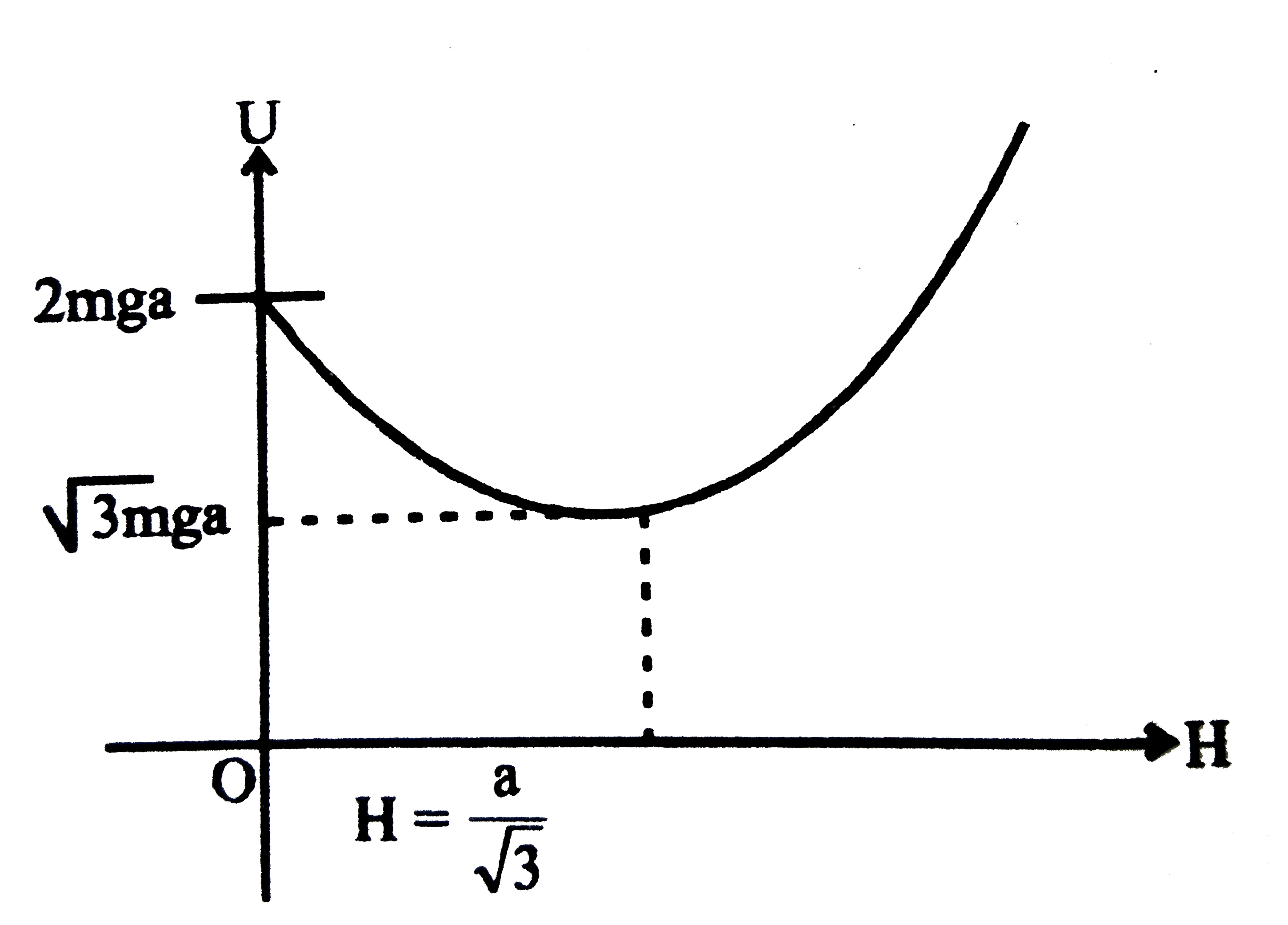
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Recommended Questions
- A non-conducting disc of radius a and uniform positive surface charge ...
Text Solution
|
- A positively charged disc is placed on a horizontal plane. A charged ...
Text Solution
|
- A flat dielectric disc of radius R carries an exces charge on its surf...
Text Solution
|
- A nonconducting disk of radius a and uniform positive surface charge d...
Text Solution
|
- A charge q is placed at the some distance along the axis of a uniforml...
