A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Two very long straight parallel wires, parallel to y-axis, carry curre...
Text Solution
|
- A long, straight wire carries a current along the z-axis. One can find...
Text Solution
|
- Two infinitely long, thin, insulated, straight wires lie in the x-y pl...
Text Solution
|
- Two long wires carrying current I1 and I2 are arranged as shown in fig...
Text Solution
|
- Two very long straight parallel wires, parallel to y-axis, carry curre...
Text Solution
|
- A long wire is along x = 0, z = d and carries current in positive y di...
Text Solution
|
- Two infinite length wires carries currents 8A and 6A respectively and ...
Text Solution
|
- Two long wires are kept along x and y axis they carry currents I&II re...
Text Solution
|
- If a current I is flowing in a straight wire parallel to X - axis and ...
Text Solution
|
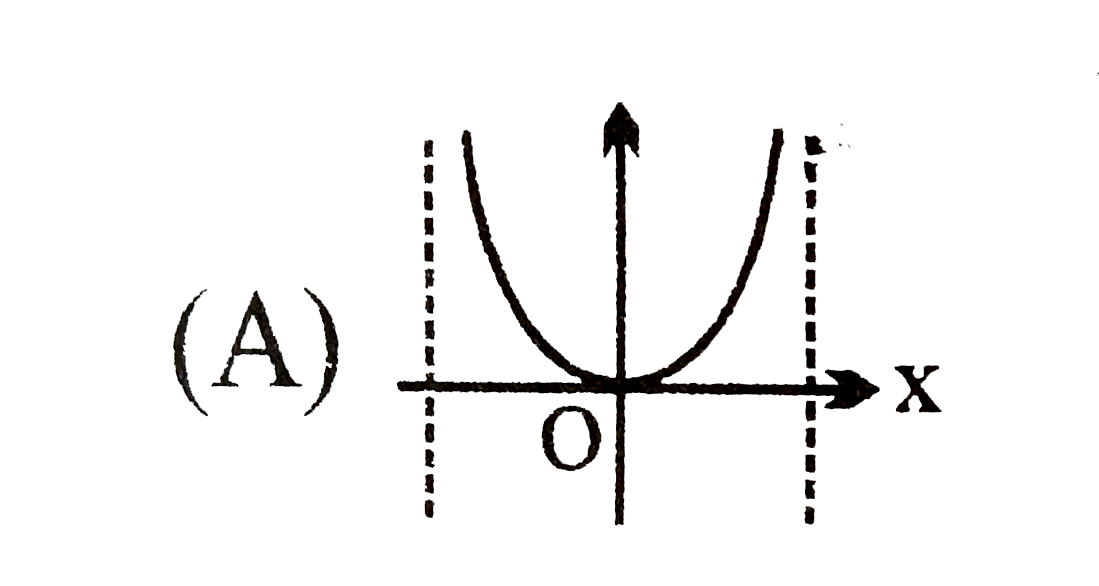
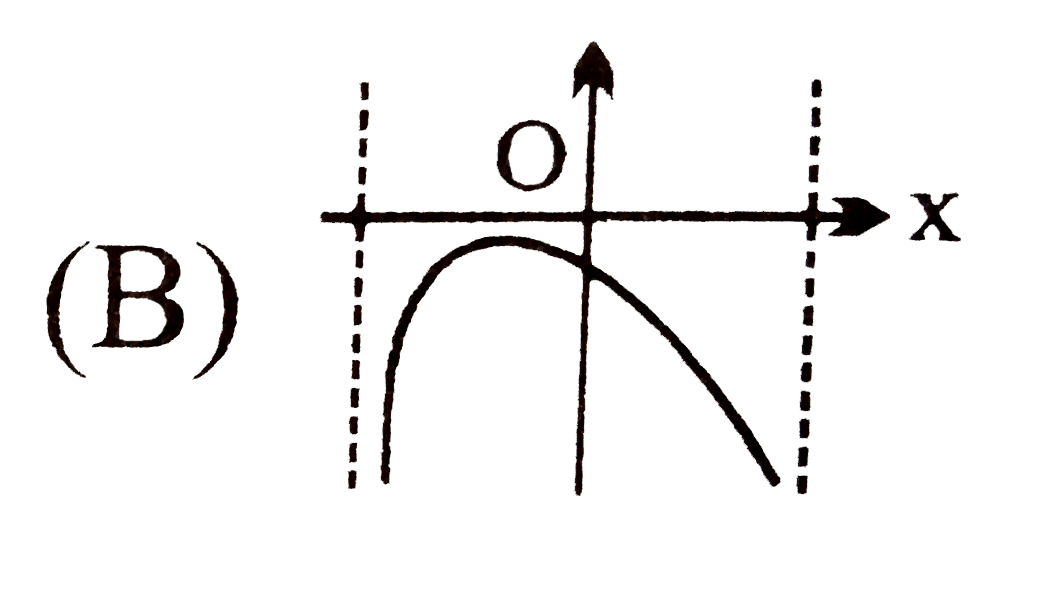
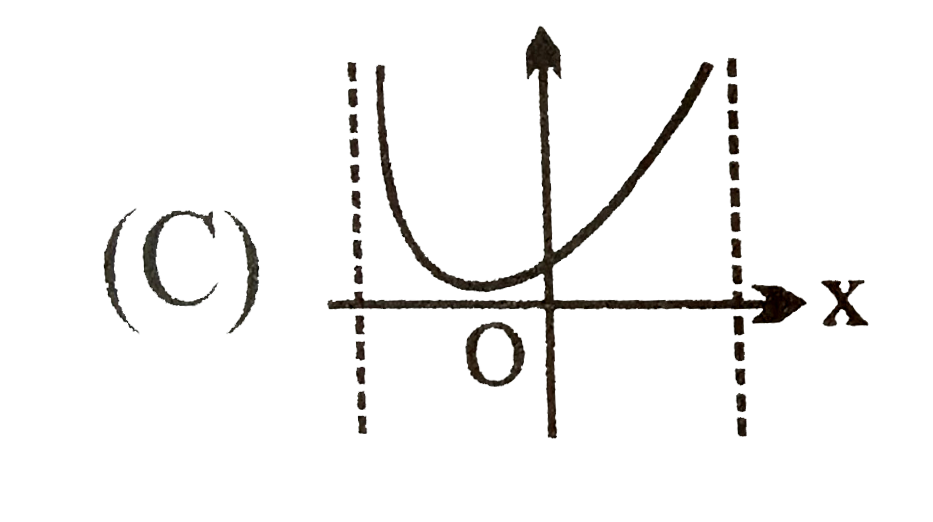
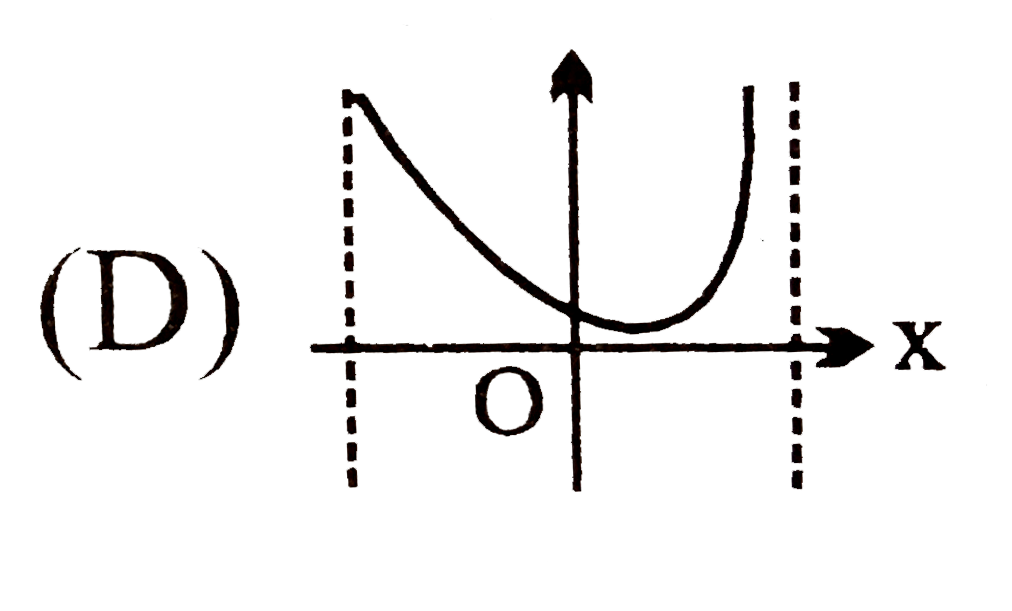
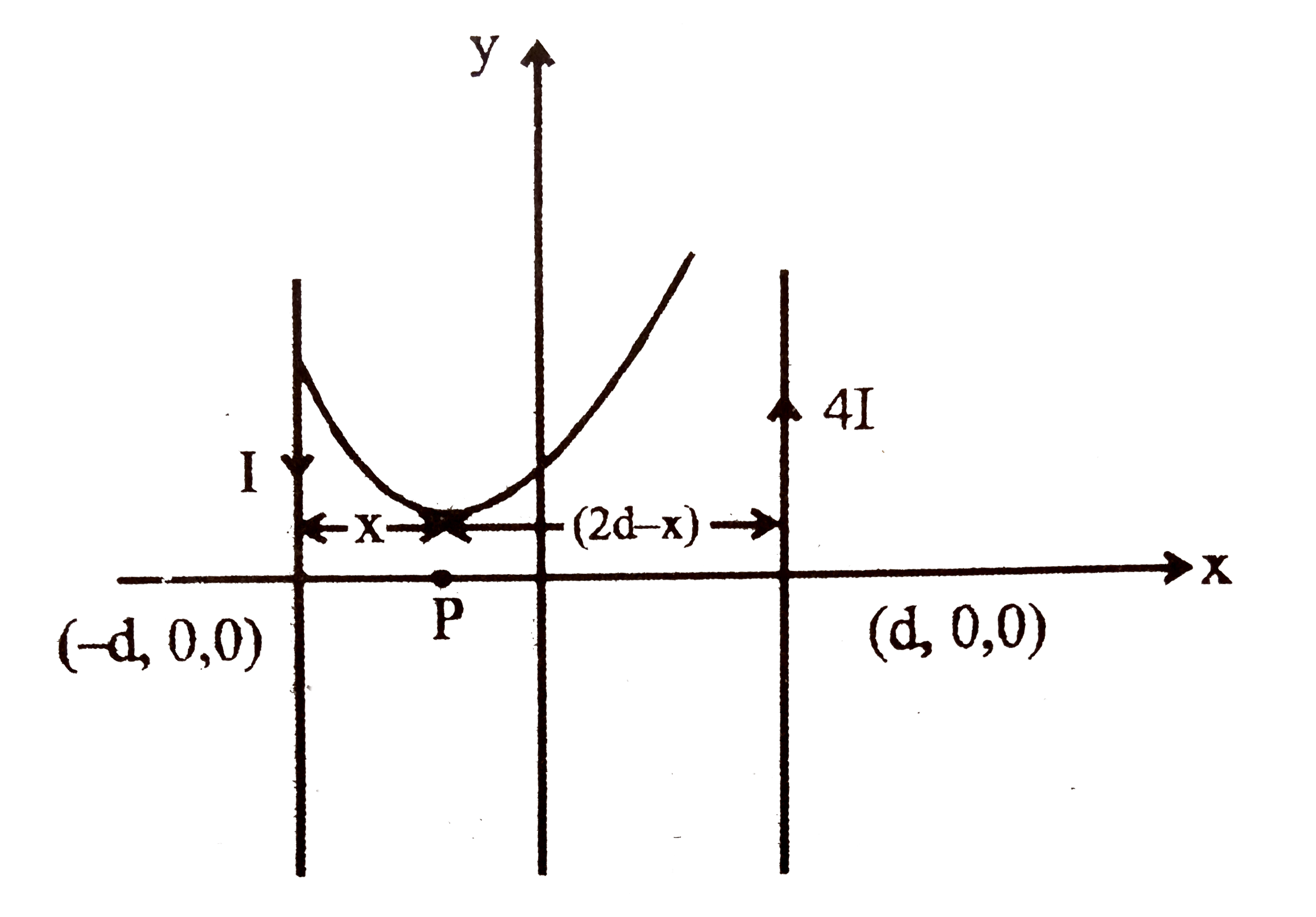 .
.