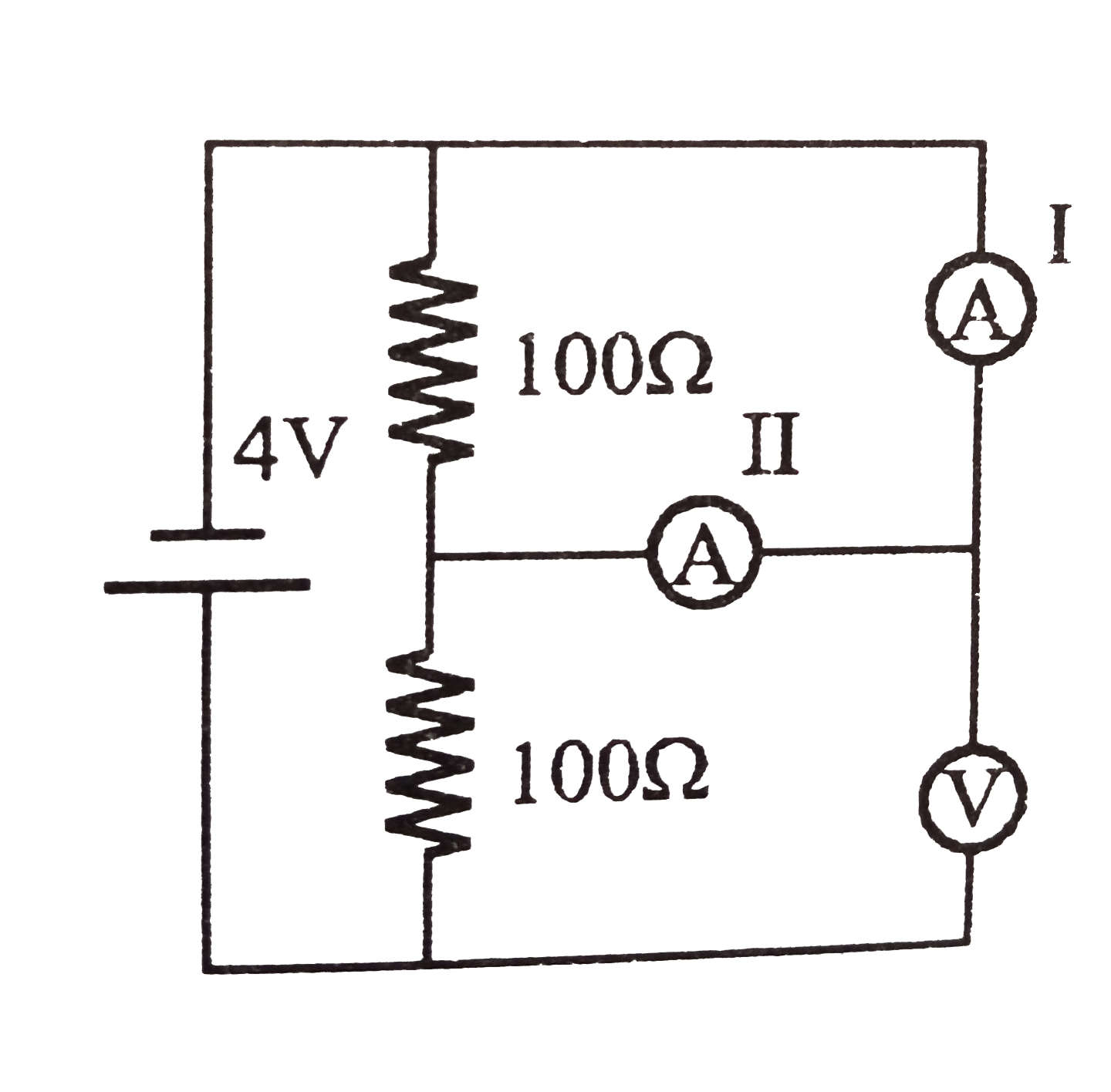
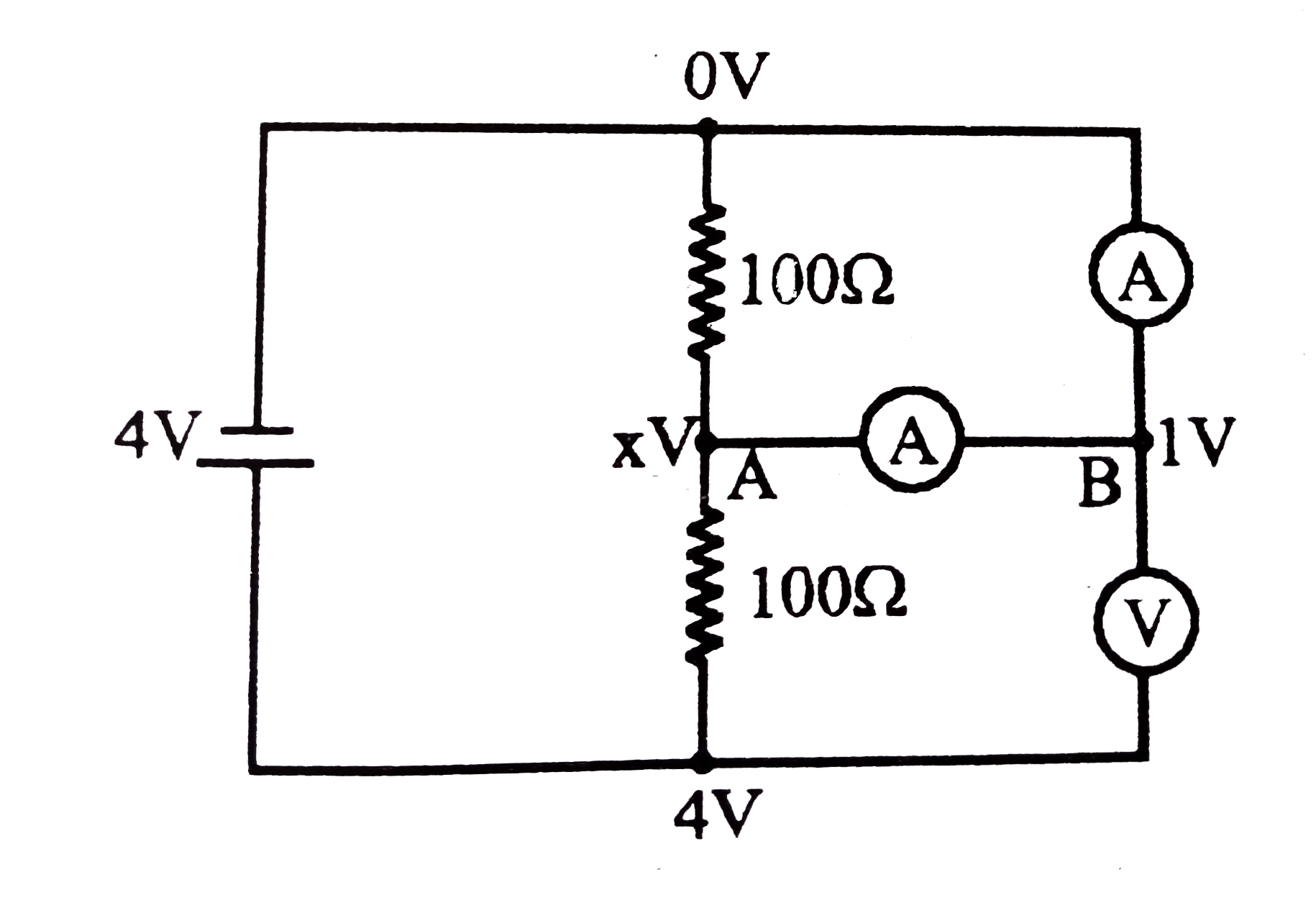
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- In the figure ammeter (i) reads a current of 10mA, while the voltmeter...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : In the circuit shown in figure ammeter and voltmeter are n...
Text Solution
|
- In Fig. 6.76, the ammeter (I) reads a current of 10 mA , while the vol...
Text Solution
|
- A voltmeter and an ammeter are connected in series to an ideal cell of...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure ammeter (i) reads a current of 10mA , while the voltmete...
Text Solution
|
- An ammeter A, a voltmeter V and a resistance R are connected as shown ...
Text Solution
|
- A student connects a voltmeters, ammeter and resistance according to t...
Text Solution
|
- A circuit is shown in the figure. The ratio of readings of ideal voltm...
Text Solution
|
- [" A non-ideal voltmeter and a non-ideal ammeter are connected as show...
Text Solution
|