Text Solution
|
- A non-conducting thin disc of radius R and mass m having charge unifor...
Text Solution
|
- A dielectric disc of radius R and uniform positive surface charge dens...
Text Solution
|
- A non-conducting disc of radius a with uniform positive surface charge...
Text Solution
|
- A non-conducting disc of radius a with uniform positive surface charge...
Text Solution
|
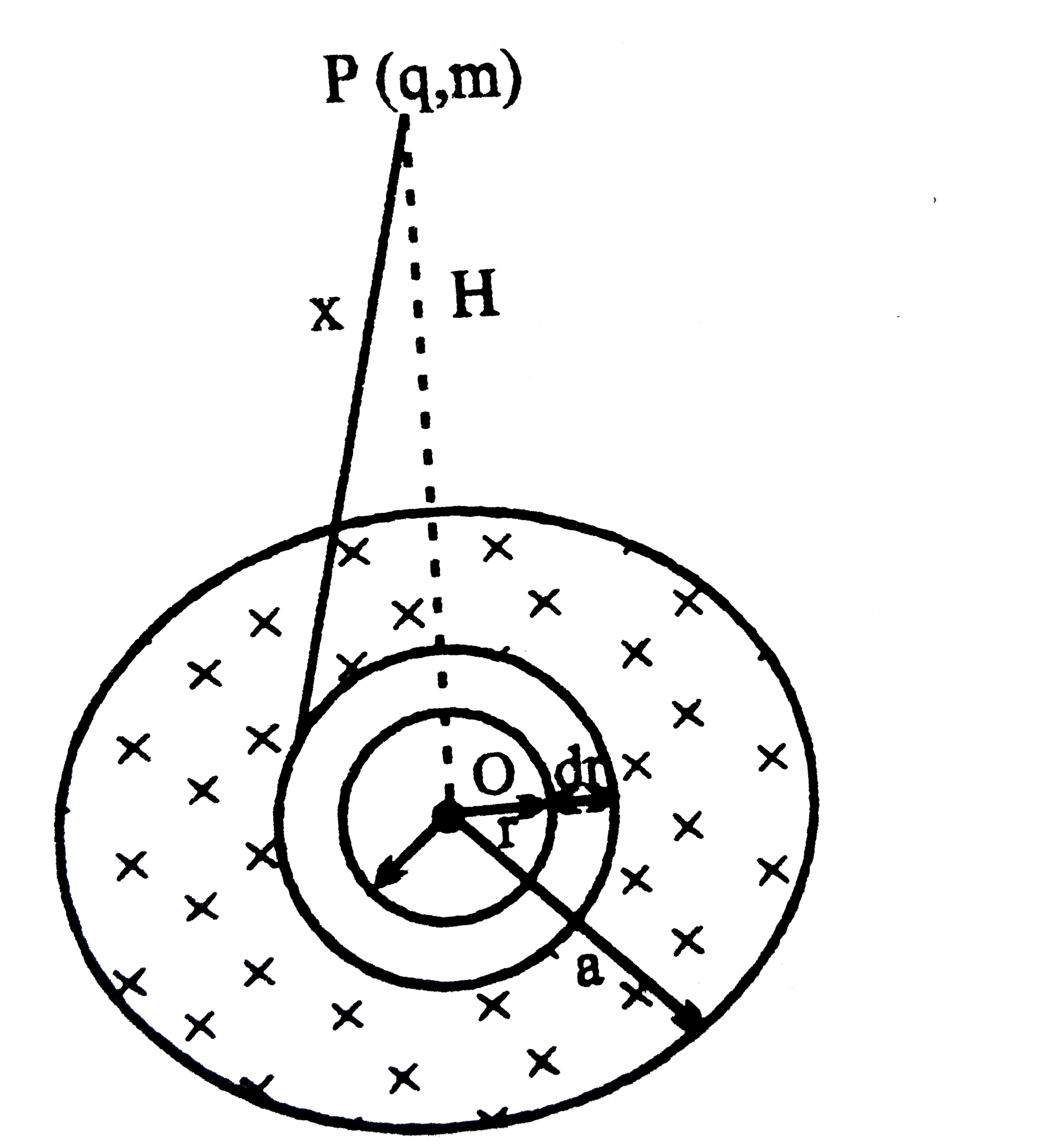 .
.