To ensure almost `100%` transmittivity, photographic lenses are often coated with a thin layer of dielectric material, like `MgF_(2)(mu=1.38)` . The minimum thickness of the film to be used so that at the centre of visible spectrum `(lambda = 5500 Å)` there is maximum transmission.
To ensure almost `100%` transmittivity, photographic lenses are often coated with a thin layer of dielectric material, like `MgF_(2)(mu=1.38)` . The minimum thickness of the film to be used so that at the centre of visible spectrum `(lambda = 5500 Å)` there is maximum transmission.
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
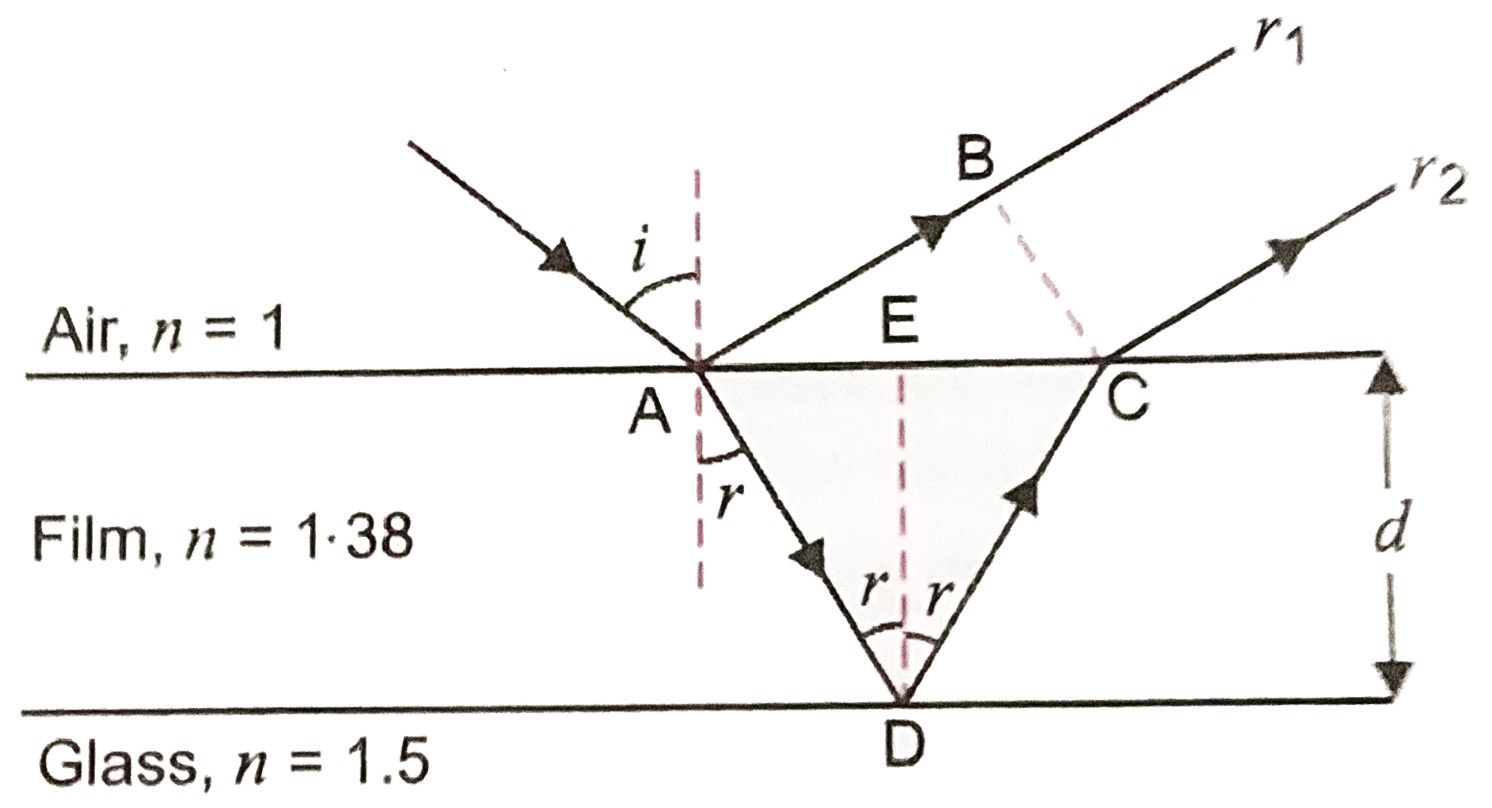
In Fig. we have shown a dielectric film of thickness `d` deposited on a glass lens. Refractive index of film `= 1.38` and refractive index of glass `= 1.5`.
