When positive terminal of the battery is connected to point A the diode `D_(1)` gets forward biased and diode `D_(2)` is reverse biased. The diode `D_(1)` offer zero resistance and diode `D_(2)` offer infinite resistsnce. Now the given circuits will be reduced to the circuit shown in Fig.
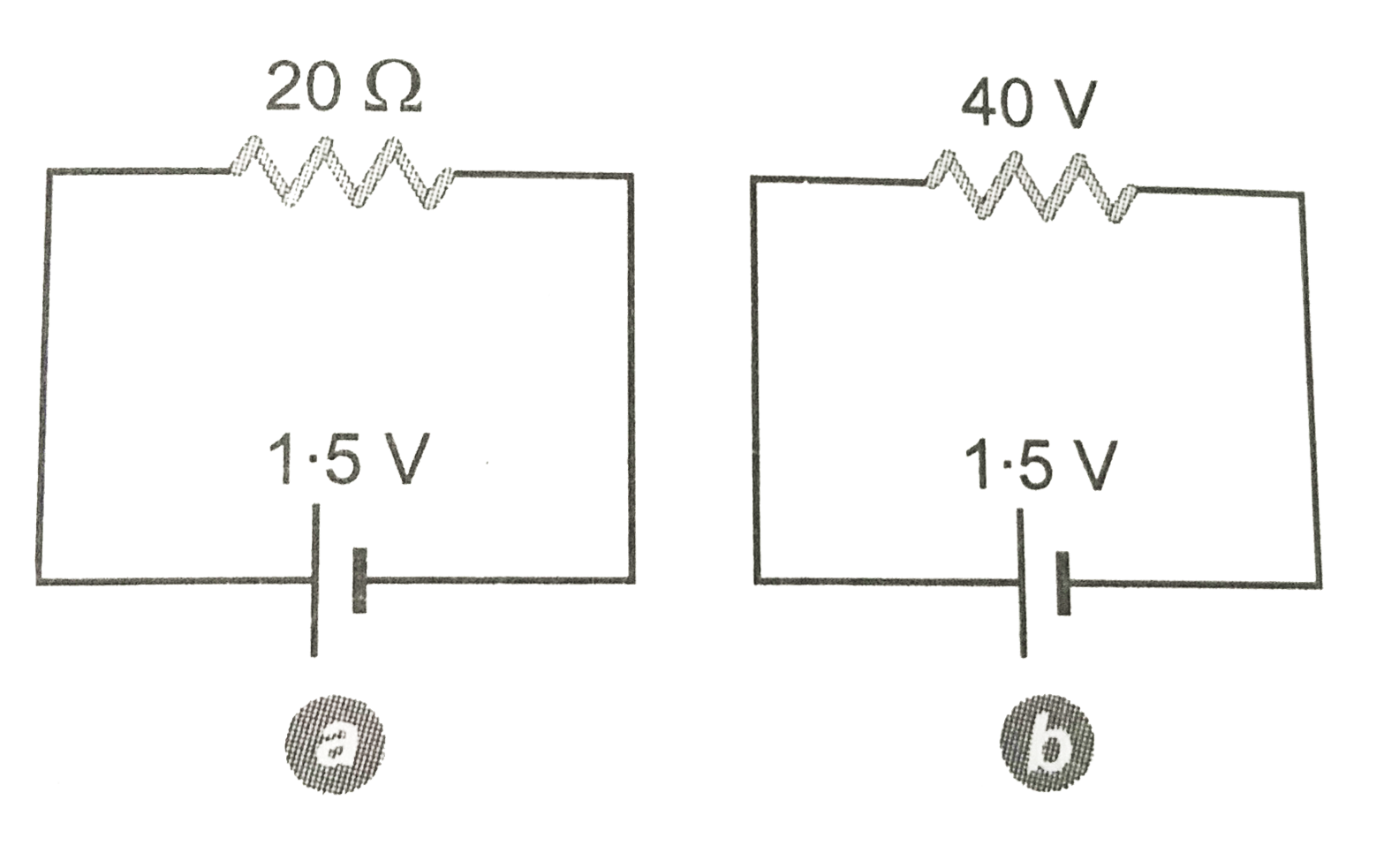
Current drawn from the battery,
`I=(1.5V)/(20Omega)=0.075A`
When positive terminal of the battery is connected to point B, the diode `D_(2)` gets forward biased and diode `D_(1)` gets reverse biased. Now the diode `D_(1)` will offer infinite resistance and diode `D_(2)` will offer zero resistance. The equivalent circuit will be as shown in Fig. 9.39. Current drawn from
the battery, `I=(1.5V)/(40Omega)=0.0375A`