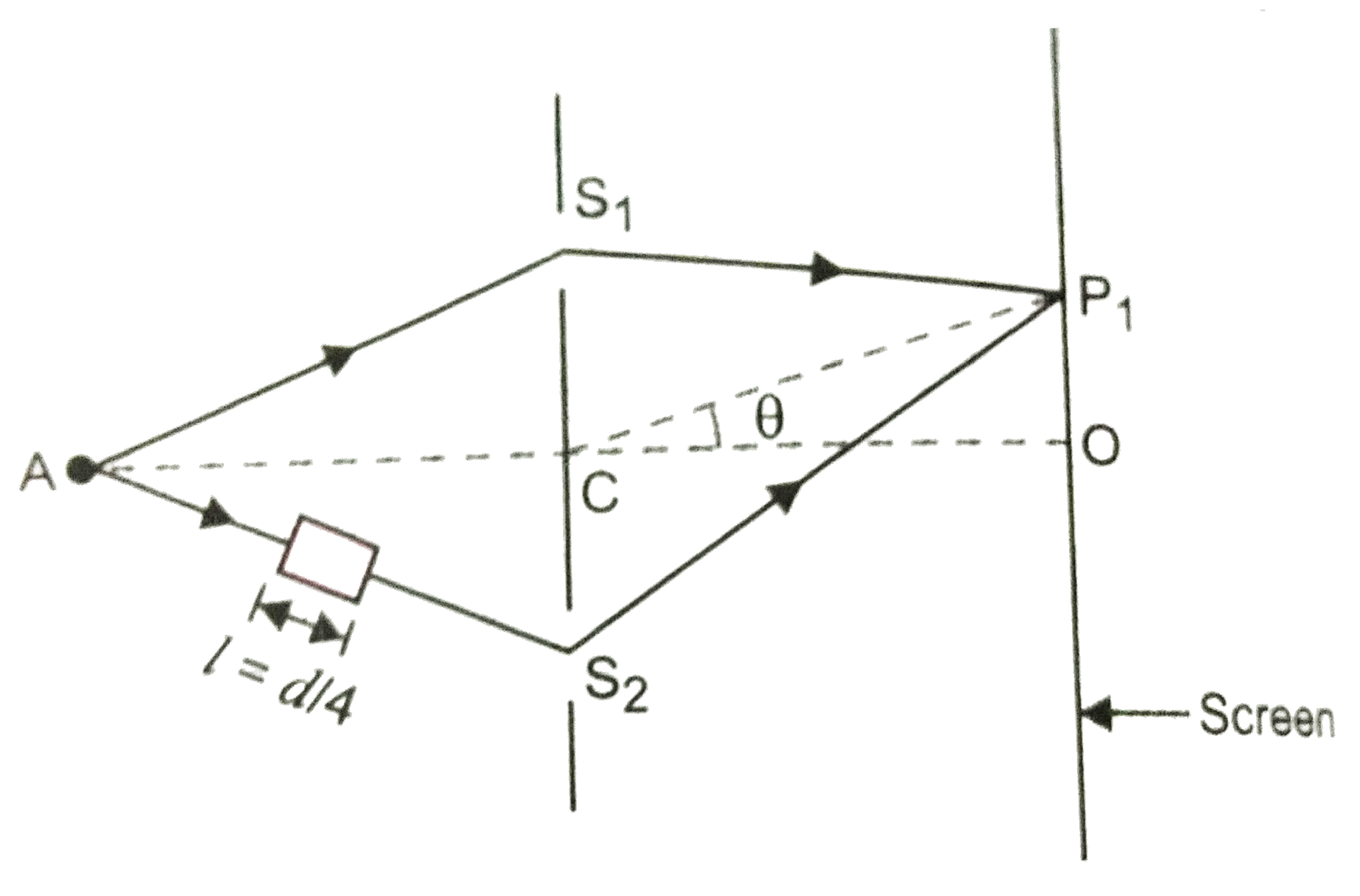
A small transparent slab `(mu = 1.5)` is placed along `AS_(2)` as shown.

`AC=CO=D,S_(1)C=S_(2)S=d lt ltD`
The distance of princpal maxima front 'O' is
A small transparent slab `(mu = 1.5)` is placed along `AS_(2)` as shown.

