Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
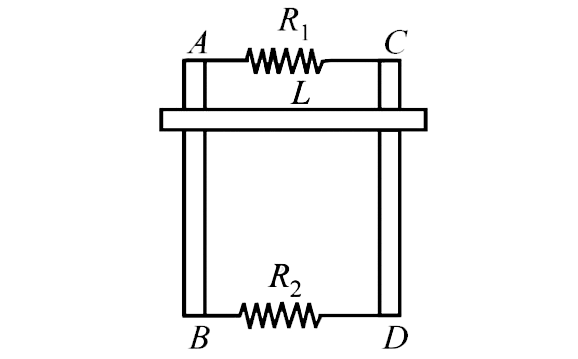
- Two parallel vertical metallic rails AB and CD are separated by 1m. Th...
Text Solution
|
- Two parallel vertical metallic rails AB and CD are separated by 1m. Th...
Text Solution
|
- Two parallel vertical metallic rails AB and CD are separated by 1m. Th...
Text Solution
|
- Two parallel vertical metallic rails AB and CD are separated by 1m. Th...
Text Solution
|
- Two parallel vertical metallic rails AB and CD are separated by 1m. Th...
Text Solution
|
- Two parallel vertical metellic rails AB and CD are separated by 1m . T...
Text Solution
|
- A copper rod of mass m slides under gravity on two smooth parallel rai...
Text Solution
|
- A vertical ring of radius r and resistance on R falls vertically. It i...
Text Solution
|
- A copper bar of mass m sides under gravity on two smooth parallel ra...
Text Solution
|