of radius `R`. As the material is of refractive index `(-1)`, therefore, `theta_(r )` is negative and `theta_(r)` is positive.
Also, `|theta_(i)| = |theta_( r)| = |theta'_(r )|`
For the incoming ray along Y-axis from the plane, total deviation of the outcoming ray is `4 theta_(i)`. The rays shall not reach the receving plate if
`(pi)/(2) le 4 theta_(i) (3pi)/(2)`
(angles are measured clockwise from Y-axis)
or `(pi)/(8) le theta_(i) le (3pi)/(8)`.
From Fig. `sin theta_(i) = (x)/(R ) = theta_(i)`, when small.
`:. (pi)/(8) le (x)/(8) le(3pi)/(8)` or `(R pi)/(8) le x le (3pi R)/(8)`
Hence, we conclude that for values of `x` lying between
`(pi R)/(8)` and `(3 pi R)/(8)`, light emitted from the laser source shall not reach the upper recreiving plane.