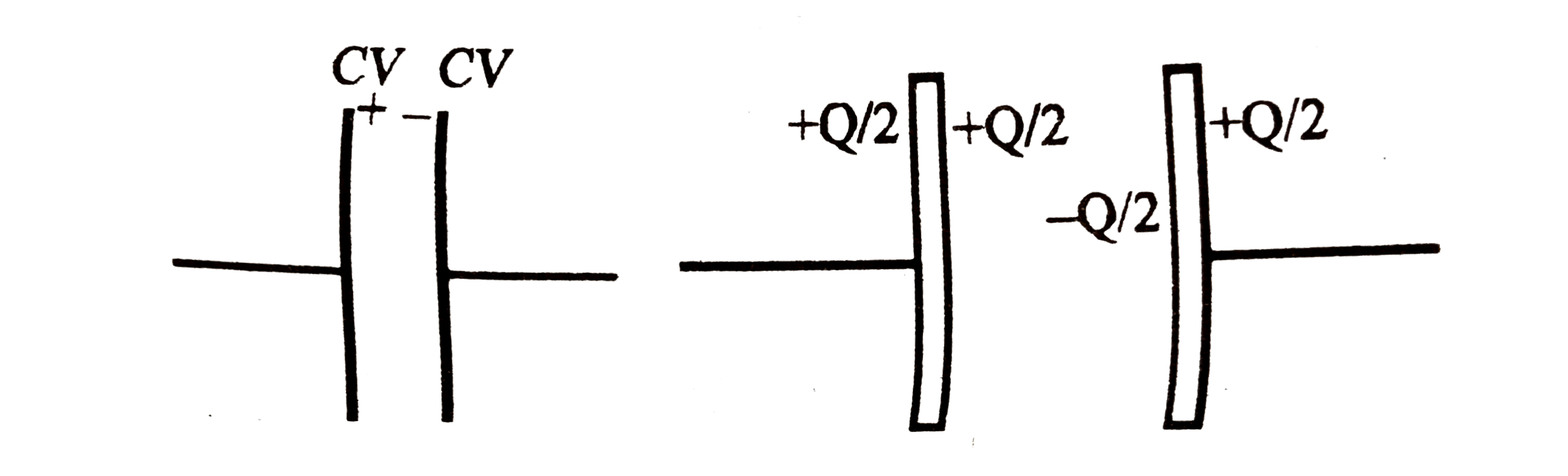A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A capacitor of capacitance C is charged to a potential difference V fr...
Text Solution
|
- A capacitor of capacitance C is charged to a potential difference V fr...
Text Solution
|
- Two capacitors of capacitances 3 muF and 6 muF are charged to a potent...
Text Solution
|
- A capacitor C is charged to a potential difference V and battery is di...
Text Solution
|
- A capacitor of capacitance 10 mu F is charged to a potential 50 V with...
Text Solution
|
- A capacitor of capacitance C is charged to a potential difference V fr...
Text Solution
|
- Two capacitors of capacitance 2muF and 4muF respectively are charged t...
Text Solution
|
- A capacitor of capacitance C is charged to a potential difference V fr...
Text Solution
|
- Two capacitor of capacitance 2muF and 3muF respectively are charged to...
Text Solution
|