Given, `lambda = 5500 Å`.
A ray is incidence on the film at angle `i`. It is reflected partially along `AB (as r_(1))` and refracted partially along `AD` in the film at angle `r`.
The refracted ray is reflected partially from film glass interface along `DC` and partially transmitted through the glass lens. At `C`, the ray is reflected partially in the film and refracted into air as `r_(2)` parallel to `r_(1)`.
As amplitude of wave goes on decreasing during successive reflections, therefore, rays `r_(1) and r_(2)` dominate the behaviour.
For maximum transmission through the centre of the lens, `r_(1)` and `r_(2)` should interfere destructively.
As both the reflections at `A and D` are from lower to higher refractive index, there is no phase change on reflection.
The optical path difference between `r_(2)` and `r_(1) = n(AD + CD) - AB`
In `DeltaADE`, `cos r = (DE)/(AD) = (d)/(AD) :. AD = (d)/(cos r)`
Similarly, `CD = (d)/(cos r)`
Again, `tan r = (AE)/(DE) = ((1)/(2)AC)/(d) :. AC = 2d tan r`
In `Delta ABC`, `sin i = (AB)/(AC) AB = AC = sin i = 2d tan r = sin i`
Putting in (i), we get Optical path difference between `r_(2)` and `r_(1)`
`x = n((2d)/( cos r)) - 2d tan r sin i`
`= (sin i)/(sin r)(2d)/(cos r) - 2d(sin r)/(cos r ) sin i`
`= 2d sin i ((1 - sin^(2) r)/(sin r cos r))`
`x = 2d = (sin i)/(sin r) cos r = 2 dn cos r`
The waves `r_(2)` and `r_(1)` will interfere destructively when their path difference
`x = (lambda)/(2), i.e., 2 dn cos r = (lambda)/(2) dn cos r = (lambda)/(4)` ...(ii)
For photographic lenses, the sources are normally in vertical plane. `:. i = r = 0^(@)`
Form (ii), `dn cos 0^(@) = (lambda)/(4) d = (lambda)/(4 n) = (5500 Å)/(4 xx 1.38) = 1000 Å`
Given, `lambda = 5500 Å`.
A ray is incidence on the film at angle `i`. It is reflected partially along `AB (as r_(1))` and refracted partially along `AD` in the film at angle `r`.
The refracted ray is reflected partially from film glass interface along `DC` and partially transmitted through the glass lens. At `C`, the ray is reflected partially in the film and refracted into air as `r_(2)` parallel to `r_(1)`.
As amplitude of wave goes on decreasing during successive reflections, therefore, rays `r_(1) and r_(2)` dominate the behaviour.
For maximum transmission through the centre of the lens, `r_(1)` and `r_(2)` should interfere destructively.
As both the reflections at `A and D` are from lower to higher refractive index, there is no phase change on reflection.