`AC=CO=D,S_(1)C=S_(2)S=d lt ltD`
The distance of princpal maxima front 'O' is

`AC=CO=D,S_(1)C=S_(2)S=d lt ltD`
The distance of princpal maxima front 'O' is
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
As is clear from Fig. path difference between waves reaching `P_(1)` from A is
`= 2d sin theta + (mu - 1)l`.
For principal maximum, path diff. `= 0`.
i.e., `2d sin theta + (mu - 1) l = 0`
`2d = sin theta + (1.5 - 1)(d)/(4) = 0 , sin theta = (-1)/(16)`
`:. OP_(1) = (CO) tan theta ~= D(-(1)/(16))`
For the first minimum, a angle `theta_(1)`, say,
path difference `= 2 d sin theta_(1) + 0.5 l = +- lambda//2`
`sin theta_(1) = (+- lambda//2 - 0.5 l)/(2d)`
As diffraction ocuurs when `d = lambda, :. sin theta_(1) = (+- lambda//2 - lambda//8)/(2 lambda) = +-(1)/(4) - (1)/(16)`
on the positive side, `sin theta_(1) = + (1)/(4) - (1)/(16) = (3)/(16)` , on the negative side, `sin theta'_(1) = -(1)/(4) - (1)/(16) = (-5)/(16)`.
The first principal maximum on the positive side is at distance (above `O`)
`= D than theta_(1) = D (sin theta_(1))/(sqrt(1 - sin^(2) theta_(1))) = (D.3//16)/(sqrt 1 - 9//256) = (3D)/(sqrt(16^(2) - 3^(2))`
On the negative side, distance of first principal maximum (below `O`) will be
`= D theta'_(1) = D (sin theta'_(1))/(sqrt(1 - sin^(2) theta_(1))) = (D(-5//16))/(sqrt (1 - (5//16))^(2)) = (-5D)/(sqrt(16^(2) - 5^(2))`
`= 2d sin theta + (mu - 1)l`.
For principal maximum, path diff. `= 0`.
i.e., `2d sin theta + (mu - 1) l = 0`
`2d = sin theta + (1.5 - 1)(d)/(4) = 0 , sin theta = (-1)/(16)`
`:. OP_(1) = (CO) tan theta ~= D(-(1)/(16))`
For the first minimum, a angle `theta_(1)`, say,
path difference `= 2 d sin theta_(1) + 0.5 l = +- lambda//2`
`sin theta_(1) = (+- lambda//2 - 0.5 l)/(2d)`
As diffraction ocuurs when `d = lambda, :. sin theta_(1) = (+- lambda//2 - lambda//8)/(2 lambda) = +-(1)/(4) - (1)/(16)`
on the positive side, `sin theta_(1) = + (1)/(4) - (1)/(16) = (3)/(16)` , on the negative side, `sin theta'_(1) = -(1)/(4) - (1)/(16) = (-5)/(16)`.
The first principal maximum on the positive side is at distance (above `O`)
`= D than theta_(1) = D (sin theta_(1))/(sqrt(1 - sin^(2) theta_(1))) = (D.3//16)/(sqrt 1 - 9//256) = (3D)/(sqrt(16^(2) - 3^(2))`
On the negative side, distance of first principal maximum (below `O`) will be
`= D theta'_(1) = D (sin theta'_(1))/(sqrt(1 - sin^(2) theta_(1))) = (D(-5//16))/(sqrt (1 - (5//16))^(2)) = (-5D)/(sqrt(16^(2) - 5^(2))`

Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
A small transparent slab (mu = 1.5) is placed along AS_(2) as shown. AC=CO=D,S_(1)C=S_(2)S=d lt ltD The distance of first minima above O is
A small transparent slab (mu = 1.5) is placed along AS_(2) as shown. AC=CO=D,S_(1)C=S_(2)S=d lt ltD The distance of first minima below the point O is
A small transparent slab containing material of mu=1.5 is placed along AS_(2) (figure). What will be the distance from O of the principle maxima and of the first minima on either side of the principal maxima obtained in the absence of the glass slab ?
Young's double slit experiment is conducted in a liquid of refractive index mu_1 as shown in figure. A thin transparent slab of refractive index mu_2 is placed in front of the slit s_2 . The magnitude of optical path difference at 'O' is
Monochromatic light of wavelength lamda passes through a very narrow slit S and then strikes a screen placed at a distance D = 1m in which there are two parallel slits S_(1) and S_(2) as shown. Slit S_(1) is directly in line with S while S_(2) is displaced a distance d to one side. The light is detected at point P on a second screen, equidistant from S_(1) and S_(2) When either slit S_(1) or S_(2) is open equal light intensities I are measured at point P. When both slits are open, the intensity is three times as large i.e. 3 I . If the minimum possible wavelength is Nd^(2) , then find the value of N (d lt lt D)
Microwave ocillators S_(1) and S_(2) are used to show interference of electromagnetic waves on a screen which in parallel to S_(1) S_(2) and 2 m away from S_(1)S_(2) . If S_(1)S_(2)=20 cm and lamda=4cm , then the distance between the successive maxima and minima will be
A Young's double slit apparatus is immersed in a liquid of refractive index mu_(1). The slit plame touches the liquid surface. A parallel beam of monochromatic light of wavelength lambda (in air) is incident normally on the slits. a. Find the fringe width. b. If one of the slits (say S_(2) ) is covered by a transparent slab of refrative index mu_(2) and thickless t as shown, find the new position of central maxima. c. Now, the other slit, S_(1) is also covered by a slab of same thickness and refractive index mu_(3) as shown in Fig. 2.49 due to which the central maxima recovers it positon, find the value of mu_(3) Find the ratio of intensities at O in the three conditions (a), (b), and (c).
In a young’s double slit experiment the distance between slits S1 and S2 is d and distance of slit plane from the screen is D (gtgt d) . The point source of light (S) is placed a distance (d) / (2 ) below the principal axis in the focal plane of the convex lens (L). The slits S1 and S2 are located symmetrically with respect to the principal axis of the lens. Focal length of the lens is f (gtgt d) . Find the distance of the central maxima of the fringe pattern from the centre (O) of the screen.
Two ideal slits S_(1) and S_(2) are at a distance d apart, and illuninated by light of wavelength lambda passing through an ideal source slit S placed on the line through S_(2) as shown. The distance between the planes of slits and the source slit is D.A screen is held at a distance D from the plane of the slits. The minimum value of d for which there is darkness at O is (dlt lt D)