The optical path difference between `r_(2)` and `r_(1) = n(AD + CD) - AB`
In `DeltaADE`, `cos r = (DE)/(AD) = (d)/(AD) :. AD = (d)/(cos r)`
Similarly, `CD = (d)/(cos r)`
Again, `tan r = (AE)/(DE) = ((1)/(2)AC)/(d) :. AC = 2d tan r`
In `Delta ABC`, `sin i = (AB)/(AC) AB = AC = sin i = 2d tan r = sin i`
Putting in (i), we get Optical path difference between `r_(2)` and `r_(1)`
`x = n((2d)/( cos r)) - 2d tan r sin i`
`= (sin i)/(sin r)(2d)/(cos r) - 2d(sin r)/(cos r ) sin i`
`= 2d sin i ((1 - sin^(2) r)/(sin r cos r))`
`x = 2d = (sin i)/(sin r) cos r = 2 dn cos r`
The waves `r_(2)` and `r_(1)` will interfere destructively when their path difference
`x = (lambda)/(2), i.e., 2 dn cos r = (lambda)/(2) dn cos r = (lambda)/(4)` ...(ii)
For photographic lenses, the sources are normally in vertical plane. `:. i = r = 0^(@)`
Form (ii), `dn cos 0^(@) = (lambda)/(4) d = (lambda)/(4 n) = (5500 Å)/(4 xx 1.38) = 1000 Å`

Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
On face of a glass (mu = 1.50) lens is coated with a thin film of magnesium fluoride MgF_(2)(mu = 1.38) to reduce reflection from the lens surface. Assuming the incident light to be perpendicular to the lens surface. The least coating thickness that eliminates the reflection at the centre of the visible spectrum (lamda = 550 nm) is about
A glass lens is coated on one side with a thin film of magnesium fluoride (MgF_(2)) to reduce reflection from the lens surface (Fig. 2.26). The Index of refraction of MgF_(2) is 1.38, that of the glass is 1.50. What is the least coating thickness that eliminates (via interference) the reflections at the middle of the visible specturm (lambda = 550nm) ? Assume that the light is approxmately perpendicular to the lens surface.
In the YDSE, the monochromatic source of wavelength lambda is placed at a distance d/2 from the central axis (as shown in the figure), where d is the separation between the two slits S_1 and S_2 . (a)Find the position of the central maxima. (b) Find the order of interference formed at O. (c)Now, S is placed on centre dotted line. Find the minimum thickness of the film of refractive indes mu =1.5 to be placed in front of S_2 so that intensity at O becomes 3/4 th of the maximum intensity. (Take lambda=6000Å, d = 6mm .)
In solar cells, a silicon solar cell (mu = 3.5) is coated with a thin film of silicon monoxide SiO (mu = 1.45) to minimize reflective losses from the surface. Determine the minimum thickness of SiO that produces the least reflection at a wavelength of 550nm, near the centre of the visible spectrum. Assume approximately normal incidence .
A lens ( mu=1.5 ) is coated with a thin film of refractive index 1.2 order to reduce the reflected form its surface at lambda=4800Å .Find the maximum thickness of the film which will minimized the intensity of the reflected light .(Assume near normal incidence)
A thin film of a specific meterial can be used to decrease the intensity of reflected light. There is destrucive inteference of wave reflected from upper and lower surface of the film. These films are called non-reflecting or anti-reflecting coatings. The process of coating the lens or surface with non-reflecting film is called blooming as shown in figure The refracting index of coating (n_(1)) is less than that of the glass (n_(2)) . 5. magnesium fluoride (MgF_(2)) is generally use as anti-reflection coating. If refractive index of MgF_(2) is 1.25, then minimum thickness of film required is (Take lambda = 500 nm )
To produce a minimum reflection of wavelength near the middle of visible spectrum (550 nm), how thick should a coating of MgF_(2) (mu = 1.38) be vaccum-coated on a glass surface?
A thick glass slab (mu= 1.5) is to be viewed in reflected white light. It is proposed to coat the slab with a thin layer of a material having refractive index 1.3 so that the wavelength 6000 Å os suppressed. Find the minimum thickness of the coating required.